What Delta Is Regular Weed? (Weed Deltas 101)
The most abundant “delta” found in the raw cannabis plant is delta-9 THC — however, trace concentrations of delta-8, delta-10, and HHC (delta-0) can also be found.
When we talk about delta, we’re referring to delta cannabinoids, and the main one is delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, also known as THC.
THC is one of the most common components found in weed and is what causes the psychoactive effects — the iconic ‘high.’ The cannabis plant primarily produces delta 9 and delta 8 naturally, but delta 9 occurs in much higher concentrations.
Delta 8 products have become popular because they can be produced from hemp, making them legal in most states. Other variants, such as delta 10, are also very popular.
If you’ve been to a dispensary or head shop recently, chances are that you’ve already come across these cannabis byproducts. So, what’s the difference between them?
Weed Deltas 101
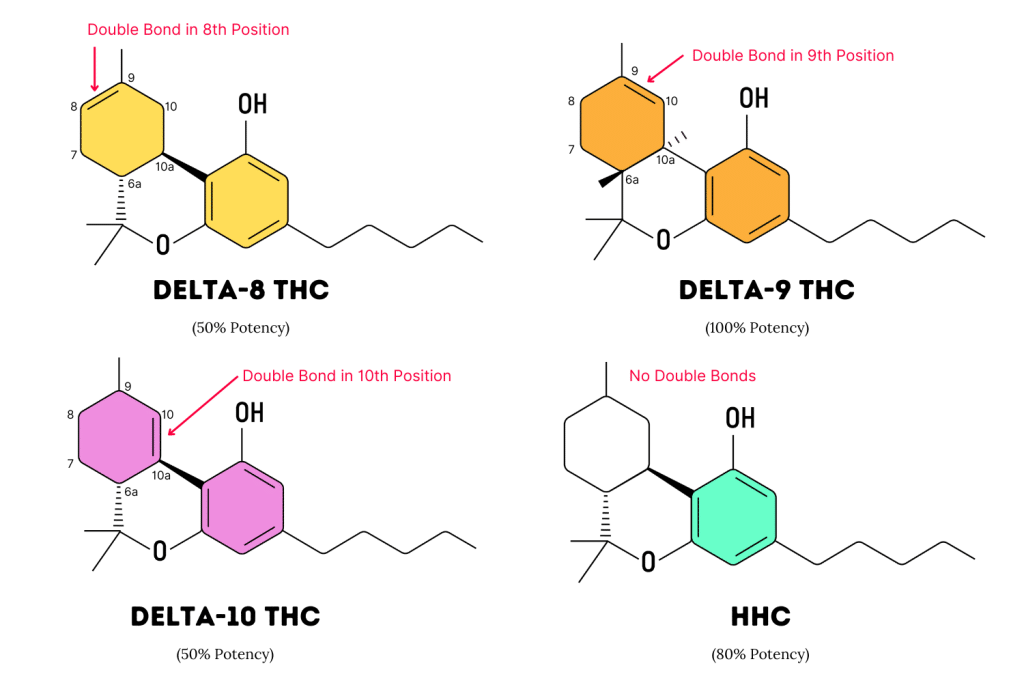
There are many types of THC in regular weed — each one differentiated by the location of a double bond in its chemical structure.
In chemistry, the word “delta” (Δ) is used to differentiate molecules with slightly different bonding configurations:
- Delta-8 THC — double bond is located on the 8th carbon.
- Delta-9 THC — double bond is located on the 9th carbon.
- Delta-10 THC — double bond is located on the 10th carbon.
- HHC (Delta-0 THC) — no double bond.
Although the differences are subtle, moving this double bond changes the strength in which THC isomers bind and activate the endocannabinoid receptors.
The strongest isomer is delta-9 THC (also the most abundant), closely followed by HHC (no double bond). Delta-8 and delta-10 THC are roughly half as potent as delta-9 THC.
