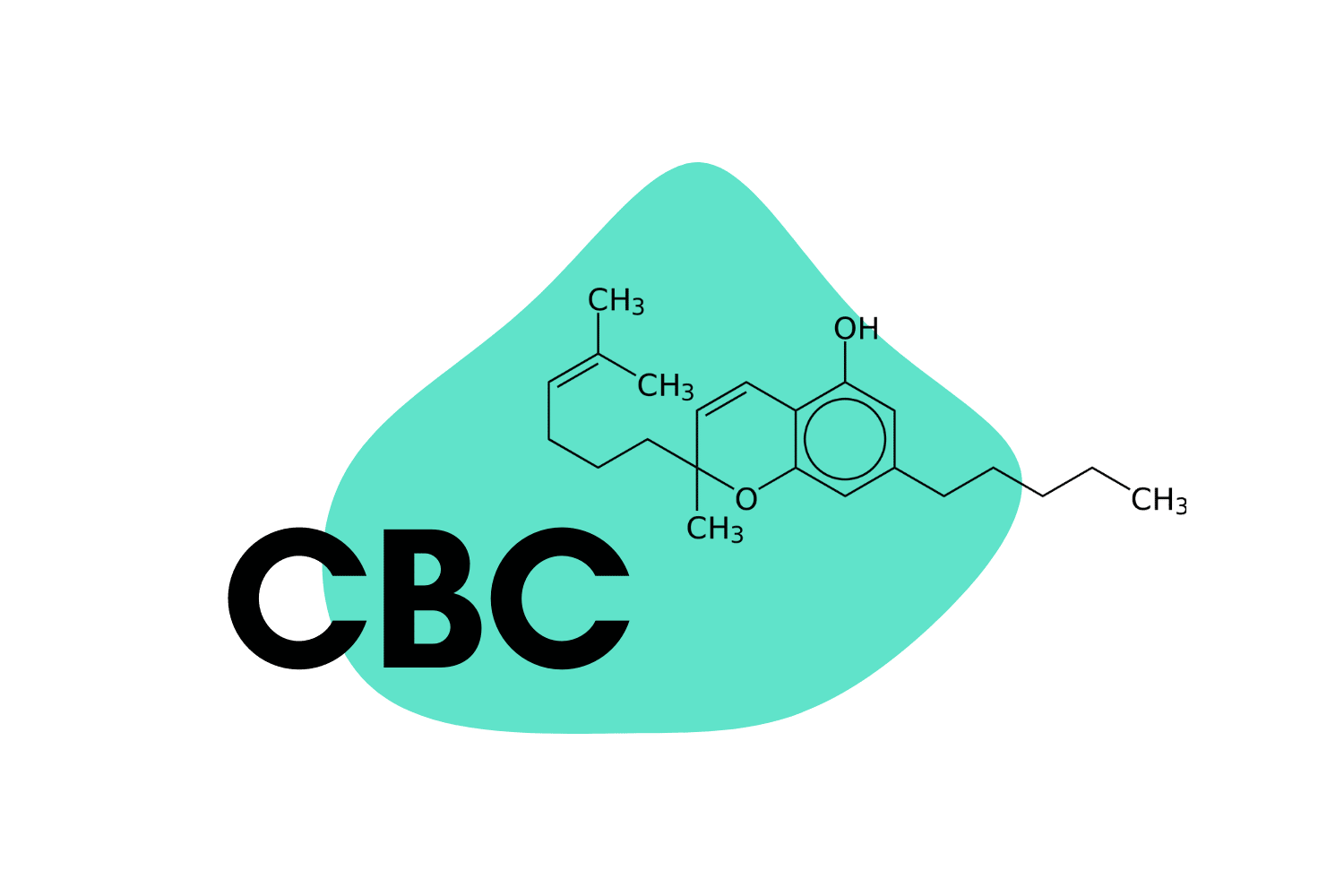
Candy with a Kick: Top 10 THC-Infused Gummies (2024)
THC Gummies are delicious, discreet, and don’t (necessarily) break the law.
THC gummies are chewy candy infused with some form of THC, the main psychoactive compound in Cannabis sativa.
In the United States, the 2018 Farm Bill kicked open a legal door, allowing the legal sale of products containing less than 0.3% delta-9 THC derived from hemp.
