2-MMC (2-Methylmethcathinone): Effects, Dosage, & Safety
2-MMC is a bit less potent than other cathinones, which is why some consider it more of a “functional” high.
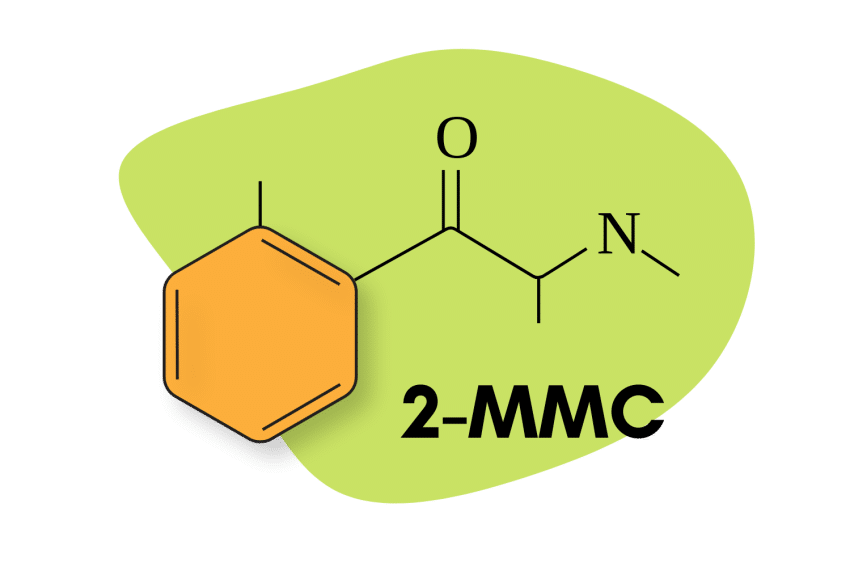
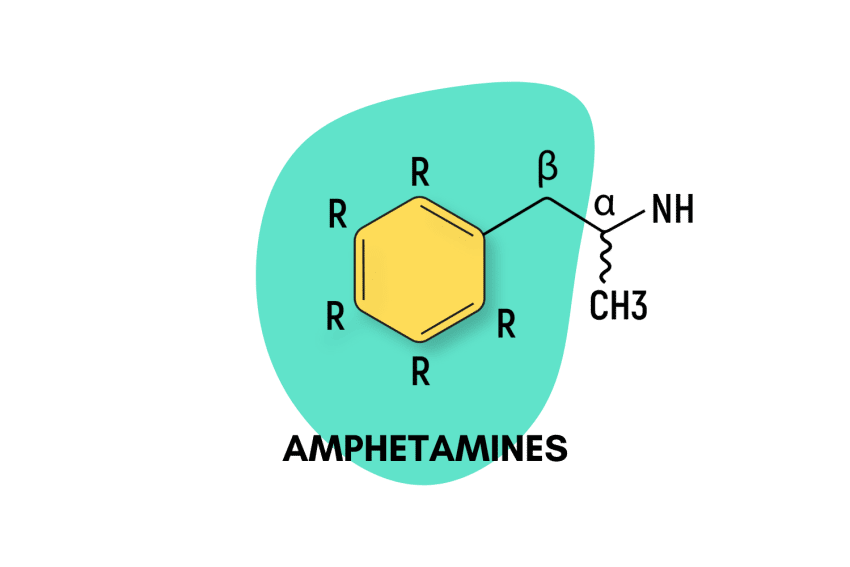
2-MMC or 2-methylmethcathinone is a research chemical related to 3-MMC and 4-MMC. It’s a member of the amphetamine family of drugs, more specifically, the synthetic cathinone subfamily, which features prominent members such as MDPV, alpha-PVP, and 3-MMC.
Most trip reports involving 2-MMC suggest very low psychedelic effects and a milder stimulating action than related cathinones.
Learn about common dosing, duration of effects, safety, and effect profile of 2-MMC here.
What is 2-MMC?
2-MMC is a synthetic analog of cathine, a naturally occurring compound found in the khat plant (Catha edulis). Many chew khat in Africa and the Middle East for its stimulant effects in recreational and work contexts. 2-MMC was first documented in Sweden in 2014 and has since spread worldwide as a legal high. The exact origins of its creation are unknown [1].
