A Complete Guide to the Lesser-Known Delta-7 THC
With so many THC alternatives, it’s hard to keep them all straight. Let me introduce you to delta-7, delta-9’s less-wild cousin.
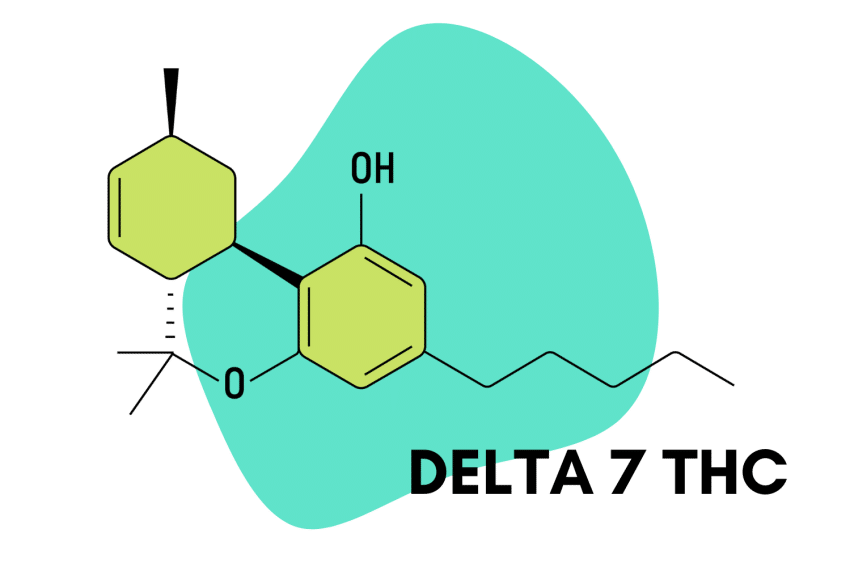
Delta 7 THC is a psychoactive cannabinoid found in the cannabis plant. Compared to various other cannabinoids, delta 7 is only found in trace quantities. For this reason, it’s considered a “minor cannabinoid.”
There’s not a lot of delta 7 THC in cannabis, so it has to be synthetically manufactured in a lab by transforming cannabinoids like CBD (cannabidiol) — which is abundant in hemp.
Compared to the two main cannabinoids, delta 9 and CBD, and other minor cannabinoids like CBG (cannabigerol), CBN (cannabinol), and even delta 8 THC, there’s limited research on delta 7 due in part to its rarity.
Delta 7 THC: Specs & Technical Details
| Active Ingredient | Delta 7 THC |
| Level of Risk | Low |
| Other Names | Δ7, D7, Delta 7 |
| Most Common Side Effects | Red eyes, increased appetite (“munchies”), increased heart rate, feelings of anxiousness |
| Duration of Effects | 2-10 hours, depending on the delivery method and dose |
| Legal Status | Legal in the United States (if derived from hemp). Some states may have restrictions. |
How Does Delta 7 THC Work?
Like most cannabinoids, delta 7 THC is believed to interact primarily with the endocannabinoid system (ECS), a complex network of receptors, signaling molecules, and enzymes that help regulate critical physiological processes like mood, stress, immune function, sleep-wake cycle, and pain perception.
There are two main types of receptors in the ECS:
- CB1 Receptors: Concentrated in the central nervous system
- CB2 Receptors: Primarily located in the immune cells and peripheral tissues
As a THC molecule, delta 7 is believed to have an affinity for CB1 receptors.
The activation of CB1 receptors is responsible for a wide range of effects, which most notably include:
- Psychoactive effects (feelings of euphoria and altered sensory perception)
- Appetite stimulation
- Pain relief
Some cannabinoids, like delta 9 and CBD, interact with other receptor sites involving relaxation, pain relief, anti-inflammation, and more [1,2].
However, since the delta 7 THC cannabinoid is newer to the scene, there’s still a lot that’s unknown about how it works and the safety of its long-term use.
What Does Delta 7 THC Feel Like?
The molecular shape of cannabinoids is important because they kind of work like keys to the locks of receptor sites. When the keys activate these sites, it initiates a chain of actions that affect different physiological processes.