The result is a literal candy store stocked with everything from soft chews with wellness vibes to supercharged edibles for the seasoned stoner.
There are many different types of THC available. Delta 9 is the classic stoned feeling and is typically what people refer to as THC and is the term we use in this article.
But now, the selection is growing to include Delta 8, Delta 10, THC-O, and THCA. Some states have moved to ban other specific cannabinoids that are not addressed currently, so be sure to know your local laws.
Different types of THC mostly provide cannabis-like effects, but the slightly different chemical compositions do translate into unique altered states.
Related: Best Delta-9 THC Gummies | Best Delta-8 THC Gummies |
Top Brands Selling THC Gummies:
| # | Brand Name | Shipping | Types of THC | Tripsitter Rating |
| 1. | Area 52 | 🇺🇸 | Delta 8, Delta 9, HHC, THCA | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| 2. | Moonwlkr | 🇺🇸 | Delta 8, Delta 9, HHC, THCA, THCP | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| 3. | Tre House | 🇺🇸 | Delta 8, Delta 9, HHC | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| 4. | Cycling Frog | 🇺🇸 | Delta 8, Delta 9 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| 5. | Harbor City Hemp | 🇺🇸 | Delta 8, Delta 9 | ⭐⭐⭐ |
| 6. | Simply Crafted | 🇺🇸 | Delta 8, Delta 9 | ⭐⭐⭐ |
| 7. | Delta Extrax | 🇺🇸 | Delta 8, Delta 9, Delta 10, HHC, THCA | ⭐⭐⭐ |
| 8. | Left Coast Gummy Co. | 🇨🇦 | Delta 8, Delta 9 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| 9. | Twisted Extracts | 🇨🇦 | Delta 8, Delta 9 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| 10. | Boost | 🇨🇦 | Delta 8, Delta 9 | ⭐⭐⭐ |
THC Gummies: Specs & Technical Details
- Active Ingredient: THC analog (there are many different kinds)
- Level of Risk: Low
- Most Common Side-Effects: Red eyes, increased heart rate, anxiety
- Duration of Effects: 4-6+ hours
- Legality: Legal in Canada, Mexico, South Africa, Georgia, Germany, Luxembourg, Malta, Uruguay, Thailand, and parts of the USA.
What’s the Dose of THC Gummies?
The dose of THC gummies depends on your level of experience, personal tolerance, and what type of THC is consumed.
For a beginner or someone who is sensitive, 1-3 mg of THC is a good starting dose — most novice users will feel some effects starting at this dose range. For many products, this will be half, or even less, of one gummy.
Be sure to double-check doses, and if you are trying any type of THC for the first time, eat a small amount.
For more experienced users, a dose in the range of 5 mg to 10 mg is usually more desirable. This usually works out to half a gummy depending on the manufacturer.
Only very heavy users who have a lot of experience with THC edibles should take more than 10 mg. Some users take as much as 50 mg.
Dosage Breakdown for THC Gummies
There are many types of THC on the market, each with different levels of potency, which we break down below.
Keep in mind that everyone responds differently and tolerance to THC can build quickly:
| Cannabinoid Name | Microdose | Beginner | Standard | Heavy |
| Delta-9 THC | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20+ mg |
| Delta-8 THC | 2 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 50+ mg |
| Delta-10 THC | 2 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 50+ mg |
| THCA | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20+ mg |
| THC-O | 0.5 mg | 6 mg | 20 mg | 50+ mg |
| HHC | 1 mg | 6 mg | 12 mg | 25+ mg |
What Do THC Gummies Feel Like?
Everyone responds a bit differently to THC, and effects will depend on the specific compound, dose, tolerance, and your body.
Some experimentation in a safe space is required. The dose that a friend with high tolerance casually takes before work might be an 18-hour psychedelic experience for someone else.
Typical effects include euphoria, racing thoughts, creative ideas, feeling self-conscious, or that life is pretty funny and strange.
THC can also be confusing and induce anxiety, paranoia, panic, looping thoughts, or strong emotions. Some people will become chatty, while others may find speaking difficult. Others may be energized, while others feel relaxed or slow.
Forms of entertainment like music, television, video games, and visual art can become more immersive and engaging. Nature can inspire awe.
Appetite can increase (particularly at the comedown), and snacks will probably be excellent.
Red eyes, dry mouth, increased heart rate, heat, or chills are fairly common. At higher doses, nausea, shaking, or, in extreme cases, vomiting can occur.