For many years, delta 9 was thought to be the only kind of THC found in weed [1]. However, a few years later several other forms were discovered in trace concentrations. No cannabis contains high levels of delta-8, delta-10, or HHC naturally.
There are also different “deltas” for other cannabinoids, including delta-8 and delta-9 THCV and delta-8 and delta-9 THCP.
1. Delta 8 THC
Delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol is a cannabinoid produced through CBD’s conversion in a process called isomerization [2]. Delta 8 gets its name from its chemical structure since it has a double bond on the 8th carbon of the THC molecular chain.
The CBD molecule’s atoms are rearranged through this process until they form delta 8. Manufacturers do this with catalysts, heat, and solvents. Delta 9 can also be used to produce delta 8 through the same isomerization process and chemical reactions, but the final product wouldn’t be legal in most states [3].
Delta 8 can help produce acetylcholine [4], the neurotransmitter in our brain in charge of memory, cognition, and arousal. Similar to THC, it stimulates the appetite when used in small doses [5] and helps relieve pain and inflammation [6].
Related: Delta-8 THC Carts | Delta-8 THC Gummies | Delta-8 THC Pre-Rolls | Delta-8 Magic Mushrooms
2. Delta 9 THC
Unlike delta 8, delta 9 THC is naturally found in high quantities in the cannabis plant. When we consume it, it interacts with our body’s endocannabinoid receptors. Specifically, it binds to our CB1 and CB2 receptors in the brain and the nervous system, resulting in the famous high we’re all familiar with.
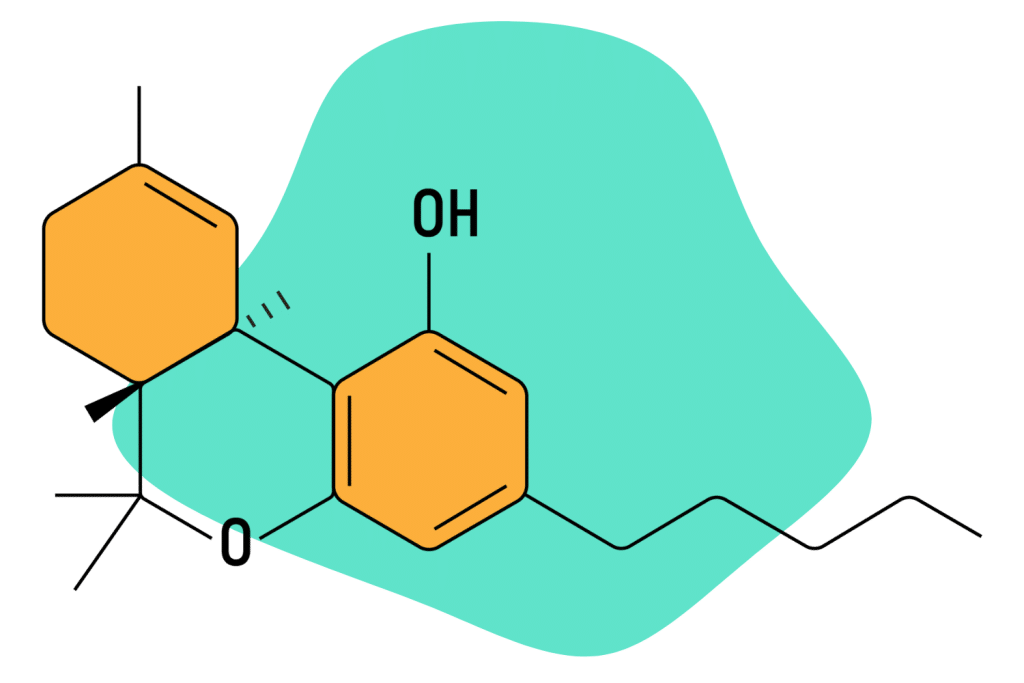
Although delta 9 is primarily famous for its psychoactive effects, it also provides other benefits. Studies show it can treat chronic pain, chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, stress, and even help with sleep regulation [7].