The subtle difference of having the double bond on the seventh carbon atom means that it doesn’t have as strong of a bond to CB1 receptors, giving it much milder effects compared to delta 9 THC. Yet, it’s still enough to produce a noticeable high that can result in the following positive outcomes, depending on the dose:
- Heightened sensitivity to music, colors, and taste
- Increased appetite
- Feelings of euphoria and an uplifted mood
- Altered perception of time (time tends to move very slowly)
- Deep relaxation in the body
- Relief from pain
Delta 9 THC vs. Delta 7 THC Comparison
As we’ve briefly mentioned, delta 9 THC is the most common form of THC found in cannabis and the primary cannabinoid responsible for the marijuana high.
When consumed, the shape of the delta 9 THC molecule has an affinity for CB1 receptors in the central nervous system, which play an important role in regulating mood, appetite, pain perception, memory, and cognition.
Most people report feeling a sense of euphoria, deep body relaxation, altered thought patterns, and an increased desire for food (aka the munchies).
While these are the desired outcomes, THC can also produce some negative side effects like anxiety and paranoia, which tend to happen in higher doses or in people more sensitive to it.
This is where THC isomers like delta 7 can come in handy.
The shape of the delta 7 molecule doesn’t give it as strong of an affinity to the CB1 receptors. However, it’s still enough to produce a subtle high that’s much more forgiving than a typical marijuana high.
Of course, the effects of delta 7 can vary from individual and the dosage. Still, it’s usually sought out as a gentler alternative.
Comparison Chart: D9 vs. D7
| Delta 9 THC | Delta 7 THC | |
| Chemical structure | Double bond on the 9th carbon chain | Double bond on the 7th carbon chain |
| Psychoactive effects | Potent psychoactive effects | Mild psychoactive effects |
| Legal status | Listed as a Schedule I controlled substance in the US (in concentrations greater than 0.3% by dried weight). | Not explicitly listed as a controlled substance when made from hemp. Laws vary by state. |
| Medical Potential | Well-studied with potential therapeutic benefits, including pain relief, appetite stimulation, and nausea reduction. | Some studies suggest anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving properties. |
| Availability | Commonly found in most strains of cannabis, well-studied, and widely available. | Rarely found in cannabis strains and not as widely available for purchase. |
Delta 7 THC Research
What we know about delta 7 THC and its effects are mostly based on anecdotal reports. It shows many of the same effects as other THC cannabinoids, such as relaxation, pain relief, and appetite stimulation.
Since most of the research on cannabis compounds centers around delta 9 THC and CBD, we don’t know much about how THC isomers work in the body.
The rise in interest in THC isomers came about when hemp was legalized in the United States with the 2018 Farm Bill.
Before this, the cultivation and use of cannabis — including hemp — and its derivatives were heavily restricted in many parts of the United States, thus limiting the ability of researchers to study these compounds.
Research on delta 7 is in its early stages, and many of which are conducted on animals, but, likely, the trend of exploring all cannabis has to offer will result in more interesting developments and new products.
One study, in particular, looked at six different cannabinoid structures, including delta 9 THC, delta 8 THC, and delta 7 THC, to understand how their structures relate to their activity.
The researchers found that the orientation of the carbocyclic ring in each molecule determined its activity and that the unique structural shape of these THC isomers plays a pivotal role in the activity of these cannabinoids [3].
How Is Delta 7 THC Made?
Delta 7 THC is not typically found in large quantities in cannabis plants, so it’s synthesized from other cannabinoids such as delta 8 THC or, more popularly, CBD, as it’s an abundant cannabinoid in hemp.
The process is called isomerization, and it involves acids to chemically transform the molecular structure of the original cannabinoid into the desired compound. This can’t be done at home, as it requires precision and heavy-duty lab equipment to execute.
As long as the manufacturing process is done professionally and has third-party lab testing to verify that the final product is free from residual chemicals, you should have a safe delta 7 THC product.
How to Dose Delta 7 THC
As a newer cannabinoid, delta 7 isn’t as widely available as CBD or THC (delta 9 and delta 8), so there’s still little information on dosing recommendations.
The best compound we can compare it to for dosing is delta 9 THC, as it’s arguably the most well-known THC cannabinoid.
According to anecdotal reports, compared to delta 9, delta 7 has much milder psychoactive effects, so it may take larger doses to achieve the same intense high with recreational marijuana.
