Acadian Coast Mushroom Strain: Appearance, Origin, Potency & More
These rare magic mushrooms were believed to have been collected around the subtropical wetlands of Louisiana around the Mississippi river.

Most psilocybin mushroom users know about the more popular mushroom strains, like Golden Teachers, Penis Envy, and Blue Meanies. Far fewer know about rarer strains, like the Acadian Coast shroom.
There’s much debate about the origins of this mysterious strain, but most users agree the potency is about average for what psilocybin mushrooms have to offer (0.60–0.80%) total tryptamines.
It’s unclear exactly where Acadian Coast shrooms were originally collected as there is conflicting information online and from enthusiasts. The most commonly held belief is that the original sample for this strain was collected along the American portion of the Acadian Coast (as their name suggests).
The Acadian Coast stretches along the eastern coast of North America, from Newfoundland to Louisiana. More specifically, it’s believed the first sample was collected near the Mississippi River.
Once collected, the Acadian Coast strain was cultured indoors, stabilized, and then sold online in the form of spores.
You can now find Acadian Coast mushroom spores from most of the mainstream spore vendors.
Acadian Coast Shrooms Specs
| Potency | Average 🍄 |
| Cultivation | Intermediate |
| Species | Psilocybe cubensis |
| Substrate Recommendation | Brown Rice Flour and Vermiculite |
| Cost | $$ |
| Sold By | Sporeslab, Spores 101, High Desert Spores, Mushroom Prints |
History of The Acadian Coast Shrooms
Unfortunately, very little is known about the origins of the Acadian Coast mushroom.
Some sources maintain that these shrooms come from samples taken exclusively along the coast of the Mississippi River, specifically in Louisiana. If this is the case, these shrooms were likely first found and potentially consumed by the Acadians. This group of people migrated from the Vendee region of Western France to Canada and were driven south to the Louisiana area. The name “Acadian” would later morph into “Cajun.”
Most of the details surrounding the origins of this strain remain a mystery. Nobody has come forward to receive the credit for collecting and developing this strain.
Acadian Coast Shroom Potency & Psilocybin Content
“Shroom potency” refers to the levels of psychedelic compounds — namely psilocin and psilocybin — in dried mushroom samples. Potency can range wildly between species, strains, and even different samples of a single strain.
Because the Acadian Coast shroom is so rare, there is minimal information available online about the specific psychedelic potency. Most sources suggest that the potency of Acadian Coast shrooms fluctuates between 0.25% – 0.75% psilocybin and about 0.00% – 0.30% psilocin (0.25 – 1.05% combined).
For comparison, the average potency of shrooms belonging to the Psilocybe cubensis species is around 0.8% psilocybin and psilocin combined (total tryptamines).
Generally speaking, Acadian Coast shrooms are considered about average when it comes to potency. With this strain, most users report roughly average visual and introspective effects but slightly higher body load.
We like to use The Oakland Hyphae Psilocybin Cup as a benchmark for assessing the current potency of magic mushroom strains. This competition involves the submission of various magic mushroom samples by expert and amateur growers alike. The samples are then tested and ranked in terms of potency.
Unfortunately, there has never been samples of the Acadian Coast strain in the Psilocybin Cup.
Acadian Coast Shroom Variations & Genetic Relatives
Many shroom strains have popular variations and genetic relatives. Oftentimes, these variations have mostly similar characteristics but maintain small but distinct differences either in physical appearance or user experience that set them apart. Some of the only “variations” or close relatives to the Acadian Coast shroom strain come from Mississippi and Louisiana.
For example, the Dixieland strain is believed to have been initially cultivated in Mississippi. Given that the soil and climatic conditions in MS are similar to those in Louisiana, the Acadian Coast strain likely shares some relationship with Dixieland mushrooms. Both strains look similar, with highly rhizomorphic mycelium and dark brown caps that lighten as the mushroom ripens.
The Mississippi strain also originates from around the same area. Still, some differences in growth characteristics lead us to believe the Acadian Coast strain isn’t as closely related as they are to Dixieland.
Where to Buy Acadian Coast Spores
Acadian Coast shrooms are not particularly popular — this is likely because they aren’t always aggressive fruiters, have an average potency, and aren’t available on most of the popular spore vendor catalogs. Other strains produce more bang for your buck (like Penis Envy, Koh Samui, or Golden Teacher). However, there are some reliable sources where you can pick up spores to experiment with if you’re interested in giving this strain a try.
