2C-B: Effects, Dosage, & Safety
The middle ground between MDMA & LSD.
Everybody has heard of MDMA (ecstasy) and LSD (lysergic acid diethylamide) — they’ve become staples in the world of mind-altering substances.
But there’s another popular psychoactive substance that’s been residing in the shadows since the 1980s. This substance is called 2C-B.
The effects of 2C-B are often described as being a mid-point between the empathogenic effects of MDMA and the hallucinogenic effects of LSD.
So what exactly is 2CB? Is it safe?
In this article, we’ll cover everything you need to know about 2C-B — including how it works, what it feels like, and how to use it safely.
What is 2C-B?
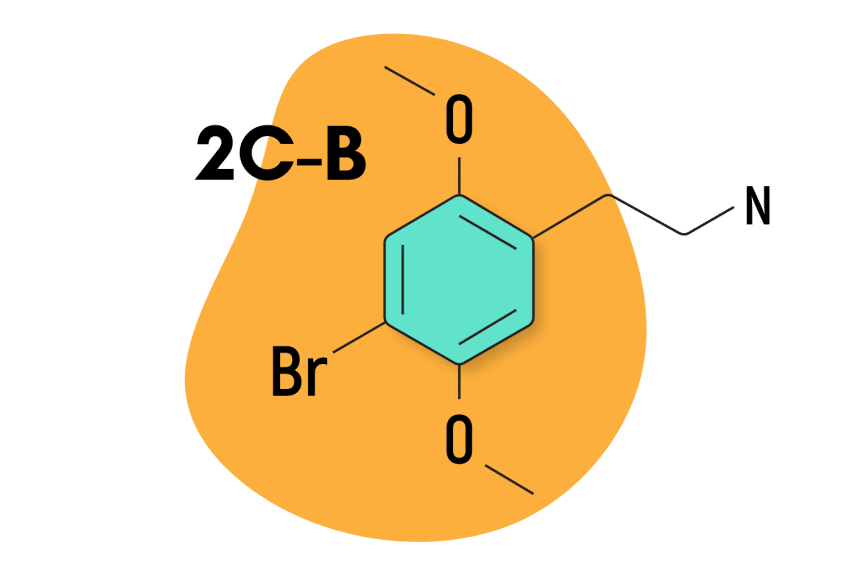
2C-B (4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine) is a synthetic psychedelic substance derived from mescaline. It was invented in 1974 by a man named Alexander Shulgin — the godfather of MDMA and creator of the entire 2C- family of substances.
Shulgin invented well over 200 psychoactive compounds in his research lab dubbed “The Farm.”
Shulgin considered 2C-B to be one of his greatest creations. In one of his books — PiHKAL (phenethylamines I Have Known And Loved) — he listed 2C-B among his “magic half dozen”.
The other five include mescaline, DOM, 2C-E, 2C-I, 2C-T2, and 2C-T7.
The effects of 2C-B have been described as a combination between LSD and MDMA — but this is a simplification. In reality, the 2C-B experience is entirely unique.
The qualities of 2C-B made it popular as a sex-enhancement drug in the 80s. The German pharmaceutical company Drittewelle started producing the drug under the name “Nexus.” It was sold in sex shops as a way to boost libido, sexual connection and increase stamina and energy. 2C-B is still considered by many to be the best psychedelic to use during sex of all time.
In Shulgin’s own words, “[2C-B] is, in my opinion, one of the most graceful, erotic, sensual, introspective compounds I have ever invented.”
2C-B reached mainstream popularity sometime after 1985 when MDMA was officially banned. It was used as a legal alternative to MDMA. 2C-B and the rest of the 2C- family were later banned in 1995.
