Delta 8 Beginner’s Guide: What is Delta 8 THC?
Delta 8 THC is a popular “legal” alternative to marijuana.
Cannabis contains an impressive collection of psychoactive compounds, including several types of THC (tetrahydrocannabinol).
In this article, we’ll explore the delta 8 form — which is often marketed as the “legal” version of the compound.
Learn how delta 8 works, where it comes from, what cautions to watch out for, and how to use it.
What is Delta 8 THC?
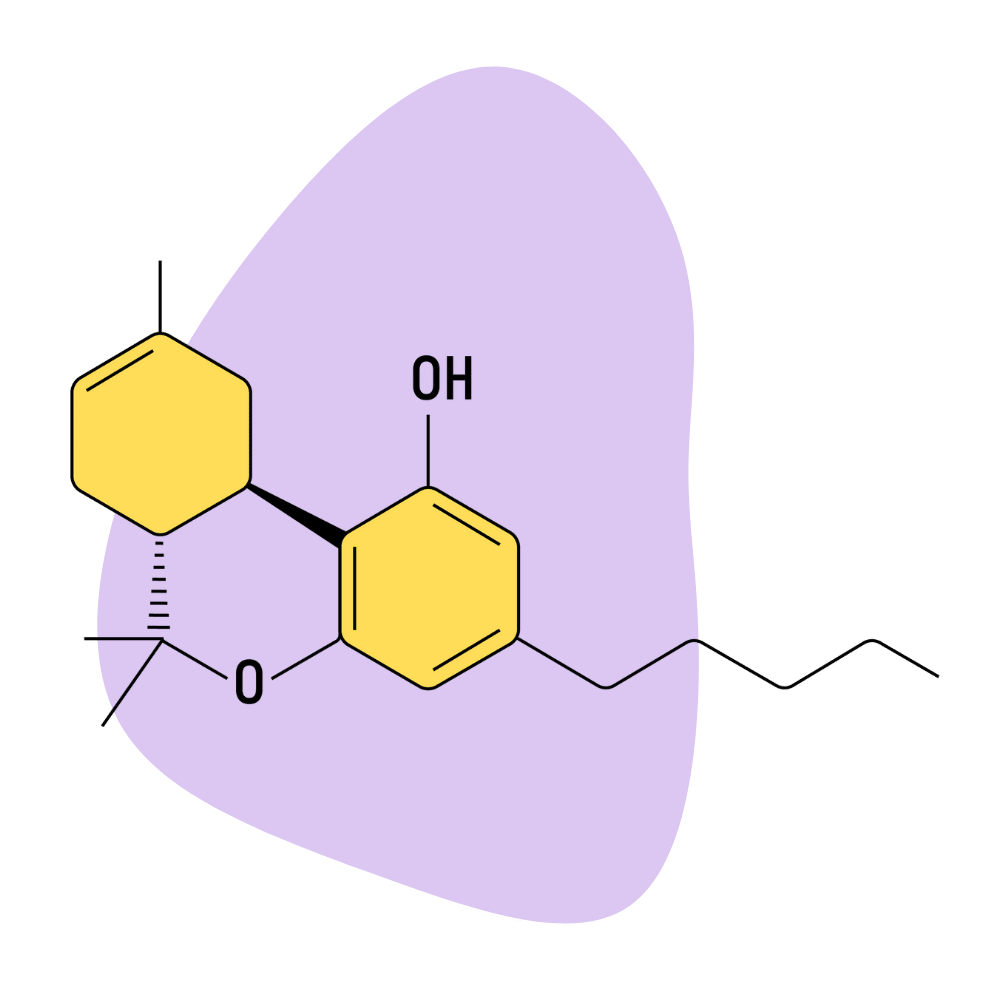
Delta 8 THC stands for Δ8-tetrahydrocannabinol. It’s an analog of delta 10 THC and delta 9 THC — which is the psychoactive ingredient in marijuana that makes users feel high. When we talk about THC, what most people are referring to is the delta 9 version.
Recently, there’s been a growing interest in the use of delta 8 THC as a “legal high.” This compound has only subtle differences in its chemical structure, but the differences are big enough that it’s classified separately from a legal perspective.
Unlike THC, which is considered a Schedule I drug in the United States, delta 8 THC is unregulated and (theoretically) legal in most states (with some exceptions).
