Estazolam (ProSom): Safety, Effects, & More
Everything you need to know about estazolam before taking it…⚠️
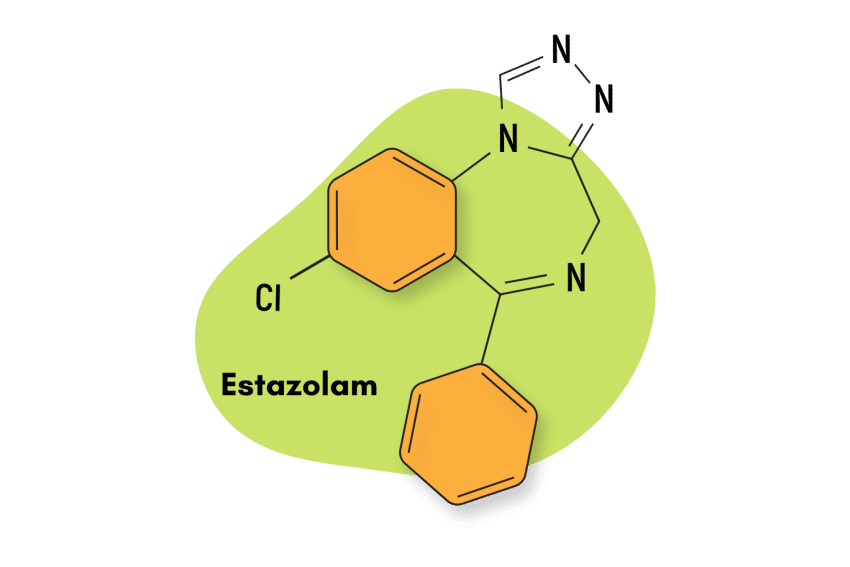
Estazolam (ProSom) is a prescription benzodiazepine of the triazolobenzodiazepine class. This benzodiazepine subtype is known for hosting some of the most potent anxiolytic and sedative drugs available today.
Estazolam has been approved in the United States for treating sleep-related conditions.
Studies have shown estazolam’s effectiveness as a hypnotic medication; it can potentially improve total sleep time, number of nocturnal awakenings, depth of sleep, and sleep quality [1].
Additionally, estazolam possesses several other benzodiazepine-related properties like anxiolytic and anticonvulsant effects and is sometimes used off-label for treating anxiety disorders.
Like most benzodiazepines, estazolam is also popular within the designer drug community. In higher dosages, estazolam acts as a potent inebriant and mildly euphoric.
Estazolam Specs
| Status | Approved 💊 |
| Common Dosage | 1–2 mg |
| PubChem ID | 3261 |
| CAS | 29975-16-4 |
IUPAC Name: 8-chloro-6-phenyl-4H-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a][1,4]benzodiazepine
Other Names: ProSom, Nuctalon.
Metabolism: The biotransformation of estazolam to 4-hydroxyestazolam is handled by the CYP3A4 enzyme.
Duration of Effects: Intermediate-Acting (10–24 hours). Peak plasma levels are achieved within 1–6 hours. Estazolam is an intermediate acting benzodiazepine. The elimination half-life of estazolam is an average of 19 hours, with a range of 8–31 hours.
Benzodiazepine Dosage Equivalency Calculator
**Caution:** Benzodiazepines have a narrow therapeutic window. Dose equivalents may not be accurate in higher doses.
This calculator does not substitute for clinical experience and is meant to serve only as a reference for determining oral benzodiazepine equivalence.
Please consult a medical practitioner before taking benzodiazepines.
How Does Estazolam Work?
Like most other benzodiazepines, estazolam’s primary mechanism of action occurs through its interaction with GABA-A receptors, a class of inhibitory neurotransmitters located throughout the brain and central nervous system (CNS).
When estazolam is ingested, it binds to GABA-A receptors and produces an allosteric effect, which means it potentiates the natural function of GABA. This is an important point of difference benzodiazepines have when compared to other compounds that affect GABA receptors, such as barbiturates, which directly activate GABA receptors in the body rather than enhancing their natural effects [2].
Enhanced activity at GABA-A receptors is responsible for the depressive effect benzodiazepines have on the CNS, which accounts for the anxiolytic, hypnotic, muscle relaxant, and anticonvulsant properties of benzodiazepines.