Many studies and tests point towards potential therapeutic applications for delta 9. Pharmaceutical companies are looking at delta 9 for possible analgesic and anti-inflammatory medicines — and even cancer treatment [3].
In the future, medications containing a mixture of delta 9 THC and CBD could become commonplace.
Related: Delta-9 THC Carts | Delta-9 THC Gummies | D8 vs. D9 (Compared & Contrasted)
3. Delta 10 THC
Much like delta 8, delta 10 THC is also an isomer of delta 9 THC, and it gets its name from having a double bond on the 10th carbon chain.
It’s naturally available in minimal quantities, so most of the delta 10 THC you usually see comes from several chemical processes. There is roughly 30% delta 9 THC in any mature weed plant and usually 1% or even less delta 10 THC.
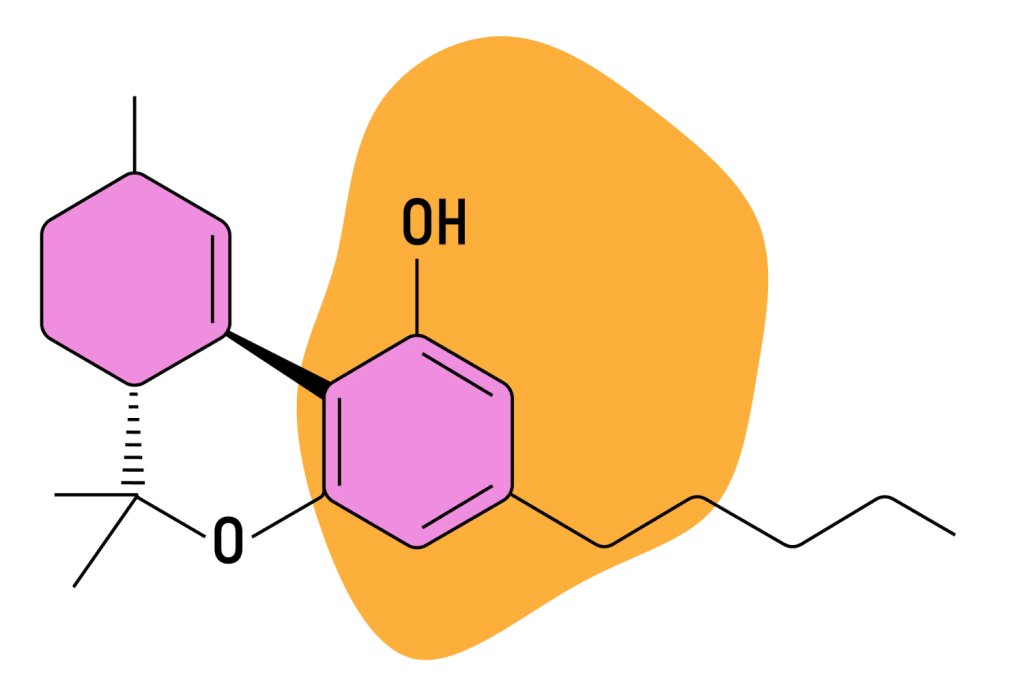
Both delta 8 and delta 10 are psychoactive compounds, which means they produce a high like delta 9 does. The critical difference is that delta 8, and especially delta 10, are much less potent.
What distinguishes delta 10 from delta 8 is its particular effects. Delta 8 produces relaxing sensations and alleviates stress, while delta 10 is said to produce an uplifting and energetic mood and increase focus and creativity.
Despite delta 10’s newfound popularity, there is little to no research on its benefits. There are many claims about its possible benefits, but the evidence is either anecdotal or part of a marketing ploy.
4. Delta-0 THC (HHC)
HHC (hexahydrocannabinol) is sometimes referred to as delta-0 THC because it contains no double bond whatsoever. This compound is created through a natural degeneration of delta-9 THC, albeit in very small amounts. Most of the delta-9 THC is degraded into a separate cannabinoid called CBN — which is roughly 10% the strength of the original molecule.