The effects of delta 8 THC are similar to the delta 9 version but about half as strong.
Going beyond the legal advantages, delta 8 THC is also much less likely to cause anxiety — which is one of the main problems users experience when using products that contain THC.
Delta 8 THC is used in the form of edibles like gummies, it’s added to vaporizers and cartridges, it’s made into oils and tinctures, and it’s sold in concentrated form as well.
Summary: The Potential Health Benefits of Delta 8 THC Include:
- Alleviates stress & anxiety
- Promotes a better quality sleep
- May alleviate pain & reduce inflammation
- Inhibits nausea & vomiting
- May boost mood
- Offers neuroprotective action
- Increases appetite
- May offer support as an adjunctive cancer therapy
Tripsitter: Safe Delta 8 THC Checklist
- Learn the four pillars of responsible psychoactive substances use — set, setting, sitter, & substance
- Know your dose — keep your dose to 30 mg or less for the first session
- Check third-party testing — always look for third-party tests when shopping for delta 8 THC (contamination is common)
- Know the timeline — the effects of delta 8 THC are going to last between 3 & 6 hours
- Know when to avoid Delta 8 THC — don’t take delta 8 THC if you or a close family member has a history of psychosis or other psychiatric disorders
What Does Delta 8 THC Feel Like?
Delta 8 THC is often described as a smoother, more clear-headed, and less anxious version of delta 9 THC. The effects are much milder and tend to have a greater focus on the body than the mind.
The intensity of the psychoactive effects is highly dependent on the dose. Lower doses (5–10 mg) are mildly stimulating and help improve focus and concentration. This dosage range is used to alleviate anxiety, promote better focus and concentration, and improve the ability to enter productive flow states.
Higher doses (10–30 mg) are strong enough to cause psychoactive effects.
Most people who use delta 8 combine it with another substance to direct the effects. For example, you can mix delta 8 THC with coffee or caffeine when using it to boost focus, with melatonin to help with sleep, or with CBD to boost the painkilling and anti-anxiety effects.
Summary: What Does Delta 8 THC Feel Like?
- You may feel a mild sense of euphoria & elevated mood
- Your perception of time may change — causing time to feel like it’s moving slower or faster
- You feel a sense of peace & relaxation
- Your body feels loose & relaxed — it’s easy to find a comfortable position to sit or lie down
- You may find it easier to enter a productive flow-state (lower doses)
- Symptoms of chronic pain diminish & become more manageable
- You may feel tired or sedated (high doses)
Is Delta 8 THC Safe?
There’s no indication delta 8 THC is any different in terms of its safety profile from the other cannabinoids in the cannabis plant — none of which have any direct toxic effects.
However, there are a few concerns to be aware of when using delta 8:
Issues With Contamination
The main safety concern when using delta 8 THC is contamination.
The most common way of making delta 8 is to convert CBD from hemp into delta 8 THC. This allows manufacturers to sell “legal” delta 8 because it’s derived from hemp (rather than marijuana).
The process of converting CBD into delta 8 requires an acid catalyst and an organic solvent. If these compounds aren’t completely removed from the final product, they can lead to damage to the neurological, renal, hepatic, or digestive systems.
CBD-derived delta 8 THC should be considered unsafe unless proper third-party testing is available to prove the absence of contaminants.
You’d be surprised how many delta 8 companies aren’t able to prove the purity of their products.
The effects of heavy metal toxicity may include:
- Diarrhea
- Nausea or vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Shortness of breath
- Tingling sensation in the hands & feet
- Poor concentration
- Increased risk of neurodegenerative disease
- Memory loss
- Muscle weakness
- Insomnia or lethargy
- Autoimmune reactions
- Hair loss
Psychoactive Effects
Inebriation from THC in any form may increase your risk of self-inflicted or accidental harm. You should never drive or operate any dangerous machinery while under the influence of THC.
Some studies have also found that delta 8 THC increases blood pressure and heart rate [8] — which may make it unsafe for people suffering from cardiovascular disease.
You should avoid using delta 8 THC (or any form of THC) if you’re taking prescription medications to control blood pressure, heart rate, or high cholesterol. Other medications that may interact negatively include benzodiazepines, barbiturates, blood thinners, diabetes medications, opiates, and alcohol.