Key Features of THC Gummies
That said, the following effects are common, but dose plays a role in how intense they are:
- Euphoria
- Anxiety
- Relaxing
- Energizing
- Increased Appetite
- Increased Heart Rate
- Red Eyes
- Strange Thoughts
- New Ideas

How Strong Are THC Gummies Compared to Other Psychedelics?
Gummies are less intense compared to psychedelics like magic mushrooms, LSD (lysergic acid diethylamide), or DMT (dimethyltryptamine). However, this depends on your tolerance, the dose, and what type of THC is taken.
While THC isn’t as strong as classic psychedelics, it still puts folks in an altered state and alters motor skills and reaction times, so take it seriously.
If it is your first time using THC, it should be treated as a big experience.
The psychedelic approach of creating an ideal set and setting also applies to THC. An open and curious attitude and a safe, comfortable space with good people, enjoyable activities, and awesome snacks go a long way.
Are THC Gummies Safe?
When carefully made from quality ingredients by a trusted source, THC gummies are safe for most healthy adults.
However, the world of THC gummies in places like the United States is unregulated, meaning organizations like the Food and Drug Administration ( FDA) do not monitor exactly what is in each gummy.
Some gummies do not contain the amount of THC on the label, and in some cases, gummies contain cannabinoids not advertised, which could pose a risk [1].
Also, THC gummies should be kept away from children, and many containers will not have child-proof mechanisms. Reports of hospitalizations and a fatality from a child consuming an entire package of gummies have made the news.
The FDA has issued a warning about children consuming THC-containing food products.
People with heart conditions, mental illness, or who are taking prescription medications should consult with a doctor before taking THC.
THC Gummies Side Effects
THC gummies do commonly cause side effects, such as:
- Red eyes
- Dry mouth
- Increased heart rate
- Changes in blood pressure
- Heat, sweating
- Chills
- Nausea
- Shaking
- Vomiting
- Lethargy
- Anxiety
- Paranoia
- Memory Issues
- Poor motor skills
First times or too big a dose (and especially both) can feel pretty scary, but deaths from THC are rare, considering the widespread use.
However, adverse events and hospitalizations can occur with high doses.
Nobody knows what an exact lethal dose of cannabis in humans is; however, doses of over 2 grams of pure THC caused severe complications for some subjects in one study [2].
How Do THC Gummies Work?
Usually, just eating THC wouldn’t do anything. However, THC gummies contain cannabinoid oil that has been decarboxylated, meaning activated by heat. The oil is added to the usual candy-making process.
When eaten, THC is absorbed by the digestive tract and enters the bloodstream. Psychoactive compounds cross the blood-brain barrier to interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system.
THC is converted into various metabolites, including 11-OH-THC, which is a psychoactive metabolite of THC. More THC is converted to 11-OH when eaten, which may contribute to different experiences of eating and smoking THC [3].
Cannabinoids are found in plants (and gummies) and can interact with endocannabinoid receptors in the brain. THC interacts with CB1 and CB2 receptors, which produce the beloved physical and mental effects.
The human body naturally produces compounds similar to cannabinoids. These are called endogenous cannabinoids and perform many functions inside the human body, including (but not limited to) functions of the immune system, appetite, pain, memory, emotions, and motivation.
It’s worth noting, too, that THC and other compounds in cannabis work through other pathways in the body beyond the endocannabinoid system.
Some examples include:
- Serotonin receptor binding [4]
- Dopamine receptors binding [5]
- Inflammation [6]
- Anti-inflammatory activity [7]
THC Gummies Benefits
Cannabis and THC have been studied and made their way to legal markets in part because of their medical benefits.
New studies are coming out all the time, but here are a few ways THC is used today:
- Sleep — Many people use THC for sleep, but research casts some doubt on the quality of THC-induced sleep [8].
- Constipation — Cannabis use decreases the odds of constipation [9].
- Epilepsy — Cannabinoids have anticonvulsant properties, with CBD being favored, but THC might help too [10].
- Anti-cancer — THC is established as inhibiting the growth of specific cancers, along with lessening symptoms associated with the disease and associated treatments, by lessening pain, and nausea, and stimulating appetite [11].
- Pain — There are plenty of studies showing THC, and THC combined with CBD can manage pain [12]. THC is also established as working in synergy with opioids [13].