Differences in how individual benzodiazepines bind to GABA-A molecules account for the variation in their effects profile. GABA-A molecules are made up of different subunits, and the relative ability of benzodiazepines to interact with these subunits affects their overall pharmacology. However, a lot in this area is still poorly understood [3].
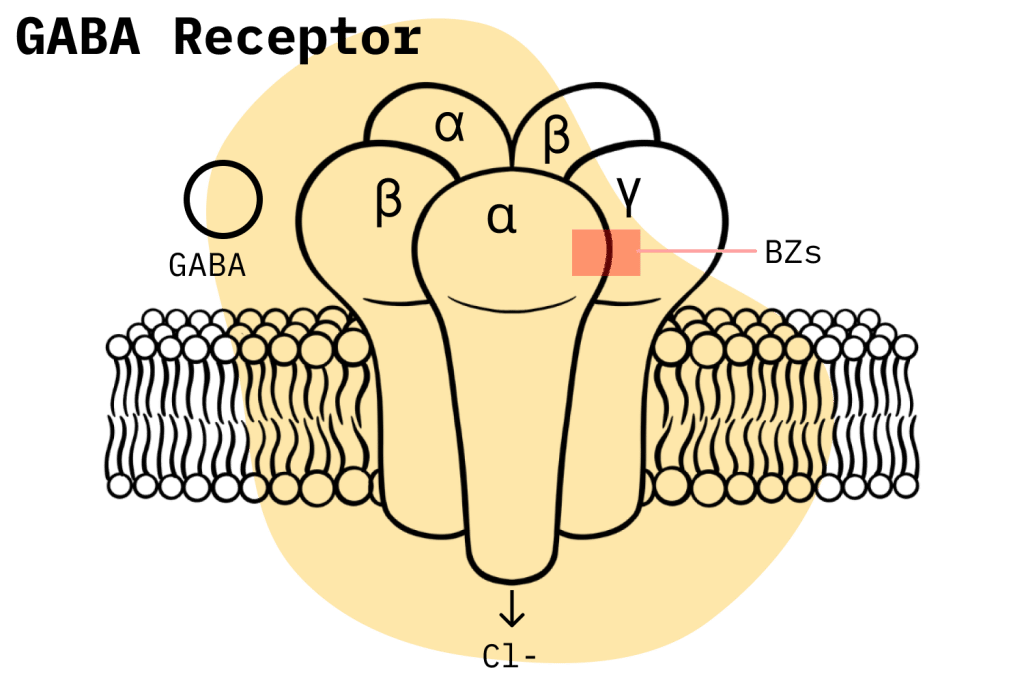
Six known α subunit isoforms compose various GABAA receptor subtypes. Two of these isoforms (α4 and α6) are labeled “benzodiazepine insensitive” due to their lack of benzodiazepine binding and action. The others can be bundled into two classes: those resulting in anxiolytic effects (α2/α3) and those responsible for sedation, ataxia, and amnesia (α1/α5).
Regarding its interaction with the different GABA-A subunits, we know that estazolam predominantly binds to the γ2 subunit [4]. However, we need more information to know how estazolam’s binding affinities determine its pharmacological profile.
Is Estazolam Safe? Risks & Side Effects
In the United States, benzodiazepines are Schedule IV drugs under the Controlled Substances Act. Despite their recognized medical uses, they still pose the potential for misuse and developing dependence and withdrawal symptoms.
Generally speaking, when used appropriately, benzodiazepines are not likely to cause a serious health event. However, recent statistics show that when misuse is factored into the equation, benzodiazepines are responsible for a considerable number of serious events.

The opioid crisis has led to an explosion of benzodiazepine misuse due to the concomitant use of opioids. This combination is extremely dangerous; the FDA has sternly warned against as it can easily lead to respiratory depression: the leading cause of death in drug overdoses.
Side Effects of Estazolam
The Mayo Clinic has identified the following common adverse effects with the use of estazolam:
- Clumsiness or unsteadiness
- Dizziness
- Lethargy
- Sleepiness or unusual drowsiness
Less common side effects include:
- Dry mouth
- Exhaustion
- Headaches
- Memory problems
- Mood swings
- Nausea and vomiting
- Poor judgment
- Trouble thinking and walking
Rare side effects include:
- Aggressiveness and anger
- Blood in urine
- Blood in the stool
- Itching, burning, and crawling sensations
- Chest pains
- Chills
- Coughs
- Decreased reflexes
- Fainting
- Irregular heartbeat
- Irritability
- Mouth sores
- Muscle spasms
- Skin rashes
Additionally, studies have found that estazolam, compared to other hypnotic benzodiazepines like flurazepam, showed similar levels of efficacy but also exhibited a lower incidence of side effects [5].