2-MMC is classified as a “substituted cathine,” which is more commonly referred to as “bath salts.” The term refers to a wide range of drugs, both legal and illegal, which got their name because traffickers label them Epsom or “bath” salts in order to sell them “legally.”
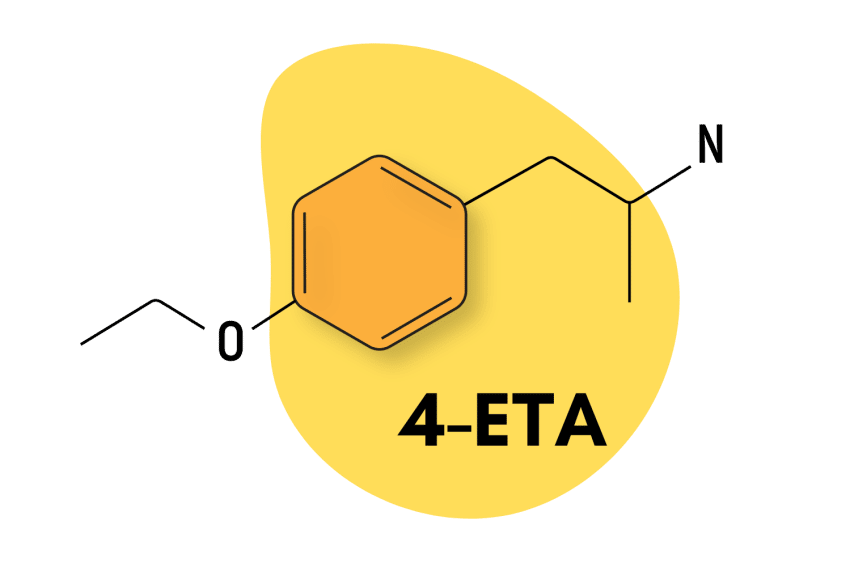
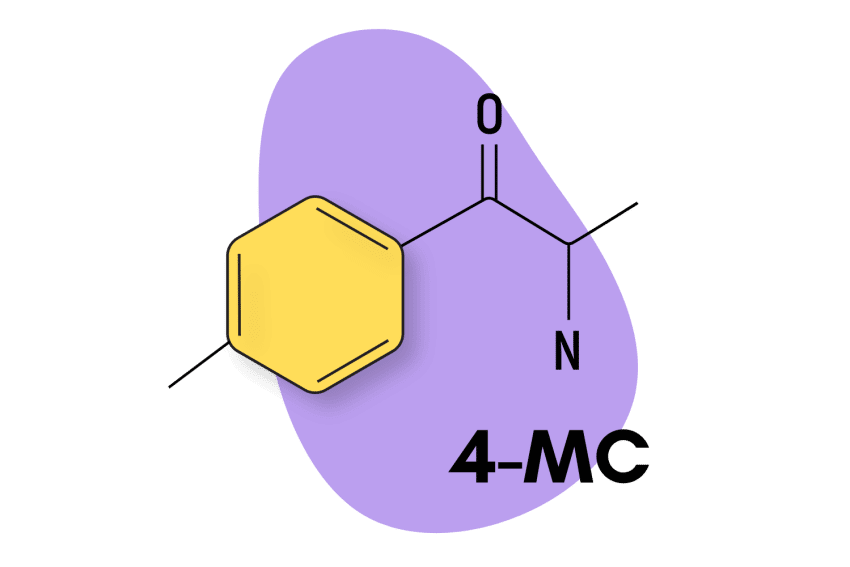
Structurally, 2-MMC is most closely related to 3-MMC and 4-MMC (mephedrone or meow meow) and has comparable stimulant effects — although online reports suggest differences, such as a less intense and shorter trip duration.
Other substituted cathinones, like 3-MMC and 4-MMC, produce euphoric and stimulant effects, which users compare to amphetamines, cocaine, or MDMA. Related compounds 3- and 4-MMC were legal MDMA substitutes in the early 2000s. The compounds have since become illegal, leading to the creation of newer drugs, such as 2-MMC, to bypass drug laws.
It’s important to note that this strategy for creating “legal” drug analogs is becoming more difficult as the legislation progresses. The Federal Analogue Act, for example, preemptively bans any isomer of a known restricted chemical. This makes it very difficult for drug manufacturers to sell new amphetamine analogs like 2-MMC legally.