- Inflammation — Through mechanisms like inhibiting inflammatory cytokines, evidence supports THC-reducing inflammation [14].
- Neuroprotective — Protective against oxidative stress, THC can be technically classified as an antioxidant [15].
- Multiple Sclerosis — THC and CBD have been used to treat tremors related to MS [16].
- Parkinson’s — A study found some evidence for reductions in symptoms related to Parkinson’s like reduction in tremors, anxiety, pain, and improved sleep [17].
The above list is painted with broad strokes, and specific cannabinoids or even cannabinoid combinations will have different effects on different conditions.
While THC has helped many people, using it to manage symptoms or treat serious medical conditions should consult with medical professionals.
THC Tolerance
As wonderful as THC can be, tolerance builds up quickly. In animal models, tolerance is shown to build in 3-7 days [18].
While this can mean taking more THC is necessary to feel effects like relief from pain, there is also evidence that, as one study author puts it, ”(frequent) users of cannabis may be innately ‘protected’ from some of the negative effects of cannabis.”
Are THC Gummies Legal?
Following the 2018 Farm Bill, hemp plants with less than 0.3% of the total dry weight can be grown and used. Various types of THC are then extracted from the plants and put into products.
The Farm Bill is often called a loophole, though. THC is still a Schedule 1 substance and other United States Legislation like the Analog Act could be interpreted to include different types of THC.
Canada has legal cannabis gummies, but a cap of 10 mg per legal gummy has kept gray-market edibles popular.
Mexico, South Africa, Germany, Georgia, Luxembourg, Malta, Uruguay, and Thailand also have legal cannabis products. A growing number of States have legal cannabis and some areas decriminalized cannabis. For a complete list, check here.
It’s best to check your local area because laws are constantly changing. The Farm Bill must be renewed every 5 years, and individual states are making their own THC laws every month.
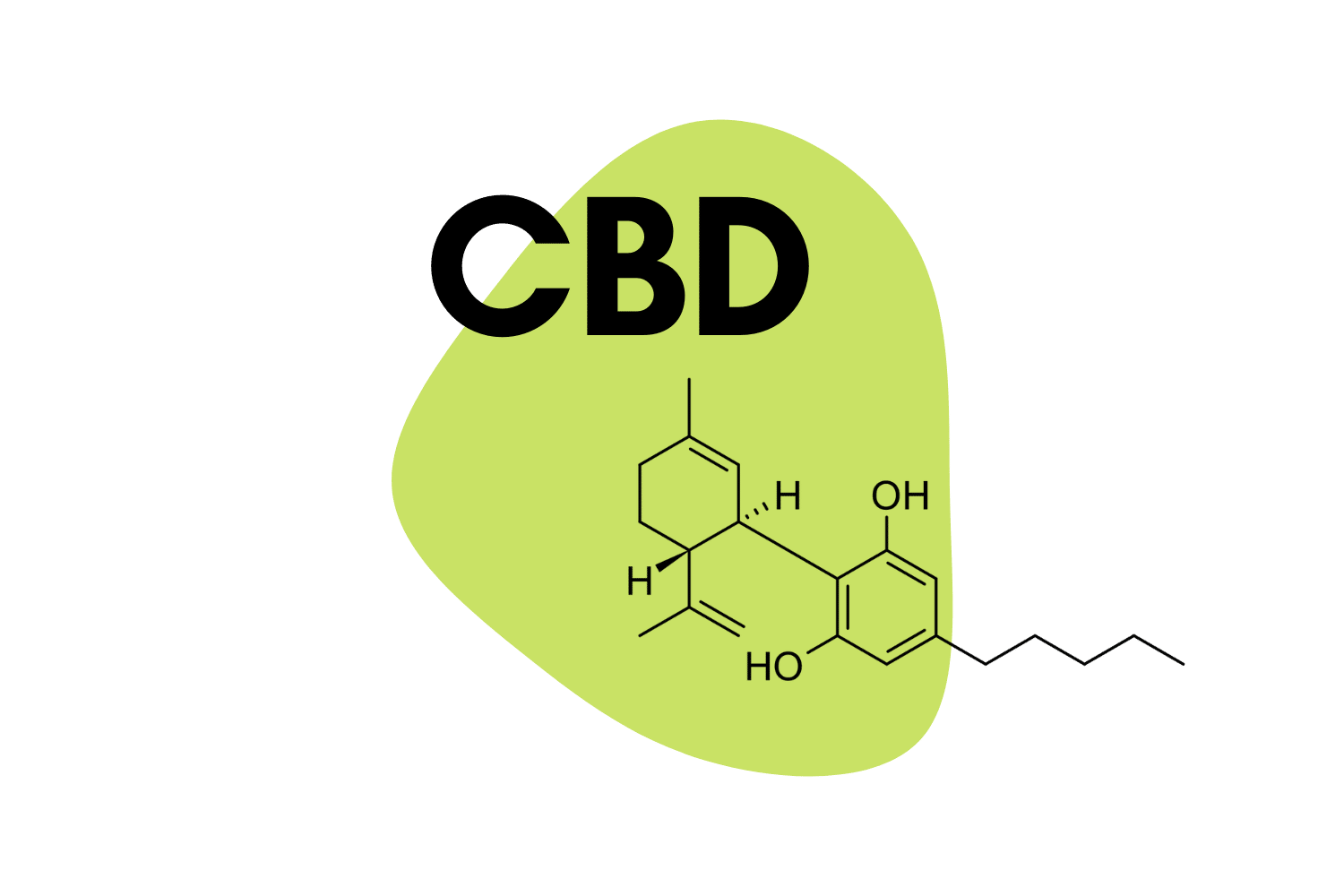
What is the Difference Between THC & CBD?
Although there are similarities, THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) is not the same as CBD (cannabidiol). Their chemical structures are different, which results in dramatically different effects on the body.
The main difference between CBD and THC is that CBD is not psychoactive. This is considered the primary “medical” constituent in the plant — offering potent anti-inflammatory and pain killing effects.