Delta 8 THC Side Effects
- Altered depth perception
- Fatigue or sedation
- Anxiety & paranoia (very rare)
- Increased heart rate
- Elevated blood pressure
- Insomnia (higher doses)
Is Delta 8 THC Legal?
Delta 8 THC is in a bit of a legal grey area in terms of its legal status — in the United States, at least.
In short, delta 8 THC itself isn’t explicitly illegal — but there’s a lot of room for interpretation. It’s possible the DEA could take action against companies selling delta 8 THC in the future.
Key Points: Delta 8 THC Legality:
- Delta 9 THC is explicitly listed as illegal according to the US federal government
- Some states have specifically banned delta 8 THC products
- Cannabis sativa plants that produce less than 0.3% delta 9 THC (dried weight) is considered hemp
- Products made from hemp are legal in the United States
- delta 8 THC can be derived from trace amounts of delta 9 THC in hemp
- Synthetically derived THC is considered illegal — which may or may not include delta 8 THC products that use chemical processes to convert delta 9 THC into the delta 8 version
The 2018 Farm Bill, signed by President Trump, made a clear distinction between marijuana products and hemp products. A distinction was made between products that contain high amounts of delta 9 THC and those that didn’t.
Any product made from Cannabis sativa plants that produce 0.3% delta 9 THC or less is considered “hemp,” — which is completely legal throughout all 50 states.
Any product made from Cannabis sativa that produces more than 0.3% delta 9 THC is considered “marijuana” and is listed as a Schedule I drug. These products are illegal on a federal level. Some state laws have their own laws, but on a federal level, marijuana remains illegal in all its forms.
However, there’s no mention of delta 8 THC in any of these regulations.
The legal status of delta 8 THC concentrates is the most hotly debated. In August of 2020, the DEA issued some slight clarity to the way they view cannabis extracts — stating that synthetically derived versions of THC are considered illegal. They didn’t mention what classifies as “synthetically-derived,” — but some interpret this to include delta 8 concentrates, which require a chemical process to convert from raw delta 9 THC.
While there’s some room for interpretation, the general consensus here is that technically, any delta 8 THC products made from hemp plants are entirely legal in the United States — despite their psychoactive effects. This gives delta 8 THC products the same legal distinction as CBD — which is now available throughout the US both online and in-store.
There are a few exceptions to this. Some states have passed bills that have specifically named delta 8 THC as a banned substance. A few examples include Alaska, Arizona, Arkansas, Colorado, Delaware, Idaho, Iowa, Montana, Pennsylvania, and Utah.
What’s The Dose of Delta 8 THC?
Delta 8 THC is roughly half as strong as delta 9 THC. The standard psychoactive dose of delta 9 THC starts around the 10 mg dose. Most people take somewhere between 5 and 30 mg.
This means the dosage range for delta 8 THC is between 10 and 60 mg.
Most people use either 20, 25, or 30 mg doses for a moderate level of effects.
Factors that can affect the dose include your size and weight, the intensity of effects you’re looking for, and your tolerance to THC. The more often you use delta 8 or delta 9 THC, the more you’ll need to take for an equivalent dose.
Delta 8 THC Dosage Chart
| Weight | Mild Effects | Heavy Effects |
| 80 lbs (35 kg) | 5 mg | 20 mg |
| 100 lbs (45 kg) | 6.5 mg | 25 mg |
| 120 lbs (55 kg) | 7.5 mg | 30 mg |
| 140 lbs (65 kg) | 9 mg | 36 mg |
| 160 lbs (72 kg) | 10 mg | 40 mg |
| 180 lbs (82 kg) | 12 mg | 45 mg |
| 200 lbs (90 kg) | 13 mg | 50 mg |
| 220 lbs (100 kg) | 14 mg | 56 mg |
| 240 lbs (108 kg) | 15 mg | 60 mg |
| 260 lbs (118 kg) | 17 mg | 65 mg |
Delta 8 THC Tolerance
Tolerance forms when the body starts to adapt to the effects of a particular substance.
When tolerance forms, we need to take a higher dose in order to receive the same set of effects as before.
The body forms tolerance to both delta 8 and delta 9 THC, as well as other cannabinoids, including CBD, CBG, and CBN.