But other factors can affect the proper cannabinoid dosing for an individual, including:
- Experience with cannabinoids (tolerance)
- Weight
- Metabolism
- Underlying health conditions
The standard psychoactive dose of delta 9 THC is around 5 mg. This is where its psychoactive effects are noticeable.
But because delta 7 is much weaker than delta 9, it’s common to see recommended doses from experienced users and brands offering delta 7 THC products starting at 10-15 mg — double to triple the amount of delta 9 products.
The effects can last anywhere from 2-10 hours, depending on the dose and how it was administered.
Typically, eating delta 7-infused products lasts much longer than vaping or smoking the compound.
1. Microdose
Microdosing THC is a technique that’s become recently popular for those who may want to manage symptoms such as pain, anxiety, or nausea without experiencing strong psychoactive effects.
While some people claim to benefit from microdosing THC, no scientific evidence supports the claims.
The microdose for delta 9 THC is 0.5–1.5 mg, so we can assume that delta 7 is about 1–3 mg.
The goal of a microdosing practice is to experience the potential therapeutic benefits of THC without getting high, so if it feels like nothing, you’re probably doing it right.
2. Low Dose
A low dose is a suitable option for those who want to manage symptoms such as pain, nausea, and anxiety without a full-blown psychoactive dose.
One of the reasons people might seek delta 7 and even delta 8 THC products is because of their milder nature. It’s not as easy to overdo the doses, so you can avoid feeling overwhelmed by the psychoactive properties that can impair cognitive function or cause drowsiness.
A low dose of delta 7 THC is around the 5 mg mark.
3. Standard Psychoactive Dose
Some people may choose a standard psychoactive dose with delta 7 THC for its euphoric effects. It can help improve mood, promote deep relaxation, and create more enjoyable sensory experiences.
At the same time, reaching a psychoactive dose of THC can be used for medicinal purposes to manage stronger symptoms of pain and anxiety.
Because delta 7 is much weaker than delta 9, reaching these effects will take a significantly higher dose. The standard psychoactive dose for delta 7 is around the 10–15 mg mark.
4. Heavy Dose
Unless you’ve got some THC experience under your belt, we don’t recommend even a heavy dose of even the milder delta 7 THC.
It can cause impairment in cognitive function, drowsiness, and in some cases, may increase anxiety and paranoia.
However, some individuals may want a heavy dose of THC to address pain symptoms. Delta 9 THC might be a better fit in these instances, as it requires smaller amounts to reach this state.
Nevertheless, you can reach a heavy dose with delta 7 THC with doses upwards of 25 mg.
What Are the Side Effects of Delta 7 THC?
Delta 7 THC is a relatively new compound, and there is currently limited research on its potential side effects. However, it is a form of THC, which is known to have common side effects, especially at higher doses.
Some potential side effects of THC, including delta 7, may include:
- Euphoria
- Feeling “high”
- Dry mouth
- Red eyes
- Increased heart rate
- Decreased blood pressure
- Impaired memory or concentration
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Anxiety or paranoia
- Psychosis, in rare cases
Is Delta 7 THC Legal?
In the United States, the legal status of delta 7 THC depends on its source.
If it’s derived from hemp — a cannabis plant containing less than 0.3% delta 9 THC — then it is legal under federal law as per the Farm Bill (2018).
However, some states have different regulations regarding THC variants from hemp.
The following states have banned the sale of all THC isomers:
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- Colorado
- Delaware
- Idaho
- Iowa
- Kentucky
- Mississippi
- Montana
- Rhode Island
- Utah
- Vermont
This means that if you’re purchasing a delta 7 product online, it may not ship to your area, and if you get caught with it, you could face legal consequences. These laws are constantly in flux, so make sure you stay up to date.
FAQs: Delta 7 THC
1. What’s the difference between delta 7 & delta 9 THC?
The main difference between delta 7 and delta 9 THC is their chemical structure.
Delta 9 THC has a double bond on the ninth carbon atom in its chemical structure, while delta 7 THC has a double bond on the seventh carbon atom. This difference in structure can result in different pharmacological effects on the mind and body.
Delta 9 THC is the primary psychoactive component of cannabis and is responsible for the “high” that many people experience when using cannabis. It’s also known for its potential medicinal properties, such as pain relief and anti-nausea effects.
Delta 7 THC is a less well-known compound present in much smaller amounts in the cannabis plant than delta 9 THC. Its effects are much milder, making it a more suitable compound for those looking for a gentler cannabis experience.