THC, on the other hand, delivers a potent psychoactive experience, which anyone who has eaten too many weed cookies or inhaled a bit too big a dab can attest to.
Both THC and CBD have many related compounds and isomers, like the various types of THC listed above, or other compounds with a structure similar to cannabidiol, like CBN and CBG. Both are cannabinoids and interact with our endocannabinoid system.
There are two receptors that send signals to various parts of the body. THC interacts with both but binds more to the CB1, which causes the psychoactive effects. CBD doesn’t seem to bind to either, but affects CB2 in some way, giving it pain relieving, calming, and anti-inflammatory properties.
DIY: How to Make THC Gummies
Store-bought gummies are made in special manufacturing facilities in large numbers, but it’s possible to make your own THC gummies at home. Gummies can be made from scratch or by infusing gummies from the store with THC.
To make THC gummies in your kitchen, you will need a few supplies:
- THC oil
- 1/2 cup water or juice (juice adds flavor)
- 1 tablespoon unflavored gelatin (if you are vegan, check for plant-based)
- 1 package JELL-O
- 1/2 teaspoon citric acid
- 1 tablespoon sweetener (optional)
- Molds
- Saucepan
- Wisk
- Squeeze bottle, dropper, or pipette
Instructions:
- Combine water and the desired amount of cannabis oil in a saucepan over low heat.
- Add gelatin powder and JELLO and whisk until dissolved, about 10-25 minutes. Don’t stop stirring!
- Add citric acid and stir until dissolved. Be careful not to bring the mixture to a boil as this can impact how the gummies set later on.
- Remove the saucepan from the heat and fill the molds with your dropper or pipette. Work quickly, because the mixture hardens as it cools.
- Place molds in the freezer for at least 30 min.
- Once solidified, remove the gummies from the freezer and place them on parchment paper to dry. Leaving them for a day or two can allow excess moisture to evaporate.
These gummies will last a couple of weeks or longer if kept in the fridge. For long-term storage, gummies can be frozen. Gummies bought from a store will have preservatives and don’t need the same storage conditions as homemade gummies.
How to Infuse THC Into Gummies
- To infuse gummies from the store with THC, simply place them in a microwave-safe dish, add a bit of water, and heat them up.
- Once melted, add some THC oil and mix well. If you have gelatin, adding a little bit can help things set nicely.
- Place in molds and pop in the freezer, just like above.