If you live in the US, you can turn to vendors like Ralphsters, PNW Spore Co., and Lil Shop of Spores.
If you live in Canada, you can check out Sporeslab, Planet Spores, or Mushroom Prints
If you live in Europe, you can check the stock at The Magic Mushrooms Shop, as this strain has been available there in the past. However, the strain was out of stock as of this writing.
You’ll likely need to keep checking back if you’re determined to give Acadian Coast shrooms a try. All the vendors listed above have carried Acadian Coast in the past, but they tend to come in and out of stock every couple of months.
How to Grow Acadian Coast Shrooms
Acadian Coast shrooms are considered an intermediate strain, so it’s not ideal for beginners. There are conflicting reports about how aggressively this strain fruits, possibly because the second and third flushes tend to produce the largest harvests, so you’ll need to be patient with this strain.
The Acadian Coast shrooms are well-known as prolific colonizers.
The process of growing Acadian Coast shrooms is similar to the process for most other strains, which we’ll detail briefly below. The only caveat with this strain is that fruiting can be slow, delayed, or even sparse. We’ve found that growing this strain in monotubs with plenty of humidity seems to produce the best yields overall, but your mileage may vary.
You can check out our complete guide to shroom cultivation for more information.
Step 1: Prepare Your Substrate
First, mix your substrate. The best mixture for Acadian Coast shrooms is 2 parts vermiculite, 2 parts brown rice flour, and 1 part water. Fill your mason jar up to about three centimeters from the rim, and then fill the rest with vermiculite.
Step 2: Sterilization
Next, sterilize your substrate. Cover your mason jar with an upside-down lid or tinfoil, and place it in a pressure cooker or Instant Pot. Increase the pressure and bring it up to sterilization temperatures (over 121 degrees F) for about 30 minutes.
Step 3: Inoculation
Next, you’ll need to carry out inoculation, which involves introducing your spores to your sterilized substrate. Take every precaution you can to ensure you don’t contaminate your substrate.
Step 4: Incubation & Colonization
Incubate your sealed jar at around 85% humidity or greater and between 70 and 80 degrees F. Keep the jar in the dark until the entire substrate is covered in the white mycelium.
Step 5: Fruiting
Add your substrate to a fruiting chamber with moist vermiculite. Keep this at around 85% humidity, but drop the temperature to between 50 and 65 degrees F until your shrooms start to fruit.
Step 6: Harvest
Once your mushrooms are ripe (the veil on the bottom side of the shrooms will break), you’re ready to harvest. You should be able to get 3–4 good flushes from each batch before they start to mold — at which point you’ll need to throw it out to avoid contaminating other batches.
With Acadian Coast, most growers report the third and fourth flush are the most prolific. If you’re having a hard time getting your shrooms to fruit for a second or third time, you can dunk them in ice water for about 20 minutes and place the tub back into your fruiting chamber.
Similar Strains to Acadian Coast
Acadian Coast shrooms are uncommon; hence, most users have not been able to try them, so there are relatively few trip reports available, and it’s challenging to say which other strains will produce similar effects.
Given the moderate potency and the experience reported by those who have tried them, good alternatives likely include Cambodian, Argentina, and Golden Teachers. Dixieland shrooms are another good alternative and were collected from the same region as Acadian Coast shrooms.

Cambodian
The Cambodian strain is known to provide users with a high potency but a trip that is reportedly more mellow than expected. It produces enjoyable visuals, similar to Acadian Coast shrooms for many users.

Argentina
Similarly, the Argentina strain is potent but also provides a milder effect than what the potency suggests. Most users report peaceful and connected feelings, as well as a somewhat calming state of euphoria.
Golden Teachers
Golden Teachers have a moderate potency, like Acadian Coast shrooms, and they’re also known to provide a more calming experience. Just like Acadian Coasts, Golden Teachers tend to offer minimal visuals but have a stronger body trip.

Dixieland
The Dixieland strain is believed to have been originally harvested in Mississippi, so it has a similar growth pattern and vitality to Acadian Coast shrooms. This species produces fruiting bodies with long, thin stems and medium-side caps that are rounded.
What’s the Difference Between a Magic Mushroom Species & Magic Mushroom Strain?
Many people — even avid magic mushroom users — misunderstand the difference between a strain of shrooms and species.
A mushroom strain refers to a specific phenotype of a mushroom that exhibits specific physical traits. In some cases, you can identify mushroom strains simply by looking at them. For example, B+ Cubensis shrooms have thin stems and caps that come up to a distinct point.