We know very little about the effects of 2-MMC on the human body because there has never been any formal study. Additionally, very few trip reports exist on this relatively obscure research chemical.
Other cathinones have caused serious physical and psychological side effects in some cases. Drug researcher and policy advisor to Professor David Nutt stated, “People are better off taking ecstasy or amphetamines than drugs we know nothing about.”
2-MMC: Specs & Technical Details
| Active Ingredient | 2-Methylmethcathinone (substituted cathinone) |
| Level of Risk | High |
| Most Common Side-Effects | Mild euphoria, alertness, anxiety, nervousness |
| Duration of Effects | 2-4 hours |
| Legality | Varies, unscheduled in some areas |
Guidelines for the Responsible Use of 2-MMC
- 🐍 I understand why psychedelics should be treated with respect.
- ⚖️ I’m familiar with the laws surrounding psychedelics in my country & state.
- 🍄 I’m familiar with and confident in the dose I’m taking (the oral dose range for 2-MMC is 50-100 mg).
- 🧪 I’ve tested a sample of the substance I’m using with a drug-testing kit.
- 💊 I’m not mixing any medications or other substances with 2-MMC.
- 🏔️ I’m in a safe & comfortable environment with people I trust.
- 🐺 One of the members of my group is responsible and sober (AKA a trip sitter).
- ⏳ I have nothing important scheduled for after the trip.
- 🧠 I’m in a sound & healthy state of mind.
What’s the Dose of 2-MMC?
2-MMC can be taken orally as a pill, snorted as a powder, vaporized, taken rectally, or injected intramuscularly or intravenously. The dose for each means of administration can vary significantly.
Typically 2-MMC comes a white crystalline powder encapsulated in gelatin or as pressed tablets — sometimes mixed with other substances like benzodiazepines, other amphetamines, or various arylcyclohexylamines.
While no form of administration can be deemed safe for this drug, oral consumption carries the lowest risk overall. The oral dose of 2-MMC ranges from 50 mg to 100 mg. Only those with very high tolerance should consider anything higher than 100 mg.
Snorting is another popular method of ingestion, but it produces a very uncomfortable burn in the nasal cavity and back of the throat. Smaller doses are needed when used intranasally (around 15–80 mg).
2-MMC can also be vaporized in a mesh vape pen, but the hit is notoriously harsh, and the taste and smell are unpleasant…to say the least. Some users report much higher anxiety levels when vaping this substance than taking it orally.
No reports of rectal use exist online, but one can assume a more rapid onset than the oral route.
Intramuscular and intravenous injection is also possible, but we don’t believe there is a safe dosage when used this way. Injecting drugs carries a significantly higher risk of side effects, overdose, and addiction.
| Dosage Breakdown for 2-MMC | Oral | Snorted |
| Threshold | 20-50 mg | 5-15 mg |
| Average | 50-100 mg | 15-40 mg |
| High | 100-135 mg | 40-80 mg |
What Does 2-MMC Feel Like?
The effects of 2-MMC are comparable to Adderall — inducing feelings of increased energy and focus with a mild dissociative-like high.
This compound lacks the empathogenic qualities of MDMA but maintains some of the euphoric effects — which can be fleeting and sporadic.
Some have described 2-MMC as a “functional stimulant” rather than a recreational drug. This means it’s used more as a means of increasing focus and productivity while working or studying than as a means of getting high.
Anecdotal reports also include that the comedown of 2-MMC may be less severe than its cousins 3-MMC and 4-MMC, a major advantage of this substance overall.
Common Effects of 2-MMC Include:
- Heightened Awareness
- Increased Focus
- Euphoria
- Increased Energy Levels
- Anxiety
- Mild Hallucinations
- Paranoia or Delusional Thought Patterns
How Long Does 2-MMC Last?
When consumed orally, reports suggest effects peak at roughly 45 minutes and last around three to five hours.
When snorted, the effects hit within minutes and seem to last about 2–4 hours, which is in line with the duration of other substituted cathinones.
When vaporizing 2-MMC, the onset comes on in seconds and lasts around 30 minutes.
All these timeframes are dose-dependent and vary between individuals.