Studies have shown we become tolerant to the effects of delta 8 THC faster than we do delta 9 THC. After using this cannabinoid for about 3 or 4 weeks consistently, you can expect to need a higher dose to get the same level of benefit as before.
If tolerance becomes too strong, you can cut back or stop using delta 8 for a week or two, so the body has time to lose its tolerance. By the end of the second week, any tolerance your body formed to delta 8 THC should be gone.

Delta 8 THC Products
Scientists have known about delta 8 since the 70s, but it’s only become popular mainstream within the last two years.
Regular cannabis products aren’t suitable for everyone. Side-effects like anxiety and paranoia are cited as the most common reasons people choose to avoid marijuana products. This has many people turning to delta 8 THC as a way to experience the same benefits without these negative side effects.
There are many different types of delta 8 THC products on the market today — covering all the major categories, you’ll find any cannabis products. You can get edibles like gummies or baked goods, capsules, oils and tinctures, concentrated extracts, vape pens and cartridges, and more.
1. Delta 8 THC Concentrates
Concentrated delta 8 THC consists of a thick, resinous, clear or off-yellow liquid. It’s made by isomerizing CBD from hemp into the delta 8 THC isomer. The conversion process isn’t perfect, so the final extract usually contains around 45–65% delta 8 and around 10% delta 9 THC. There usually ends up being around 5% CBD and trace amounts of other cannabinoids in the final product as well.
This extract is usually further refined to bring the total delta 9 THC content below the threshold of 0.3%.
Some delta 8 concentrates then have the terpene profiles added back into the final mix to give it a more fluid consistency and improve the overall potency of the extract.
These products are relatively cheap when you look at the cost per mg of the active ingredient and deliver the strongest impact overall.
2. Delta 8 THC Gummies
Gummy candies are another popular way of using delta 8. They mask the bitter flavor of the hemp extract and provide consistent doses of the active ingredient. You can find gummies with all different potencies of delta 8. Some contain as little as 5 mg of the cannabinoid per piece; others contain up to 40 mg per piece.
Make sure you’re aware of the potency of the gummies you’re using to avoid taking too much by mistake.
3. Delta 8 THC Cartridges
Inhalable forms of THC have the fastest onset of effects, by far. Just a few hits from a vape pen start producing effects in as little as 5 minutes, but it’s usually much quicker than that.
A vape is designed to heat delta 8 THC concentrate, or an e-liquid formula that contains delta 8 THC to a temperature hot enough that forces it to evaporate into the air — but not hot enough to cause it to combust.
There Are three main options when looking for vaporizer forms of delta 8 THC:
- Delta 8 THC Vaporizers — Disposable vaporizers come prefilled with delta 8 in a small pen-sized device. To use, simply start inhaling through the mouthpiece. Sensors will automatically turn on the heating element and convert the extract into a gaseous form.
- Delta 8 THC Cartridges — A vape cartridge is designed to be used with a reusable vaporizer. They come in all different sizes and thread-types to fit your existing vaporizer pen. Once the cartridge is empty, you can throw it out.
- Delta 8 THC E-Liquids — An E-liquid consists of a blend of vegetable glycerin, propylene glycol, and delta 8 THC concentrate. When these compounds are heated, they’re converted into a thick white plume. This is different from smoke because there’s no combustion taking place in this reaction.
4. Delta 8 THC Tinctures
When we think of cannabis tinctures, most people think of CBD oil — the quintessential version of CBD millions of people are taking on a daily basis to manage chronic pain, anxiety, and sleep disorders.
Delta 8 THC comes in the same convenient format as CBD oils. The advantage of using oil is the long shelf-life, fast absorption, discrete method of consumption, and ability to take precise doses.
A tincture is made by first concentrating the delta 8 THC on its own before infusing it into a carrier oil. The oil acts as a solvent to dissolve the THC evenly throughout the liquid.
Tinctures are very easy to use. You can simply drop a few drops of the oil underneath your tongue for fast onset of effects, or add it to any food or beverage of your choice. Most people just take the oil directly.
To find the right dose of a tincture, you need to first identify its potency. Every tincture has a different potency based on the total amount of delta 8 THC in the bottle and the volume of oil contained inside.