Penis Envy shrooms, on the other hand, have unusually thick stems and a smaller, rounded cap.
Despite the physical differences between these two strains, both belong to the same species (Psilocybe cubensis) and have the same genetic makeup. Two strains of the same species can be bred to produce viable offspring.
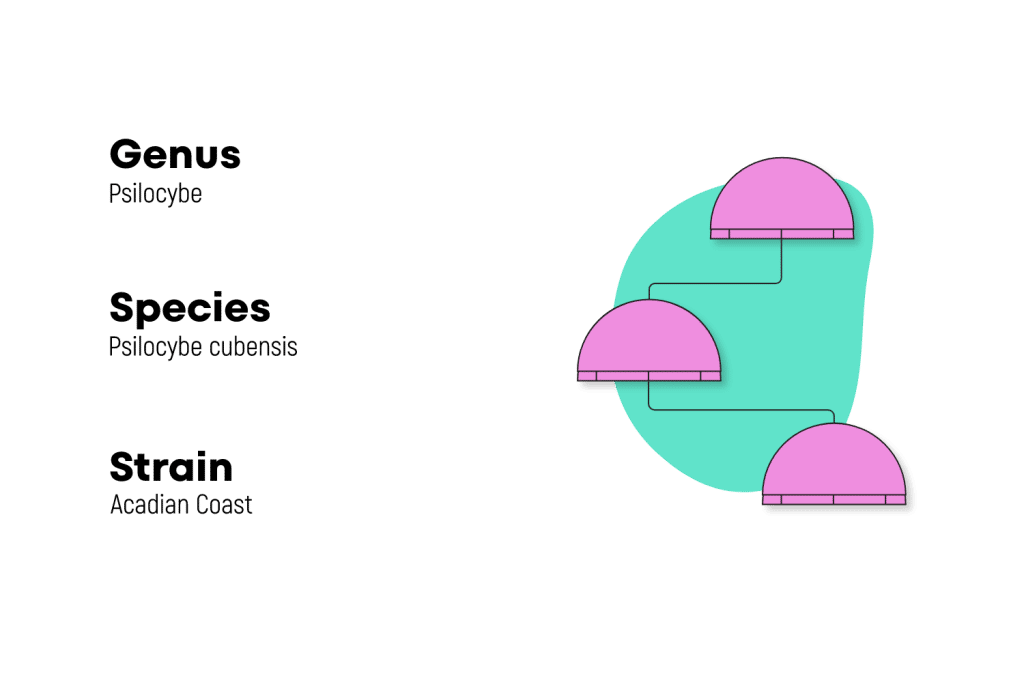
A magic mushroom species is a scientific classification given to genetically unique samples. For example, Psilocybe cubensis has a unique genetic profile from Psilocybe semilanceata. The two cannot be bred together to produce viable offspring.
The confusion between strains and species arises most often because users conflate the appearance of a shroom strain with its genetic makeup. Two strains can look wildly different and even have different potencies while still belonging to the same genus and species. Strain names — like Acadian Coast — are used to describe samples that have been isolated from nature and contain distinct physical traits — such as the size of the cap or psilocybin content.
These differences are largely based on epigenetic responses to the environment in which the shroom grows and are not based on differences in genetics.
The distinction between strains is not unique to the fungi. Strains also exist in the plant kingdom, and they’re often used to describe differences between plants that humans consume regularly. A great alternative example is the cannabis plant. Marijuana strains — like Northern Lights, Gorilla Glue, and Granddaddy Purp — all refer to different strains of the same plant species: Cannabis sativa. The main differences are in potency, appearance, terpene profile, and optimal cultivation methods. Other examples include kava, kratom, coffee, tea, and various flowers (like roses or tulips).
Final Thoughts: Acadian Coast Shrooms
Acadian Coast shrooms are a relatively uncommon strain, and their origin and natural habitat are debated. The common consensus is that the original sample was collected somewhere in Louisiana near the Mississippi River.
Acadian Coast shrooms are moderately challenging to grow because they can be finicky when it comes time to fruit. They are aggressive colonizers, and they’re known to produce the most fruiting bodies in the second and third flushes. Novice users may find that their mycelium will mold before reaching the prolific third or fourth flushes.
The Acadian Coast strain is known to produce mild visuals and a more intense body-centered trip, making them similar to more popular strains like Golden Teachers, Cambodians, and the Argentinian strain.