Benzodiazepine Withdrawal & Dependence
Developing physical or mental dependence symptoms due to a benzodiazepine prescription is a very real possibility. In fact, it’s one of the main concerns doctors have to deal with when assessing whether to give out a benzodiazepine prescription. Benzodiazepines are usually prescribed for the shortest time frame possible, usually around four weeks, for this reason.
Being on the lowest tier of controlled substances in the Controlled Substances Act has led to the common misconception that benzodiazepine treatment poses little risk when done correctly. However, the reality is that even if there is no misuse, users have a meaningful chance of developing physical dependence. Also, if one has a history of abusing either drugs or alcohol, the risk is much higher.
One study examined the likelihood of developing benzodiazepine dependence when using a given benzodiazepine for more than four weeks and found that over one-third of participants had withdrawal symptoms upon cessation [5].
Fatalities stemming from withdrawal symptoms related to benzodiazepines, alcohol, and opioids are rare, but they are not at all unheard of. In general terms, these three drug types exhibit the most intense withdrawal symptoms.
A good rule of thumb to follow when dealing with prescription pharmacological medications is this: the more you take the drug, and the longer you take it, the more of a chance of developing a dependence.
When it comes to estazolam, apart from the possibility of developing physical dependence, it has also been found that users generally develop a pharmacological tolerance to the drug’s effects and that this can happen in just a manner of days [6].
Harm Reduction: Estazolam
If the goal is to stay safe while using a pharmacological prescription medication like estazolam, there are plenty of general considerations one must keep in mind. Firstly, one should always take care to avoid any possible misuse. Obviously, any recreational use falls into the category of misuse, but there are plenty of more subtle ways that users can end up misusing their prescriptions.
For example, it’s easy to misuse a legitimate prescription if it is taken at the wrong time or with an improper dosage. It is also not unknown for users to begin taking their benzodiazepine prescription to help them treat new ailments for which their specific drug was not prescribed.
Simply stated, users must strive to follow their doctor’s instructions when taking benzodiazepines. However, there are also plenty of things to consider before jumping for a benzodiazepine prescription.
Potential benzodiazepine users should take the time to weigh the possible risks of dependence and withdrawal against whatever makes them seek a prescription. It is no secret that doctors, acting with financial interests in mind, can overprescribe medications like benzodiazepines.
In the vast majority of cases, potential benzodiazepine users have a variety of non-pharmacological alternatives open to them. They could try a behavior-related solution, such as exercise or therapy, or go for a plant-based medicine with a far more benign side effect profile. When it comes to dealing with anxiety and depression, there are many promising options, primarily related to psychedelics and other dissociative therapies.
Estazolam Drug Interactions
Here is some important information regarding the drug combination you should avoid when taking estazolam.
CNS Depressants (Opioids and Alcohol)
When dealing with benzodiazepines, one should always avoid a couple of drug interactions, mainly: opioids and alcohol. Polydrug abuse of CNS depressant compounds like benzodiazepines and opioids has a significant role in drug fatalities in the United States.

In general, users should always be quite wary of mixing two prescription medications. Drugs like benzodiazepines are prescription medications for a reason. Users should only mix prescription drugs with a doctor’s approval; if you’re planning on mixing two prescription drugs for recreational purposes, still consult with a doctor or at least look up the interaction online.
If in doubt, make sure to avoid these drugs and drug types:
- 1. Alcohol
- 2. GHB
- 3. Other benzodiazepines
- 4. Barbiturates
- 5. Opiates
Contraindicated Drug Interactions
Drug interactions can be very complicated, and plenty of esoteric drug combinations could seriously harm us. That’s why doctors always ask patients what drugs they usually take when considering whether to give out a prescription. Doctors must ensure they’re not exposing you to a dangerous drug combination.
If you’re on a benzodiazepine prescription, always check with your doctor if you plan to take a new drug (prescription or otherwise).
CYP Drug Interactions
Besides dangerous pharmacological interactions, users must also be aware of any possible CYP drug interactions. CYP enzymes are a superfamily of enzymes that almost always have a role to play in metabolizing pharmacological compounds.