How Strong is 2-MMC Compared to Other Psychedelics?
2-MMC is considered as less potent than related compounds like 4-MMC and 3-MMC. It’s significantly weaker than the strongest members of this class, MDPV and Alpha-PVP. However, it’s still a strong stimulant lasting several hours, which does come with some euphoria alongside the potential for anxiety, hallucinations, and paranoia.
The effects of this drug are qualitatively very different from other popular amphetamines like MDMA — which carries a strong empathogenic component (feelings of connection to others and the environment). In fact, 2-MMC is more similar to dissociatives since it tends to make people turn inward and isolate themselves from others.
There are some conflicting reports on this, however. It appears this drug interacts differently depending on the mental state of the individual before taking it.
People seek 2-MMC for its euphoric and stimulating effects, a contrast to the “journey” people seek when taking classical psychedelics like psilocybin or LSD.
Is 2-MMC Safe? What Are the Risks?
It’s impossible to say for certain whether 2-MMC is safe or dangerous because there isn’t enough information on its effects (both scientific and anecdotal). All unstudied research chemicals carry a higher risk than substances that have been thoroughly studied over the years.
Because of 2-MMC’s stimulant effects, there are obvious cardiac concerns, a strong potential for addiction, a risk of overdose, and issues with dehydration and hyperthermia.
There’s at least one report involving 2-MMC-induced myocarditis (inflammation of the heart). The patient was hospitalized after combining high doses of 2-MMC with another amphetamine called 2MA. The same report says 3-MMC, 4-MMC, and other substituted cathinones have led to hospitalizations, often involving heart complications. Some of these cases resulted in death. There are also stories of serotonin syndrome with high doses of cathinones, which can be fatal [2].
Published research suggests a related substance called mephedrone may cause neurotoxicity. However, results are inconsistent, with some reports showing no lasting nerve damage.
Much of what we know about substituted cathinones comes from emergency department reports and may show the worst side of the compound. One study even suggested some cathinones could have lower toxicity than MDMA.
Clearly, more research into these compounds is necessary [3].
One of the biggest risks of 2-MMC, as with all synthetic cathinones and most amphetamines, is the high potential for addiction. Drugs that alter dopamine homeostasis carry a significantly higher risk of causing compulsive behavior than other drugs. Repeated use of dopaminergic stimulants can cause serious mental and physical health problems.
How to Test 2-MMC With A Drug Reagent Kit
Because 2-MMC is a less common drug, no specific tests verify its purity. However, it is possible to use a Marquis reagent test to detect the presence of other alkaloids (indicating adulteration).
This test is presumptive, and while it cannot test for 2-MMC specifically, a reagent test is helpful to determine if something you do not want is in your powder. In some cases, the adulterants are much more dangerous than the 2-MMC itself. Drugs like fentanyl, MDPV, and alpha-PVP are significantly stronger than 2-MMC and can result in a fatal overdose if used at equivalent doses.
It’s important to understand that the Marquis test cannot reveal a complete profile of the compounds in a given powder.
Side Effects of 2-MMC
Some of the physical side effects of cathinones include:
- Teeth grinding
- Sweating
- Twitching
- Headache
- Painful urination
- Heart palpitations
- Arrhythmia
- Increased blood pressure
- Chest pain
- Heart attack
Psychological side effects of 2-MMC include:
- Anxiety
- Nervousness
- Irritability
- Confusion
- Difficulty sleeping
- Paranoia
Many psychological complications can occur after overindulging in stimulating compounds like 2-MMC. Psychosis and life-threatening self-harm have happened under the influence of cathinones and related compounds.
Is 2-MMC Legal?
Like many research chemicals, 2-MMC is shrouded in a complicated legal situation. As the compound is not very well known, some countries have not passed specific laws against it. Others, like the United States, have established legislation prohibiting analogs to already scheduled drugs, making 2-MMC a Schedule 1 drug.
2-MMC is a controlled substance in the UK.
In many countries, 2-MMC likely exists in a gray area without specific legislation addressing it.
How Does 2-MMC Work?
The specific effects of 2-MMC have not been studied, but based on what we know about other substituted cathinones, 2-MMC likely works by blocking or reversing the flow of dopamine. This leads to an increased concentration of dopamine in the synapses, similar to how drugs like 4-MMC, MDMA, and methamphetamine work.