To find the potency, simply divide the total amount of delta 8 by the volume of the bottle. For example, a 300 mg bottle of delta 8 tincture in a 30 mL (1 oz) bottle works out to a potency of around 10 mg per mL. So for a 10 mL dose, you would need to take 1 full milliliter (1 dropperful). For a 20 mg dose, take two dropperfuls and so on.
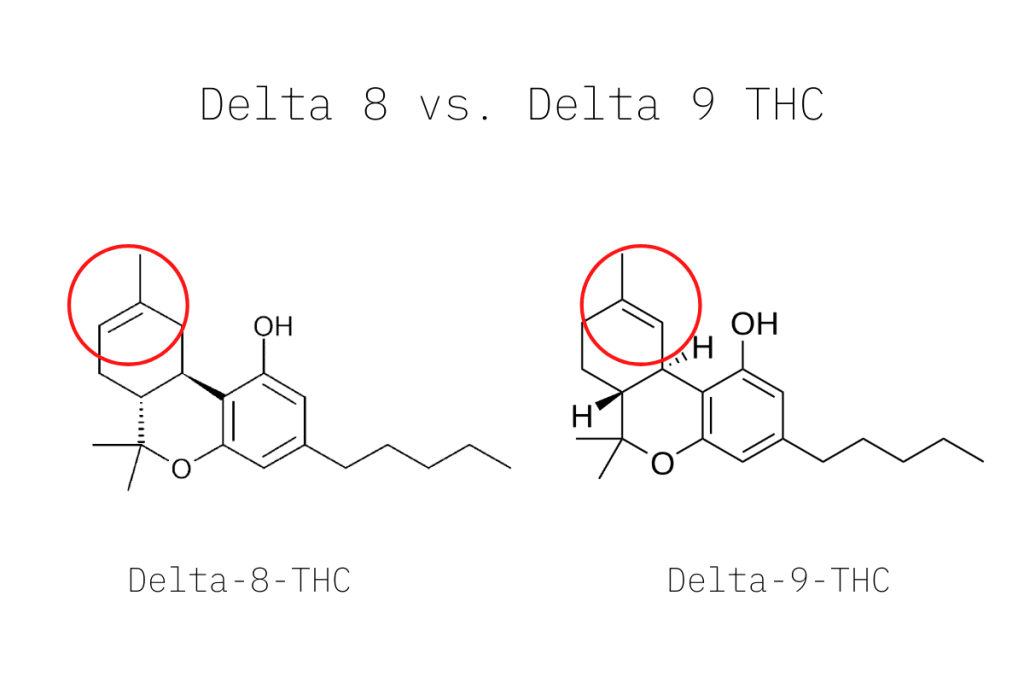
Delta 8 THC vs. Delta 9 THC
Summary: What Are The Advantages & Disadvantages of Delta 8 THC vs. Delta 9 THC?
- (+) delta 8 THC is much less likely to make you feel anxious after using it
- (+) delta 8 THC has a significantly longer shelf-life
- (+) delta 8 THC is better for improving appetite than delta 9 THC
- (+) delta 8 THC is legal in most US states
- (+) delta 8 THC is a more clear-headed high than delta 9
- (–) delta 8 THC is only about 50% as strong as delta 9 THC
Delta 8 and delta 9 are analogs of each other.
An analog is a compound that’s almost identical to another molecule. In the case of delta 8 vs. delta 9 THC, the difference is the placement of a double bond in the chemical structure.
In delta 8, the bond is at the 8th carbon chain, while delta 9 THC has this bond at the 9th carbon chain.
The difference is subtle, but it’s enough for these two compounds to have slightly different effects.
Both compounds activate the CB1 and CB2 endocannabinoid receptors to exert their effects. When this happens in the brain, it triggers a cascade of serotonin release — resulting in the characteristic “high” experienced when we use marijuana products.
Delta 8 THC has about half the potency as delta 9 THC — which means you need to use about twice as much to get the same intensity of effects.
Despite being weaker, there are a few advantages of using delta 8 THC in terms of legal, side-effects, and use for certain conditions compared to delta 9 THC.
For example, delta 8 THC isn’t listed as a schedule I illicit substance like delta 9 THC — making it much easier to get legally than conventional THC products.