2C-B: Specs & Technical Details
| Chemical Name | 4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine |
| Level of Risk | Low |
| Street Names | Venus, Bromo, Bees, Toonies, Erox, XTC, & Nexus |
| Most Common Side-Effects | Jitteriness, rapid heartbeat, headache |
| Duration of Effects | 4 – 8 hours |
| Legality | Illegal in most parts of the world |
Trip Sitter Safe 2C-B Guidelines
- 🐍 I understand why psychedelics should be treated with respect
- ⚖️ I’m familiar with the laws surrounding psychedelics in my country & state
- 🍄 I’m familiar and confident in the dose I’m taking (dose range for 2C-B is 5-20 mg)
- 🧪 I’ve tested a sample of the substance I’m using with a drug testing kit
- 💊 I’m not mixing any medications or other substances with 2C-B
- 🏔 I’m in a safe & comfortable environment with people I trust
- 🐺 One of the members of my group is responsible and sober (AKA a trip sitter)
- 📆 I have nothing important scheduled for after the trip
- 🧠 I’m in a sound & healthy state of mind
- 🌶 I’m aware of the increased risk of heatstroke & dehydration with this compound
- 📚 I’m familiar with the four pillars of responsible psychedelic use — set, setting, sitter, & substance.
- ⏳ Know the timeline — the effects of 2C-B can last between 4 and 8 hours
- 🙅♀️ Know when to avoid stimulants — don’t take 2C-B if you have underlying heart, neurological, or psychiatric disorders
What’s The Dose of 2C-B?
The dosage range for 2C-B is between 5 mg and 35 mg. Most tablets or capsules contain 5 mg of 2C-B each.
Lower doses of around 5 mg have effects most similar to MDMA or Adderall, while the higher doses (more than 15 mg) offer formidable hallucinogenic effects comparable to LSD, psilocybin, or mescaline.
The dosage range of 2C-B includes:
- 1 mg — Microdose
- 5 mg — Threshold dose (stimulant-like effects)
- 5–20 mg — Standard psychoactive dose (hallucinogenic & stimulant effects)
- 20–35 mg — High psychedelic dose (strong hallucinogenic & stimulant action)
- 35–60 mg — Heroic dose (unpredictable effects, not recommended)
2C-B has a high level of safety. Shulgin, the inventor of the drug, reportedly took 100 mg by accident. This is a dose nearly three times what’s considered a high dose for the substance. He didn’t suffer any severe side effects from the experience.
With that said, higher doses can be intense. Most people who use more than 35 or 40 mg of the drug report intense, often scary, or confronting hallucinations.
The higher the dose, the stronger the visuals. Some could even describe the visuals at higher doses to be “cartoon-like” — which is similar to the visuals experienced with higher doses of mescaline.
What Does 2C-B Feel Like?
The effects of 2C-B could be described as a combination of MDMA and LSD.
While there’s truth to this, it’s not perfectly accurate. 2C-B has empathogenic effects like MDMA and hallucinogenic effects like LSD — but the experience is unique in and of itself. The overall effects of 2C-B share much more resemblance to mescaline.
As part of our ongoing experience surveys, we ask our readers to share their experiences to better understand the effects and common dosages of substances.
Most of the responses we’ve received throughout our 2C-B survey had a positive sentiment. Many people taking part in our surveys and in the psychedelic community at large consider 2C-B to be their favorite psychedelic.
Commonly 2C-B Experiences Include:
- Increased energy (92%)
- A greater sense of empathy with others (86%)
- Introspection (80%)
- Visual hallucinations (78%)
- Sexual arousal (78%)
- Laughter (76%)
- Auditory hallucinations (67%)
- Ego death or dissolution (65%)
2C-B is most often used in place of MDMA at concerts, parties, or music festivals. The stimulating and euphoric effects make people feel more social and engaged, it creates a strong sense of empathy and connectedness with other people, and it won’t inhibit your ability to sleep at the end of the night.
Here’s what you can expect to feel while taking 2C-B:
Introspection
Users often report feelings of introspection, ego-dissolution, and a stronger sense of empathy and connection with others. It’s not uncommon for people using 2C-B to come to some sort of “realization” about their life. This realization may remain after the trip, but it may also be forgotten.
In a clinical setting, 2C-B is thought to connect the user with former emotions and repressed memories.
Hallucinations
2C-B is a hallucinogen through and through. In smaller doses these effects are limited, but higher doses of 2C-B produce intense changes in sensory perception. This includes sight, sound, and touch.
The visuals of 2C-B remind me of the videogame Borderlands — where some details pop much more than others and make the world look almost as though it was traced over with a pencil
Energized
Sometimes 2C-B can feel a little bit “speedy” or “tweaky” — especially in the higher doses.