Cathinones also affect serotonin, norepinephrine, and a variety of other neurotransmitters in the brain. Subtle differences in how these drugs alter neurotransmitter levels are responsible for qualitative differences between various substances.
2-MMC FAQ
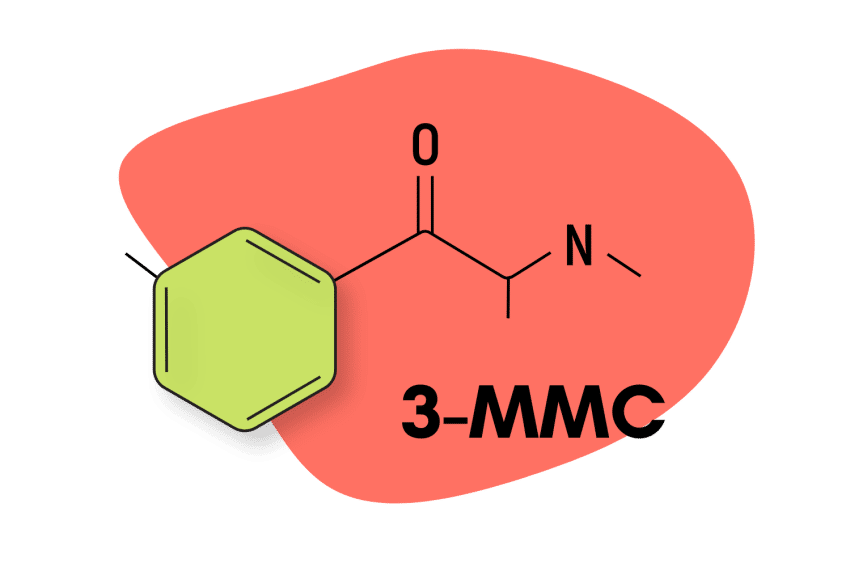
1. What’s the Difference Between 2-MMC and 3-MMC?
Chemically, both 2-MMC and 3-MMC are very similar substituted cathinones. Their chemical structures differ slightly, with methyl groups attached in the second position in the case of 2-MMC and in the third position for 3-MMC. While the difference seems insignificant, there appears to be a change in effects, notably a higher degree of euphoria and stimulation from 3-MMC.
2. Does 2-MMC Show Up On a Drug Test?
Standard drug panels do not look for 2-MMC or related substituted cathinones. However, if use is suspected, certain laboratories can do advanced testing with liquid or gas chromatography-mass spectrometry on blood or urine samples. Some evidence suggests that cathinones are not stable for long periods in body fluids, potentially complicating testing. This testing would have difficulty identifying 2-MMC specifically, likely only identifying cathinone use [4].
3. Are There Any Medical Uses for 2-MMC?
There are no current approved uses for 2-MMC or its relatives. However, there is interest in 3-MMC, with the company MindMed holding a patent for its use in psychotherapy. The suggested uses are for PTSD, generalized anxiety disorder, and “relationship distress.”
4. Does 2-MMC Have a Comedown?
Some users of 2-MMC have described 2-MMC as having less difficult comedowns than its cousins, 4-MMC and 3-MMC. While the consensus seems that 4-MMC and 3-MMC are more intense, stimulating, and euphoric trips, 2-MMC is gentler. Some users prefer this feature, looking to 2-MMC as a functional high or study drug.
References
- EMCDDA, E. (2014). EMCDDA—Europol 2013 Annual Report on the Implementation of Council Decision 2005/387/JHA. Luxembourg: Publications Office of the European Union.
- Assis, S., Gulyamova, N., Kneller, P., & Osselton, D. (2017). The effects and toxicity of cathinones from the users’ perspectives: A qualitative study. Human Psychopharmacology: Clinical and Experimental, 32(3), e2610.
- Pantano, F., Tittarelli, R., Mannocchi, G., Pacifici, R., Di Luca, A., Paolo Busardò, F., & Marinelli, E. (2017). Neurotoxicity induced by mephedrone: an up-to-date review. Current neuropharmacology, 15(5), 738-749.
- Adamowicz, P., & Malczyk, A. (2019). Stability of synthetic cathinones in blood and urine. Forensic science international, 295, 36-45.