Additionally, delta 8 THC is significantly less likely to trigger anxiety as a side-effect — which is the most common side-effect of using THC products and one of the main reasons people choose to avoid marijuana.
Comparing Delta 8 THC with Delta 9 THC: Side-By-Side:
| Metrics | Delta 8 THC | Delta 9 THC |
| Psychoactivity | Mild-Moderate | Moderate-High |
| Cost | $$ | $ |
| Concentration in Cannabis | Less than 1% | Up to 30% |
| Receptors | CB1 & CB2 | CB1 & CB2 |
| Typical Dose | 10–40 mg | 5–20 mg |
| Effects on Appetite | Strong Stimulant | Moderate Stimulant |
| Anxiety Side-Effects | Very Mild | Mild to Moderate |
| Legality | Legal-Grey Area | Illegal |
Health Benefits & Medical Research For Delta 8 THC
Most of the health benefits associated with delta 8 THC come from anecdotal reports and early animal testing. There are virtually no published studies outlining the effects of delta 8 THC specifically. The vast majority of research involves the more common analog — delta 9 THC.
With that said, there are some conclusions and promising findings that have begun to surface more recently on the potential benefits of delta 8 THC.
1. Delta 8 THC & Anxiety
There have not been any official studies on the effects of delta 8 THC for anxiety — however, there’s a ton of anecdotal reports of people switching from delta 9 THC to delta 8 THC for the sole purpose of avoiding anxious side-effects.
It’s clear the delta 8 version is less likely to cause anxiety — but this doesn’t necessarily mean it can actively reduce anxiety either.
What we do know is that delta 8 THC activates the CB1 receptors the same way as delta 9 THC. Activation of this receptor has been shown to play a key role in the anti-anxiety qualities of marijuana at lower doses [4]. But the region of the brain affected plays a pivotal role in whether THC causes anxiety or inhibits anxiety.
Higher doses of delta 9 THC can actually cause anxiety. It’s one of the most common side-effects of marijuana. It’s believed that higher doses of THC cause a stronger activation of the CB1 receptors in the amygdala — the region of the brain involved with regulating emotions such as fear and anger.
Delta 8 THC is believed to have less of an effect on the amygdala — which is likely why this cannabinoid rarely causes anxiety, even at higher doses. By targeting CB1 receptors in regions of the brain like the prefrontal cortex and ventral hippocampus — it’s likely delta 8 THC can even actively reduce feelings of panic, fear, and anxiety.
More research is needed to fully understand the potential role of delta 8 THC in managing stress and anxiety disorders.
2. Delta 8 THC & Appetite
One of the most common findings from anecdotal reports of people using delta 8 THC is a stronger appetite compared to delta 9 THC.
One study looked at the impact of both delta 8 and delta 9 THC on the appetite in mice.
The short-term findings showed a 16% increase in the appetite of mice in the THC group compared to the placebo and a 22% increase by the time the trial came to a conclusion 50 days later [5]. The Delta 8 THC group was reported to lead to a much stronger impact on appetite than the delta 9 THC group.
There were two more interesting findings from this study.
The first was that even the lowest dose of delta 8 THC (0.001 mg/kg) had a strong impact on appetite. This dose works out to around 0.08 mg of delta 8 THC for the average 175 lb human. This dose is in the sub-milligram range, which would classify as a microdose.
The second interesting finding was that the mice in the delta 8 THC group showed clear signs of cognitive improvement using the standard maze test. This effect was thought to be the result of improvements in dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin signaling in mice exposed to CB1 agonists like delta 8 THC.
3. Delta 8 THC & Pain
There is a lot of research available to support the painkilling effects of THC — however, virtually all of this research involved the delta 9 version of the compound.
One study in particular involved 172 patients suffering from neuropathic (nerve) pain given 7.5–25 milligrams of delta 9 THC per day [1]. At the end of the 7-month trial, 92% of the patients that finished the study indicated the treatment was able to reduce the level of pain they were experiencing. 3% of patients reported no change, and 5% indicated a higher level of pain after the treatment.
Nearly 25% of the participants in this study dropped out due to side-effects of the THC — primarily involving anxiety and insomnia. Researchers are now shifting focus to look at the delta 8 version of THC because it’s believed to offer a similar impact on alleviating pain and a lower chance of producing anxious side-effects.