2C-B is also used for its sexual-enhancement purposes as a way to explore a deeper connection between partners and enhance libido and physical stamina.
Disorientation
Reports from people who took part in our survey that used very high doses (40 mg or higher) or mixed 2C-B with other psychedelics like LSD or psilocybin often mention the experience to be “disorientating” (37%).
Does 2C-B Have Medical Value?
2C-B isn’t used medically because of its current standing as a Schedule I substance in the United States. It’s classified under equivalent filings in other countries, such as the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, Germany, and Europe.
The drug’s creator, Alexander Shulgin, suggested 2C-B was a good follow-up treatment in psychotherapy after MDMA. He suggested 2C-B as a way to open up the emotional, intuitive and archetypal area of your psyche to help solve the problems uncovered during the MDMA session.
More research is needed before we can make any reasonable assumptions about the potential for using 2C-B in psychotherapy.
Can 2C-B Cause A Bad Trip?
Yes, 2C-B is a strong psychedelic — especially in higher doses. However, when used within the standard psychoactive range (5–15 mg), 2C-B is unlikely to lead to what can be considered a “bad trip.”
The higher you go over the 15 mg dose, the more likely you are to experience challenging or uncomfortable experiences. The hallucinations on 2C-B can escalate very quickly at higher doses.
Sometimes, bad trips are the result of adulterants (ingredients you weren’t expecting to be in there). Samples of 2C-B have been shown to contain substances such as methamphetamines, MDA, PMA, PMMA, NBOMe, or various opiates.
You should also always test a sample of your 2C-B using a reagent test liquid before you use it. It’s impossible to know what’s in a pill or powder without testing.
Testing 2C-B is very easy to do, it’s cheap, and it only requires you to sacrifice trace amounts of your tablet or powder — only a sample the size of a grain of sand is necessary to run the safety tests that could save your life.
Does 2C-B Cause a Hangover?
One of the biggest benefits of using 2C-B over MDMA is the lack of a hangover the following morning.
Of our respondents, only 7% reported any negative impact the following morning after using doses lower than 35 mg of 2C-B. A big reason for this comes down to the fact that 2C-B rarely interferes with sleep. Getting a good night of rest after using 2C-B is one of the best ways to avoid hangovers.
With that said, hangovers are still possible — and are especially common with the higher doses. Of the survey respondents that too more than 35 mg of 2C-B, nearly 28% of them had a hangover the following morning.
The best way to avoid a 2C-B hangover is to drink plenty of water throughout the experience and ensure you’re getting a full 8 hours of sleep afterward. Taking some electrolytes or magnesium before you go to bed can go a long way as well.
How Long Does 2C-B Last?
2C-B usually lasts between 4 and 8 hours.
The effects usually begin to appear within about 45 minutes to an hour after taking it and peak around the 2-hour mark.
Peak effects last between 1 and 2 hours before tapering off. The comedown on 2C-B is very slow and gradual — which is considered one of the advantages of this substance. Most amphetamines or other stimulants tend to produce a rapid comedown — which can make users feel depressed. 2C-B is much more gradual and gentle.
How is 2C-B Used?
2C-B comes as either a white crystalline powder or pressed tablets.
Tablets contain either 5, 10, 20, or 25 mg of 2C-B each — so a normal dose can range anywhere from 1–7 tablets. Always check the dose of your tablet before you take it.
The powder is usually used in a “parachute” — which involves weighing the dose of powder on a small scale and wrapping it up into a rolling paper. This is then taken just like you would a capsule, by essentially swallowing it whole.
Other people prefer to fill their own capsules using the raw powder or snorting it (insufflation). Be very careful when snorting any substance. The effects will be much stronger and appear much more quickly. Take a lower dose than you normally would and give it time to take effect. It’s easy to take too much using this method.
In general, we advise against snorting any substance. It’s far too easy to take too much, and it can be extremely damaging to the nasal cavity.
Additionally, always weigh your dose using a small scale if you’re taking the raw powder. Never attempt to eyeball your dose of 2C-B of any powdered drugs. Scales are cheap (less than $20) and could mean the difference between having a positive experience and ending up in a hospital.
2C-B can also be vaporized — but this isn’t a common way of using it, and the long-term health effects of taking 2C-B this way aren’t well understood. Many compounds will change when heated like this, and the byproducts of vaporized 2C-B are not well understood.