When two drugs are CYP competitors or inducers, they can end up affecting the body’s metabolic process, which can lead to several negative outcomes. Inhibiting the metabolic clearance of a compound within the body will usually cause it to build up over time and thus raises the risk of an adverse reaction. When a drug is taken long-term, inhibiting its metabolism could lead to serious health events.

On the other hand, sometimes, a given drug can have a potentiating effect on the CYP enzyme of another drug. This speeds up the metabolic clearance of the later drug and, in turn, makes it less effective.
Estazolam Contraindications
Most prescription drugs have a number of contraindications associated with them. Typical contraindications include special statuses like pregnancy, hepatic impairment, chronic conditions that complicate treatment, etc.
Contraindications are a common way that users will unknowingly expose themselves to risk. If you plan on using a drug that has not been prescribed to you, make sure you find out if you qualify for a contraindication, as this could potentially elevate your risk factors.
Estazolam Proper Dosage
Proper dosage is one of the key factors to control if you want to stay safe when taking benzodiazepines. Due to the high number of complicating factors, such as body weight and formulation, it can be hard to determine the proper dosage.
Luckily, there are plenty of online resources which can help. Just remember that formulaic dosage guidelines found on the internet can never account for all the possible complicating factors; a doctor’s visit is required.
According to the Mayo Clinic, the proper dosages for estazolam (tablets) are the following:
For insomnia:
- 🧒🏼 Children — Use and dose must be determined by your doctor.
- 🧑🏻 Adults — At first, 1 milligram (mg) at bedtime. Your doctor may adjust your dose if needed.
- 👨🏽🦳 Older adults (65 or older) — At first, 0.5 milligrams (mg) at bedtime. Your doctor may adjust your dose if needed.
Similar Benzodiazepines
As a triazolobenzodiazepine, estazolam has certain characteristics that it tends to share with other benzodiazepines. However, it is also comparable in other ways to more classical benzodiazepines.
Diazepam
Diazepam — also known as Valium — has certain pharmacokinetic properties similar to estazolam. They are both short-acting and have a fast onset of action.
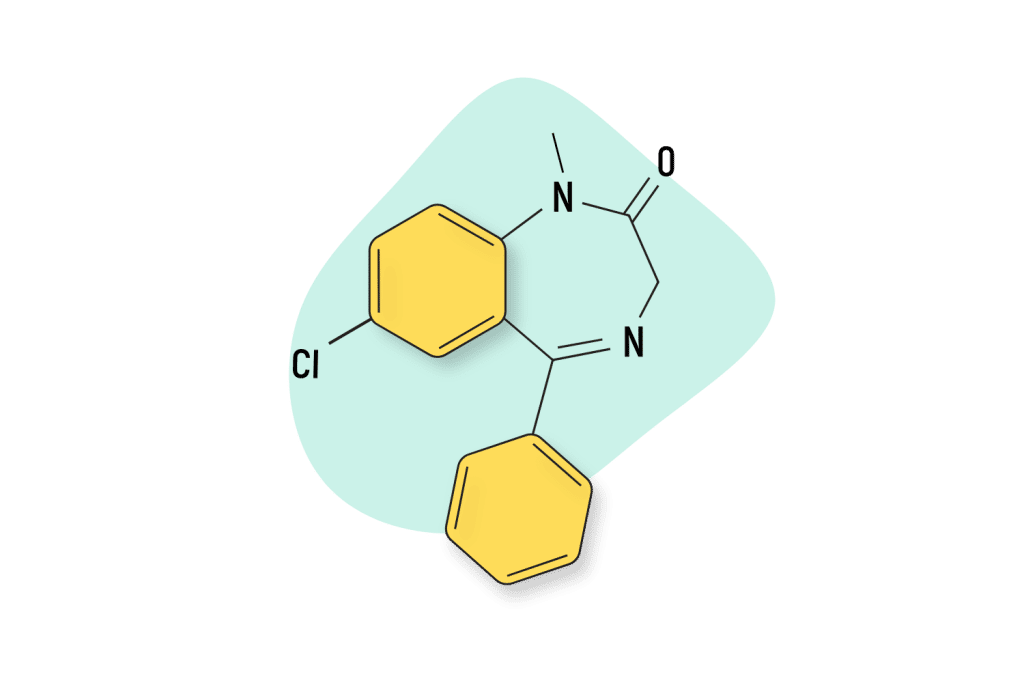
Flurazepam
Flurazepam is one of the few benzodiazepine medications approved for treating sleep-related issues in the United States. It has a mechanism of action comparable to estazolam and many similar pharmacokinetic properties. The significant difference between them is that flurazepam is much more potent.