The only studies exploring the specific painkilling effects of delta 8 THC involve animal studies. One study looking at the analgesic effects of delta 8 THC applied a topical extract to mice with corneal damage. The study found a significant reduction in pain and inflammation in the mice treated with THC [2].
Other (older) animal studies have shown similar findings [3], but there has not yet been any research on the painkilling effects of delta 8 THC in humans.
4. Delta 8 THC & Nausea
Chemotherapy is notorious for its nauseating side effects, and THC products, in general, are considered one of the most effective therapeutic options for managing this uncomfortable side-effect.
There are already plenty of studies available that demonstrate a clear improvement in nausea symptoms from delta 9 THC [6]. There are now several pharmaceutical preparations of THC that have been approved for treating nausea in patients undergoing chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
The question isn’t whether or not THC is able to reduce nausea — the evidence clearly shows this is the case. The question is which analog of THC does this job most effectively.
At the moment, there isn’t enough research to know for sure which version of THC is the strongest for alleviating nausea. However, an older study (1995) exploring the anti-nausea effects of the delta 8 analog in children undergoing chemotherapy resulted in a complete inhibition of vomiting [7].
None of the patients treated with delta 8 THC had a single incident of vomiting after the chemotherapy, which clearly shows the delta 8 molecule offers either the same or stronger anti-nausea effects than the delta 9 version.
5. Delta 8 THC & Sleep
There aren’t any clinical studies that explore the impact delta 8 THC products have for promoting sleep — however, there’s a large amount of anecdotal data that supports this effect.
Participants in the subreddit R/delta8 often describe the positive impact this cannabinoid has had on their ability to sleep — especially when combined with other sleep-supportive cannabinoids, melatonin, or other sleep supplements.
The general consensus among delta 8 users is that this cannabinoid produces a high but lacks a particular direction unless you take it with other sleep-supportive compounds.
Many people find success when using delta 8 for improving sleep by mixing it with melatonin (2–5 mg) or with other sleep-supportive cannabinoids such as CBD or CBN.
6. Neuroprotective Effects of Delta 8 THC
Despite there only being a handful of studies on delta 8 THC so far, several of them have suggested the cannabinoid exerts a protective action on the neurological system.
We now know that delta 8 THC activates the same CB1 and CB2 receptors as the delta 9 version of the molecule, so it’s not too far-fetched to assume that this cannabinoid can provide a similar level of benefit through these effects.
THC and other CB1 and CB2 receptor agonists have been shown to protect the sensitive nerve cells in the brain in several different models of neurological stress and degeneration — including HIV-1-induced damage [9], Huntington’s disease [10], hypoxia [11], and Alzheimer’s disease [12].
7. Anti-Cancer Effects of Delta 8 THC
The research is still far too early to suggest delta 8 THC as a treatment for cancer — but the research is promising thus far.
According to a study published in 2013 by the National Cancer Institute, delta 8 THC was one of several cannabinoids shown to inhibit the growth of cancerous tumors in the lungs [13]. This research comes from both in vitro and in vivo animal research.
Can Delta 8 THC Make Me Fail A Drug Test?
Delta 8 THC has a very similar structure to delta 9 THC — which is what drug tests are designed to detect. Due to these similarities, as well as some similarities in the metabolites they produce after being processed by the body, it’s very likely that delta 8 THC will show up on a THC drug test.
If you’re required to take a drug test for any reason, it’s wise to avoid using delta 8 THC.
Where Does Delta 8 THC Come From?
Delta 8 THC begins its life as another cannabinoid called CBG (cannabigerol). Enzymes convert CBG into either THC, CBD, or CBC — depending on the strain and growing conditions of the plant.
However, these enzymes can only convert CBG into the delta 9 version of THC. The plant doesn’t have any enzymes that create delta 8 THC directly.
Instead, delta 8 THC forms as the original delta 9 molecule breaks down and degrades. Most of the delta 9 THC breaks down into another compound called CBN — which is only about 10% as strong as THC. A small percentage of delta 9 degrades into the more stable form of delta 8.
Even high THC strains of marijuana only have about 1% or less delta 8 THC by weight.