It’s best to stick to the tried and tested oral route when taking 2C-B.
Other Members of the 2C- Family
2C-B is just one of many substances in its family. Most of them were invented around the same time by Alexander Shulgin and documented in one of his books PiHKAL.
All 2C- substances contain methoxy groups on the 2 and 5 positions of a benzene ring of its chemical structure. They each have a unique chemical group attached to the 4th position on the benzene ring, which is what differentiates them in terms of their chemical structure and effect profile.
When various government regulators started banning 2C-B, they did so by banning the entire 2C-x family — as defined by the chemical structure above.
The most notable members of the 2C- family include:
- 2C-B — this is by far the most popular member of the family.
- 2C-C — this 2c compound differentiates itself through its relaxing, even mild sedative action and powerful visuals.
- 2C-E — this 2C compound is milder than 2C-B, has a slightly higher likelihood of side effects, and lasts about 3 hours longer.
- 2C-I — these substances tend to produce effects similar to LSD but less introspective. The most common is 2C-I-NBOMe, which has been proven to be dangerous & should be avoided
- 2C-P — a strong, but mellow psychedelic with empathogen underpinnings.
- 2C-T — there are several iterations of this compound, including 2C-T-2, 2C-T-3, 2C-T-4, 2C-T-7, & 2C-T-16. The most popular, by far, is 2CT-7.
List of all 2C-Substances
- 2C-B
- 2C-Bn
- 2C-Bu
- 2C-C
- 2C-C-3
- 2C-CN
- 2C-CP
- 2C-D
- 2C-E
- 2C-EF
- 2C-F
- 2C-G
- 2C-G-1
- 2C-G-2
- 2C-G-3
- 2C-G-4
- 2C-G-5
- 2C-G-6
- 2C-G-N
- 2C-H
- 2C-I
- 2C-IP
- 2C-N
- 2C-NH2
- 2C-PYR
- 2C-PIP
- 2C-O
- 2C-O-4
- 2C-MOM
- 2C-P
- 2C-Ph
- 2C-Se
- 2C-T
- 2C-T-2
- 2C-T-3
- 2C-T-4
- 2C-T-5
- 2C-T-6
- 2C-T-7
- 2C-T-8
- 2C-T-9
- 2C-T-10
- 2C-T-11
- 2C-T-12
- 2C-T-13
- 2C-T-14
- 2C-T-15
- 2C-T-16
- 2C-T-17
- 2C-T-18
- 2C-T-19
- 2C-T-21
- 2C-T-21.5
- 2C-T-22
- 2C-T-23
- 2C-T-24
- 2C-T-25
- 2C-T-27
- 2C-T-28
- 2C-T-30
- 2C-T-31
- 2C-T-32
- 2C-T-33
- 2C-DFM
- 2C-TFM
- 2C-TFE
- 2C-YN
- 2C-V
- 2C-AL
How Strong is 2C-B vs. Other Psychedelics?
The intensity of effects from 2CB increases steadily along with the dose.
Lower doses (5 mg) resemble Adderall or MDMA and don’t produce strong visuals.
The higher the dose, the more psychedelic it gets. The 35 mg dose is a potent psychedelic — and very high doses (50 mg or more) are profoundly psychedelic and have even been known to induce out-of-body experiences.
2C-B vs. LSD
2C-B is often compared to LSD because the visual effects of these two drugs are very similar. Users experience light trails, geometric patterns, and objects that appear to merge together.
The intensity of the trip is very similar for these two drugs, but 2C-B is generally much more euphoric. Some people argue the euphoria induced by 2C-B isn’t “earned.” This means you don’t actually have to do anything to feel the euphoria; it’s merely a byproduct of the substance itself.
With LSD, the euphoria needs to be earned through experience and mindset. It doesn’t have an inherent euphoric quality to it, so those without the right mindset may not feel any euphoria whatsoever.
In terms of dose, LSD is many times more potent than 2C-B. The psychoactive dose of LSD is measured in sub-milligram doses, while the threshold dose for 2C-B is around 5 mg.