Modern HHC preparations are created by hydrogenating THC. This process swaps the double carbon bond with two additional hydrogen bonds. It’s a process similar to the hydrogenation used to create margarine from unsaturated fatty acids.
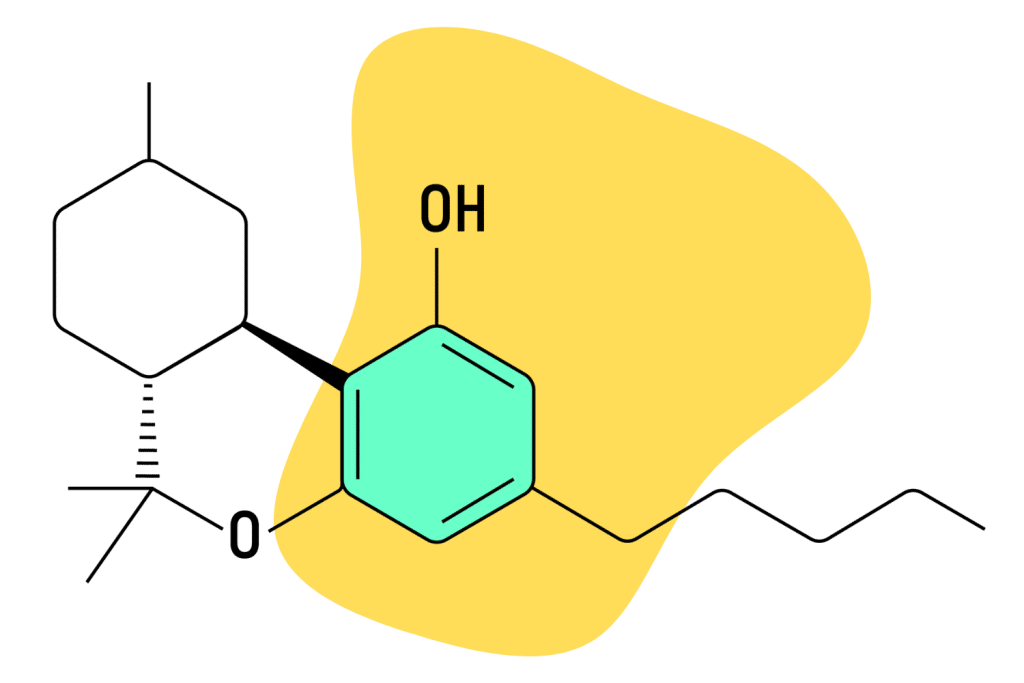
The main benefit of HHC (aside from legal loopholes in some states) is its exceptionally long shelf-life. This molecule is very stable and resists further degradation for many years. Nobody knows for sure how long HHC will remain viable.
Related: HHC Carts | HHC vs. THC (Key Differences Explained)
Which Delta is Better?
The answer to this question will depend entirely on what you’re looking for.
If you want a potent high, go for delta 9. If you want to relax or relieve pain, delta 8 might be the one for you.
Delta 10’s effects are supposedly milder than those of delta 9 and delta 8, so it may be worth considering if you want a more beginner-friendly variant.
THC products are varied enough to satisfy consumers’ needs on both medical and recreational ends, so look for the one that suits your needs.
Legality of the Different Deltas
As mentioned before, delta 9 is illegal under federal law.
However, since the introduction of 2018’s Farm Bill, cannabis plants with less than 0.3% delta 9 are considered industrial hemp and can be grown legally.
Despite delta 9 being illegal federally, many states have legalized marijuana for recreational use.
But what does it mean for weed to be illegal federally but legal in certain states?
In short, it means that even though it’s illegal, the federal government stays out of the matter and leaves it to the state to handle such issues.
The following states have legalized delta 9 THC (from marijuana):
- Arizona
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Illinois
- Maine
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Montana
- Nevada
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- Oregon
- Rhode Island
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- Maryland
- Missouri
But what about delta 8 then? As long as the delta 8 is made from CBD that’s derived from hemp, it’s not considered illegal under the already established marijuana federal laws.