Final Thoughts: The Future of Delta 8 THC
This cannabinoid is in a bit of a grey area at the moment from a legal perspective. In the US, the only cannabinoid specifically banned on a federal level is the delta 9 isomer, but there’s room in the wording that could include delta 8 or other forms of THC as well.
At the moment, there’s a growing industry of delta 8 providers using hemp-derived cannabinoids like CBD to create synthetically modified forms of delta 8 “legally.” This process requires a lot of harsh or toxic ingredients to work, which can be difficult to remove fully without using some pretty high-level chemistry.
It’s very likely that delta 8 will become a common product choice in the near future as cannabis laws loosen and more companies start to carry their own forms of this THC isomer. It’s considered a better option for people who experience anxiety as a side effect while using THC, or people who want a more subtle high.
Subscribe To Get a Weekly Dose of Psychedelics In Your Inbox
References
- Weber, J., Schley, M., Casutt, M., Gerber, H., Schüpfer, G., Rukwied, R., … & Konrad, C. (2010). Tetrahydrocannabinol (Delta 9 THC) treatment in chronic central neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia patients: results of a multicenter survey. Anesthesiology research and practice, 2009.
- Thapa, D., Cairns, E. A., Szcześniak, A. M., Toguri, J. T., Caldwell, M. D., & Kelly, M. E. (2018). The cannabinoids Δ8THC, CBD, and HU-308 act via distinct receptors to reduce corneal pain and inflammation. Cannabis and cannabinoid research, 3(1), 11-20.
- Hine, B., Torrelio, M., & Gershon, S. (1977). Analgesic, heart rate, and temperature effects of Δ8 THC during acute and chronic administration to conscious rats. Pharmacology, 15(1), 65-72.
- Rubino, T., Guidali, C., Vigano, D., Realini, N., Valenti, M., Massi, P., & Parolaro, D. (2008). CB1 receptor stimulation in specific brain areas differently modulate anxiety-related behaviour. Neuropharmacology, 54(1), 151-160.
- Avraham, Y., Ben-Shushan, D., Breuer, A., Zolotarev, O., Okon, A., Fink, N., … & Berry, E. M. (2004). Very low doses of Δ8 THC increase food consumption and alter neurotransmitter levels following weight loss. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, 77(4), 675-684.
- Parker, L. A., Rock, E. M., & Limebeer, C. L. (2011). Regulation of nausea and vomiting by cannabinoids. British journal of pharmacology, 163(7), 1411-1422.
- Hine, B., Torrelio, M., & Gershon, S. (1977). Analgesic, heart rate, and temperature effects of Δ8 THC during acute and chronic administration to conscious rats. Pharmacology, 15(1), 65-72.
- Sultan, S. R., Millar, S. A., O’Sullivan, S. E., & England, T. J. (2018). A systematic review and meta-analysis of the in vivo haemodynamic effects of Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol. Pharmaceuticals, 11(1), 13.
- Xu, C., Hermes, D. J., Nwanguma, B., Jacobs, I. R., Mackie, K., Mukhopadhyay, S., … & Fitting, S. (2017). Endocannabinoids exert CB1 receptor-mediated neuroprotective effects in models of neuronal damage induced by HIV-1 Tat protein. Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience, 83, 92-102.
- Scotter, E. L., Goodfellow, C. E., Graham, E. S., Dragunow, M., & Glass, M. (2010). Neuroprotective potential of CB1 receptor agonists in an in vitro model of Huntington’s disease. British journal of pharmacology, 160(3), 747-761.
- Panikashvili, D., Mechoulam, R., Beni, S. M., Alexandrovich, A., & Shohami, E. (2005). CB1 cannabinoid receptors are involved in neuroprotection via NF-κB inhibition. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism, 25(4), 477-484.
- Tripathi, H. L., Vocci, F. J., Brase, D. A., & Dewey, W. L. (1987). Effects of cannabinoids on levels of acetylcholine and choline and on turnover rate of acetylcholine in various regions of the mouse brain. Alcohol and drug research, 7(5-6), 525-532.
- Blázquez, C., Casanova, M. L., Planas, A., Gómez del Pulgar, T., Villanueva, C., Fernández‐Aceñero, M. J., … & Guzmán, M. (2003). Inhibition of tumor angiogenesis by cannabinoids. The FASEB journal, 17(3), 1-16.