Where to Buy THC Gummies Online
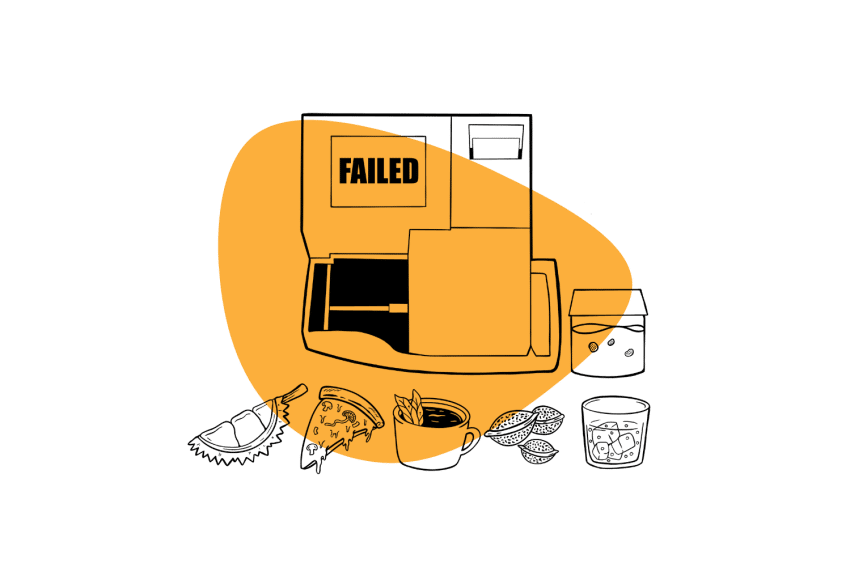
It’s not hard to find THC gummies online, the trick is finding quality, trusted brands. There are hundreds or suppliers with thousands of products, with quite a few scams out there, too.
Verify a company is legit by looking for reviews on their website or on social media like Reddit. These reviews and comments can offer insight into whether their products are consistent and work as advertised.
If possible, it helps to verify lab testing. Every single batch should be lab-tested for potency and to screen for contaminants. Some post reports online, but take this with a grain of salt, as these can be faked. Also, be sure to check reports for contaminants, not only THC content.
Some reputable spots to find gummies online include:
- United States — Area 52, Delta Extrax, Moonwlkr, Tre House
- Canada — Left Coast Gummy Co., Twisted Extracts, Boost

FAQs: THC Gummies
This section covers some questions people often have about THC gummies.
1. Are there any side effects to consuming THC gummies?
Yes, like any substance, THC gummies can have side effects, especially when consumed in high doses. The most common side effects include dry mouth, red eyes, increased appetite, drowsiness, and altered perception of time. Some individuals may also experience anxiety or paranoia, particularly with high doses.
2. How long does it take for THC gummies to expire?
THC gummies, like any edible product, have a shelf life that can vary depending on the ingredients, preservatives used, and how they’re stored. Generally, they can last for about 6 months to a year if stored properly in a cool, dark place. After this time, they may lose potency and may not be as effective.
3. Can I take THC gummies on an empty stomach?
Consuming THC gummies on an empty stomach may lead to a faster onset of effects because the THC is absorbed more quickly. However, this can also result in a more intense experience, which might not be comfortable for everyone. Eating a small meal or snack before taking THC gummies can help moderate the absorption rate and potentially lead to a more pleasant experience.
4. What effect do THC gummies have on libido?
Cannabis is documented to enhance sexual experiences and satisfaction, although chronic use might have an inhibitory effect on libido [19]. Effects like relaxation and improved blood flow could contribute to arousal, but the jury is out. You will just have to experiment.
5. THC Gummies vs. THC Chocolate: Which is Best?
Choosing between THC gummies and chocolate bars is a personal choice. Gummies can be found in a variety of flavors and it’s possible to find low sugar products. Chocolate contains other compounds like theobromine which can have stimulating effects, which is good or bad, depending on what your goal is.
6. How Long Do THC Gummies Effects Last?
THC gummies (and other edibles) usually take around 1–2 hours to kick in and tend to last most of the day (5–9 hours). High doses may last even longer (up to 18 hours) and smaller doses tend to linger for around 3–5 hours.
Subscribe to Tripsitter For More Psychedelic Knowledge Drops
References
- Holt, A. K., Poklis, J. L., & Peace, M. R. (2022). ∆ 8-THC, THC-O Acetates and CBD-di-O Acetate: Emerging Synthetic Cannabinoids Found in Commercially Sold Plant Material and Gummy Edibles. Journal of Analytical Toxicology, 46(8), 940-948.