2. Are delta 7 products safe to use?
As a relatively new compound, limited studies are available on the safety of delta 7 THC products specifically. But it’s deemed to be relatively safe for the most part, as cannabis-based cannabinoids are generally non-toxic.
The biggest safety concern is choosing a reputable supplier that can provide third-party testing to prove the quality of their products.
Even with a good product, delta 7 THC is a form of THC and has potential risks and side effects, such as impaired cognitive function and psychological distress, especially at higher doses.
To ensure safety when using delta-7 THC products, it is important to:
- Research the product and the manufacturer to ensure that it is reputable and safe.
- Follow all applicable laws related to cannabis products in your area.
- Consult with a licensed healthcare professional before using any cannabis product for medicinal purposes.
- Start with low doses and increase slowly to understand your tolerance and mitigate potential side effects.
- Use cannabis products responsibly and avoid operating heavy machinery or driving while under the influence, as it can impair your coordination and judgment.
3. How does delta 7 compare to delta 8 THC products?
Delta 7 and delta 8 are isomers of the delta 9 THC cannabinoid, all producing psychoactive effects.
Delta 8 occurs in higher concentrations in the cannabis plant compared to delta 7 — though it is still a minor cannabinoid — and there is more research surrounding its use. Subsequently, delta 8 is much easier to source.
Delta 8 is about half as potent as the delta 9 THC compound and is enjoyed for its clear-headed, mellow high, while delta 7 is even weaker than delta 8.
It’s worth mentioning that individuals may have varying experiences with cannabinoids, so what works and is more enjoyable for one person may be different for the next.
4. Is delta 7 a naturally occurring or synthetic cannabinoid?
Delta 7 has been found naturally in cannabis plants but in trace concentrations, which means it’s difficult to extract in meaningful quantities.
Most delta 7 THC is produced in a lab by chemically transforming the CBD cannabinoid.
It’s not technically a synthetic cannabinoid like K2 or Spice, which aren’t found in nature and made in a lab. These have no potential therapeutic benefits and a high potential for harm.
Delta 7 is “semi-synthetic” — it’s found in nature and is made by taking a naturally occurring cannabinoid and altering its chemical structure.
5. How long do the effects of delta 7 THC last?
Depending on the dose, the effects of delta 7 can last anywhere from 2–5 hours, but like other cannabinoids, this varies due to several factors, including the amount taken (dose), method of consumption (smoking, gummies, oil), and the individual’s body chemistry (metabolism, weight, tolerance).
In general, when smoking or vaping delta 7, you should feel the effects within a matter of seconds, but it doesn’t last as long as eating them, which can take up to an hour before they kick in.
Key Takeaways: What Is Delta 7 THC?
Some companies are now marketing delta 7 THC as an alternative to delta 9 THC for individuals looking for a milder psychoactive experience or living in areas where recreational marijuana is illegal.
Delta 7 THC is a naturally occurring minor cannabinoid. Still, most delta 7 THC products on the market are lab produced, meaning they are created in a laboratory using chemical processes rather than extracted directly from the plant.
People who’ve tried delta 7 experience feeling a gentle, mellow high compared to delta 9, but the effects of the compound can vary by dose and the individual.
Because marijuana remains a controlled substance, delta 7 is often marketed as a legal alternative if it’s derived from Farm Bill-compliant hemp crops. Still, some states banned all THC, regardless of its source.
Overall, delta 7 THC is still new on the scene, with limited research on its effects and potential benefits or risks. Before trying a delta 7 product, research the brand and its manufacturing methods, and don’t jump into the doses too quickly.
References
- Bakas, T., Van Nieuwenhuijzen, P. S., Devenish, S. O., McGregor, I. S., Arnold, J. C., & Chebib, M. (2017). The direct actions of cannabidiol and 2-arachidonoyl glycerol at GABAA receptors. Pharmacological research, 119, 358-370.
- Zygmunt, P. M., Andersson, D. A., & Högestätt, E. D. (2002). Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabinol activate capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerves via a CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptor-independent mechanism. Journal of Neuroscience, 22(11), 4720-4727.
- Reggio, P. H., Greer, K. V., & Cox, S. M. (1989). The importance of the orientation of the C9 substituent to cannabinoid activity. Journal of medicinal chemistry, 32(7), 1630-1635.