2C-B vs. Mescaline
Most people suggest the effects of 2C-B are a combination of LSD and MDMA. However, it’s more accurate to suggest the effects of 2C-B resemble mescaline — which is actually the molecule used as inspiration for creating the entire 2C class of drugs, to begin with.
2C-B is more stimulating than mescaline and has much less “headspace.” Headspace refers to the introspective and existential thoughts that accompany the psychedelic experience.
Both 2C-B and mescaline are thought of as being “gentle” when compared to other psychedelics and the visuals are very similar between the two.
In lower doses, their visuals are very “flowy”, while higher doses are much more “cartoon-like.”
2C-B vs. MDMA
2C-B is often used as an alternative to MDMA (ecstasy) at concerts, music festivals, or parties. Lower doses of 2C-B are the most similar to MDMA for creating a greater sense of connectedness with the people around you. Both substances produce a feeling of euphoria, can enhance the enjoyment of music, and stimulate the sensual feedback from touch.
The more 2C-B you take, the further the experience diverges from MDMA. High doses are very psychedelic and can make being at public events very uncomfortable — unlike MDMA.
One of the main benefits of 2C-B over MDMA is that users usually don’t experience difficulty falling asleep after the experience.
Is 2C-B Safe?
There are no reported overdose deaths from people who took 2C-B. Additionally, the few clinical trials that are available involving 2C-B have all reported the drug had little to no side effects and that the drug had a high level of safety.
Anecdotal reports on sites like Reddit, as well as through our own surveys, suggest some people prefer to take large doses of the drug (over 50 mg) — without experiencing any severe side effects.
The lethal dose of 2C-B has never been found.
Some users, including Shulgin, have reported taking as much as 100 mg of 2C-B without serious side effects. However, these doses are rarely enjoyable and can even be quite scary.
2C-B has been around since the 1970s, and while it didn’t really become popular until the 90s, it still has over 30 years of mainstream use behind it. If 2C-B was inherently dangerous, it would be crystal clear by now.
With that said, there is a serious lack of research available on the safety of 2C-B. There are virtually no toxicology studies available. Due to the heavily restricted status of this substance, it’s unlikely we’re going to see this research anytime in the near future.
This isn’t the case with other 2C substances — such as 2C-E and 2C-I — which have proven themselves dangerous over the years.
With that said, 2C-B isn’t without its risks.
2C-B Adulteration
The main risk of this compound is adulteration (mixing or swapping other substances into 2C-B tablets or powder).
It’s not uncommon for someone to order 2C-B online only to receive something completely different in the mail. You can never trust what’s inside your pills or powders unless you test it first. And even with testing, you can’t be 100% sure it’s free from harmful chemicals.
→ Learn how to test a sample of 2C-B for adulterants
2C-B & Drug Interactions
Certain drugs or medications may also interact negatively with 2C-B.
This substance is largely metabolized by an enzyme called monoamine oxidase (MAO) [2]. It’s the main enzyme responsible for breaking down neurotransmitters, including dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine. People taking MAO inhibitor medications (a type of antidepressant) may have a hard time metabolizing 2C-B — which could lead to side effects.
2C-B is also likely to interact negatively with other stimulating substances, such as amphetamines (Adderall), MDMA, MDA, cocaine, caffeine, and nicotine. Combining these substances could lead to side effects and harm involved with increased heart rate and blood pressure, changes in breathing patterns, jitteriness and muscle tension, dehydration, headaches, blood sugar regulation, and anxiety or panic.
Mixing 2CB with other psychedelics like LSD, mescaline, or magic mushrooms can lead to much stronger hallucinations. This can cause intense fear, panic, or anxiety.
It’s wise to avoid any other substances while taking 2C-B to avoid negative interactions. This includes alcohol, cigarettes, and prescription medications.
People taking heart medications, immune system regulators, antibiotics, or ADHD medications should avoid 2C-B altogether.
2C-B Side-Effects
- Fear, panic, or anxiety
- Disorientation
- Nausea & vomiting
- Digestive discomfort
- Rapid heart rate
- High blood pressure
Is 2C-B Addictive?
2C-B is not inherently addictive — however, people can form addictions to any mind-altering substance, including 2C-B.