Delta 9 (and marijuana) remain strictly illegal in the following states:
- Alaska
- Colorado
- Delaware
- Idaho
- Iowa
- Montana
- New York
- Nevada
- North Dakota
- Oregon
- Rhode Island
- Vermont
- Utah
- Washington
Arizona, California, Minnesota, and Mississippi have unclear or dubious legislation in this matter, in which case the regulation might depend on federal law. Delta 10 is less regulated, so I recommend checking out your local regulations before buying anything.

FAQs: Delta THC Variants
Next, we’ll answer some questions we often get about weed and the different deltas.
1. Is delta 9 the same as weed?
Delta 9 (THC) is a component of weed and produces the high that weed is known for, but it technically isn’t weed. You can think of it as a compound in the plant, but not the whole plant.
2. What delta is most powerful?
To date, delta-9 THCP is the most potent. It’s possible there are other potent isomers out there that we have yet to discover.
3. Will all deltas cause you to test positive?
Yes, just like delta 9, delta 8 and other milder variants like delta 10 will likely appear in any urine or blood drug tests you take [8].
4. What Are the Main Differences Between Delta 8, Delta 9, & Delta 10 THC?
Delta 8, Delta 9, and Delta 10 THC are all isomers of THC, meaning they have the same chemical formula but different structures. Delta 9 is the most common and potent, known for its strong psychoactive effects. Delta 8 is milder and often used for its relaxing properties, while Delta 10 is even milder and is said to enhance focus and creativity.
5. How Is Delta 8 THC Made from CBD?
Delta 8 THC is typically produced through a process called isomerization, where CBD (cannabidiol) is chemically altered to create Delta 8. This involves using catalysts, heat, and solvents to rearrange the atoms in the CBD molecule.
Subscribe For More 🍄
References
- Pertwee, R. G. (2006). Cannabinoid pharmacology: the first 66 years. British Journal of Pharmacology, 147(S1). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0706406
- Tagen, M. and Klumpers, L. E. (2022). Review of delta‐8‐tetrahydrocannabinol (δ8‐thc): comparative pharmacology with δ9‐thc. British Journal of Pharmacology, 179(15), 3915-3933. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.15865
- Boggs, D. L., Peckham, A., Boggs, A. A., & Ranganathan, M. (2016). Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol: Separating the chemicals from the “weed,” a pharmacodynamic discussion. The mental health clinician, 6(6), 277–284. https://doi.org/10.9740/mhc.2016.11.277
- Revuelta, A. V., Cheney, D. L., Costa, E., Lander, N., & Mechoulam, R. (1980). Reduction of hippocampal acetylcholine turnover in rats treated with (-)-delta 8-tetrahydrocannabinol and its 1′,2′-dimethyl-heptyl homolog. Brain research, 195(2), 445–452. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(80)90078-5
- Avraham, Y., Ben-Shushan, D., Breuer, A., Zolotarev, O., Okon, A., Fink, N., Katz, V., & Berry, E. M. (2004). Very low doses of delta 8-THC increase food consumption and alter neurotransmitter levels following weight loss. Pharmacology, biochemistry, and behavior, 77(4), 675–684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2004.01.015
- Burstein, S. H., Friderichs, E., Kögel, B., Schneider, J., & Selve, N. (1998). Analgesic effects of 1′,1′ dimethylheptyl-delta8-THC-11-oic acid (CT3) in mice. Life sciences, 63(3), 161–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0024-3205(98)00256-2
- The health effects of cannabis and cannabinoids: The current state of evidence and recommendations for Research. (2017). . The National Academic Press. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK423845/
- Krüger, J. and Kruger, D. J. (2022). Delta-8-thc: delta-9-thc’s nicer younger sibling? Journal of Cannabis Research, 4(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42238-021-00115-8