- Hartung, B., Kauferstein, S., Ritz-Timme, S., & Daldrup, T. (2014). Sudden unexpected death under acute influence of cannabis. Forensic science international, 237, e11-e13.
- Schwilke, E. W., Schwope, D. M., Karschner, E. L., Lowe, R. H., Darwin, W. D., Kelly, D. L., … & Huestis, M. A. (2009). Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), 11-hydroxy-THC, and 11-nor-9-carboxy-THC plasma pharmacokinetics during and after continuous high-dose oral THC. Clinical chemistry, 55(12), 2180-2189.
- Viñals, X., Moreno, E., Lanfumey, L., Cordomí, A., Pastor, A., de La Torre, R., … & Robledo, P. (2015). Cognitive impairment induced by delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol occurs through heteromers between cannabinoid CB1 and serotonin 5-HT2A receptors. PLoS biology, 13(7), e1002194.
- Bloomfield, M. A., Ashok, A. H., Volkow, N. D., & Howes, O. D. (2016). The effects of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol on the dopamine system. Nature, 539(7629), 369-377.
- Gaffal, E., Cron, M., Glodde, N., & Tüting, T. (2013). Anti‐inflammatory activity of topical THC in DNFB‐mediated mouse allergic contact dermatitis independent of CB 1 and CB 2 receptors. Allergy, 68(8), 994-1000.
- Dawidowicz, A. L., Olszowy-Tomczyk, M., & Typek, R. (2021). CBG, CBD, Δ9-THC, CBN, CBGA, CBDA and Δ9-THCA as antioxidant agents and their intervention abilities in antioxidant action. Fitoterapia, 152, 104915.
- Dawidowicz, A. L., Olszowy-Tomczyk, M., & Typek, R. (2021). CBG, CBD, Δ9-THC, CBN, CBGA, CBDA and Δ9-THCA as antioxidant agents and their intervention abilities in antioxidant action. Fitoterapia, 152, 104915.
- Adejumo, A. C., Flanagan, R., Kuo, B., & Staller, K. (2019). Relationship between recreational marijuana use and bowel function in a nationwide cohort study. Official journal of the American College of Gastroenterology| ACG, 114(12), 1894-1903.
- Perucca, E. (2017). Cannabinoids in the treatment of epilepsy: hard evidence at last?. Journal of epilepsy research, 7(2), 61.
- Dariš, B., Verboten, M. T., Knez, Ž., & Ferk, P. (2019). Cannabinoids in cancer treatment: Therapeutic potential and legislation. Bosnian journal of basic medical sciences, 19(1), 14.
- Longo, R., Oudshoorn, A., & Befus, D. (2021). Cannabis for chronic pain: a rapid systematic review of randomized control trials. Pain Management Nursing, 22(2), 141-149.
- Cichewicz, D. L. (2004). Synergistic interactions between cannabinoid and opioid analgesics. Life sciences, 74(11), 1317-1324.
- Miller, H. P., Bonawitz, S. C., & Ostrovsky, O. (2020). The effects of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) on inflammation: A review. Cellular Immunology, 352, 104111.
- Hampson, A. J., Grimaldi, M., Axelrod, J., & Wink, D. (1998). Cannabidiol and (−) Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol are neuroprotective antioxidants. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 95(14), 8268-8273.
- Haddad, F., Dokmak, G., & Karaman, R. (2022). The efficacy of cannabis on multiple sclerosis-related symptoms. Life, 12(5), 682.
- Urbi, B., Corbett, J., Hughes, I., Owusu, M. A., Thorning, S., Broadley, S. A., … & Heshmat, S. (2022). Effects of cannabis in Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Parkinson’s Disease, 12(2), 495-508.
- D’souza, D. C., Ranganathan, M., Braley, G., Gueorguieva, R., Zimolo, Z., Cooper, T., … & Krystal, J. (2008). Blunted psychotomimetic and amnestic effects of Δ-9-tetrahydrocannabinol in frequent users of cannabis. Neuropsychopharmacology, 33(10), 2505-2516.
- Moser, A., Ballard, S. M., Jensen, J., & Averett, P. (2023). The influence of cannabis on sexual functioning and satisfaction. Journal of Cannabis Research, 5(1), 1-11.