There really isn’t such a thing as a “good drug” or a “bad drug.” Substances like 2C-B are just molecules that exist in the world around us. It’s our relationship to them and the way we use them that can be described as “healthy” or “unhealthy.”
An unhealthy relationship with a substance like 2C-B would involve regular, repeated use of the substance either out of compulsion or to find a release from reality.
This is essentially what addiction is. They’re using a substance to escape the way they feel or to escape a reality they deem “undesirable.”
2C-B makes us happy, carefree, relaxed, social, and euphoric. It changes our perspective of the world and allows us to forget our biggest fears and stressors.
While this can be extremely beneficial for helping someone acknowledge the source of their problems internally and acts as a reminder that life, in its essence, is good — it can also become a crutch for people with more of a nihilistic or doomer perspective on life.
Compulsive use of any substance would be an example of having an unhealthy relationship with the substance. It’s what defines addiction.
Psychedelics like 2C-B should be used for personal growth and healing — not to escape reality.
2C-B & Physical Addiction: Dependence & Tolerance
There are two types of addiction — behavioral addiction and physical addiction.
As described above, behavioral addiction is the type of addiction we can have for the way a substance or activity makes us feel. Our body isn’t dependent on the substance, but we still seek it out in order to feel a certain way. We can also become behaviorally addicted to gambling, sex, masturbation, or shopping.
Physical addiction is differentiated from behavioral addiction in that there is a physical change to the body’s homeostatic default settings in response to the drug. When we take a substance repeatedly, the body makes changes to adapt to the presence of the substance. This is called dependence because we depend on having the drug in our system to maintain balance. As soon as the drug wears off, we’re no longer in balance — causing side effects referred to as withdrawal.
2C-B can eventually lead to physical addiction if used repetitively over long periods of time.
Is 2C-B Legal?
All 2C substances are illegal globally. The entire family of research chemicals was originally banned in the United States in 1995. 2C-B was specifically added to the UN Convention of Psychotropic Substances in 2001. This led to the banning of this substance in all UN-member countries.
In the US, 2C-B is listed as a Schedule I drug — along with heroin, LSD, and cocaine.
It’s classified as a Schedule III substance in Canada, which means it’s only available for research purposes.
In the United Kingdom, 2C-B is a Class A drug — which implies the drug poses a significant danger to public health and brings the most severe punishments to those caught in possession of the drug.
Related: What is psychedelic-assisted psychotherapy?
How 2C-B Works
There isn’t much research available on 2C-B, but we do have a general understanding of how it works.
Most psychedelics work by activating the 5-HT2A serotonin receptors. This is the primary mechanism of action employed by substances, including LSD, DMT, and psilocybin.
2C-B and related phenethylamines like mescaline have a much weaker action on this receptor. This suggests there are other mechanisms involved with the drug’s hallucinogenic effects. Some studies even suggest 2C-B may act as an inhibitor of the 5-HT2A receptor [3].
Some studies suggest 2C-B activates another serotonin receptor called 5-HT2C — which also produces hallucinogenic effects [4].
Other serotonin receptors may also be involved, such as the 5-HT1A receptors, which could be involved in the emotional changes induced by 2C-B [5]. This substance is reported to influence the emotional response through both top-down and bottom-up cognitive processes.
Compared to other 2C-x drugs, 2C-B is the second most potent agonist of serotonin receptors only to 2C-I. 2C-D and 2C-H have a much lower affinity for these receptors.
2C-B has also been shown to have some action at the alpha-adrenergic receptors [3]. This is likely one of the main mechanisms involved with the substance’s stimulating effects.
Research on 2C-B is seriously lacking. Despite how popular this substance is, there are no clinical trials or even toxicology studies to date. The only data we have available comes from anecdotal reports, observational studies, and in vitro research. If you want to contribute your experience to improve our understanding of 2C-B or other psychedelics, consider filling out one or more of our psychedelic surveys and sharing your experience.
Frequently Asked Questions About 2C-B
1. How Do I Test The Purity of 2C-B?
Everybody should test their drugs before using them to avoid mistakenly consuming toxic alternatives.
The best way to test a sample of 2C-B is to use a reagent test kit. Only a small sample of the drug is needed to run the test (the size of a grain of sand).
Regent tests won’t tell you the purity of a substance. They can only tell you whether or not a sample contains a certain substance or not.
The best reagent to use is the Marquis reagent. It will turn a yellowish-green color in the presence of 2C-B. The reagent will turn purple if the sample contains MDMA, and NBOMe substances will turn red.
2. Will 2C-B Show Up On A Drug Test?
Most drug tests won’t detect 2C-B. Only specialized drug tests using mass spectrometry or gas chromatography will be able to differentiate 2C-B in a blood or urine sample.
There have been reports of 2C-B triggering a false-positive on amphetamine tests, but this is very rare.
With that said, if you’re expecting a drug test for any reason, it would be wise to avoid 2C-B.
3. Is 2C-B Dangerous?
All psychoactive drugs have an inherent level of risk associated with their use. 2C-B has stimulating effects that could be dangerous for people with heart disease or who are taking heart medications.
The hallucinogenic effects of 2C-B could bring an increased level of risk to people with psychiatric disorders.
2C-B has never been associated with any overdoses or deaths, but there’s been one case of reported psychosis after using 2C-B [7].
4. Can I Microdose 2C-B?
Microdosing is the process of taking very small, sub-perceptual doses of a substance. They’re used to increase focus and concentration, improve empathy and connectedness with others, and help achieve a higher level of productivity.
Some users have reported taking microdoses of 2C-B similarly to other psychedelics like magic mushrooms or LSD. It’s been reported to increase tactile awareness, increase the clarity of thought, and boost mental energy and stamina.
It’s not clear whether or not microdoses of 2C-B are safe long term.
Final Thoughts: What Is 2C-B?
2C-B is one of the most popular psychoactive substances globally — despite there being virtually no research available on its safety or effect profiles in the medical literature.
It’s often used as an alternative to MDMA at lower doses and an alternative to LSD in high doses.
Compared to other psychedelics, 2C-B is considered gentle — which effects described as being a combination of MDMA and LSD. A better comparison is mescaline — which is the molecule Alexander Shulgin used to derive the 2C class of drugs, to begin with.
We’re running a continual survey on the use of 2C-B to better understand the effects and use patterns surrounding this unique psychedelic substance.
If you’ve tried 2C-B and want to contribute to this research, you can anonymously enter details of your experience through this 6-minute 2C-B survey. We greatly appreciate your participation!
Subscribe To Get a Weekly Dose of Psychedelics In Your Inbox
References
- Carmo, H., Hengstler, J. G., De Boer, D., Ringel, M., Remião, F., Carvalho, F., … & de Lourdes Bastos, M. (2005). Metabolic pathways of 4-bromo-2, 5-dimethoxyphenethylamine (2C-B): analysis of phase I metabolism with hepatocytes of six species, including human. Toxicology, 206(1), 75-89.
- González, D., Torrens, M., & Farré, M. (2015). Acute effects of the novel psychoactive drug 2C-B on emotions. BioMed research international, 2015.
- Villalobos, C. A., Bull, P., Sáez, P., Cassels, B. K., & Huidobro‐Toro, J. P. (2004). 4‐Bromo‐2, 5‐dimethoxyphenethylamine (2C‐B) and structurally related phenylethylamines are potent 5‐HT2A receptor antagonists in Xenopus laevis oocytes. British journal of pharmacology, 141(7), 1167-1174.
- Rickli, A., Luethi, D., Reinisch, J., Buchy, D., Hoener, M. C., & Liechti, M. E. (2015). Receptor interaction profiles of novel N-2-methoxybenzyl (NBOMe) derivatives of 2, 5-dimethoxy-substituted phenethylamines (2C drugs). Neuropharmacology, 99, 546-553.
- González, D., Torrens, M., & Farré, M. (2015). Acute effects of the novel psychoactive drug 2C-B on emotions. BioMed research international, 2015.
- Papaseit, E., Farré, M., Pérez-Mañá, C., Torrens, M., Ventura, M., Pujadas, M., … & González, D. (2018). Acute pharmacological effects of 2C-B in humans: an observational study. Frontiers in pharmacology, 9, 206.
- Huang, H. H., & Bai, Y. M. (2011). Persistent psychosis after ingestion of a single tablet of’2C-B’. Progress in neuro-psychopharmacology & biological psychiatry, 35(1), 293-294.