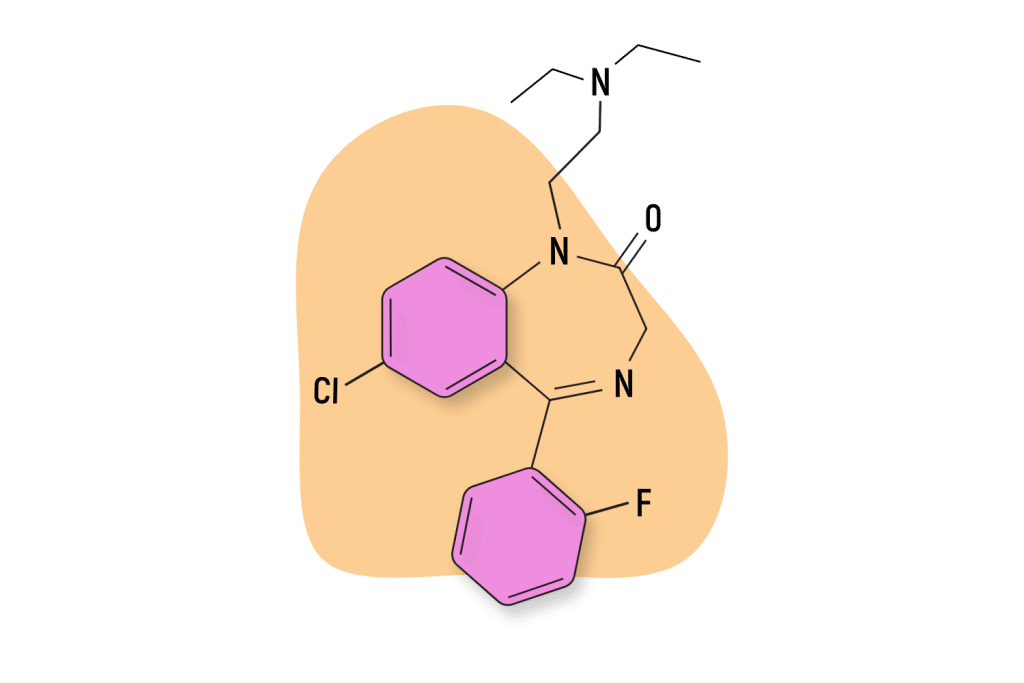
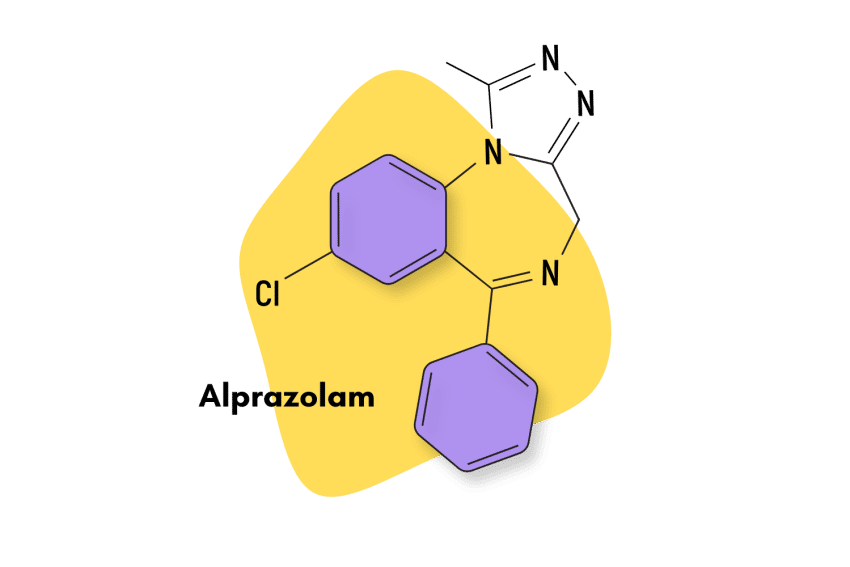
Alprazolam (Xanax)
Most benzodiazepines in the triazolobenzodiazepine subclass are either prodrugs, homologs, or metabolites of alprazolam. Like estazolam, alprazolam is algo highly potent and is an intermediate-acting benzodiazepine.
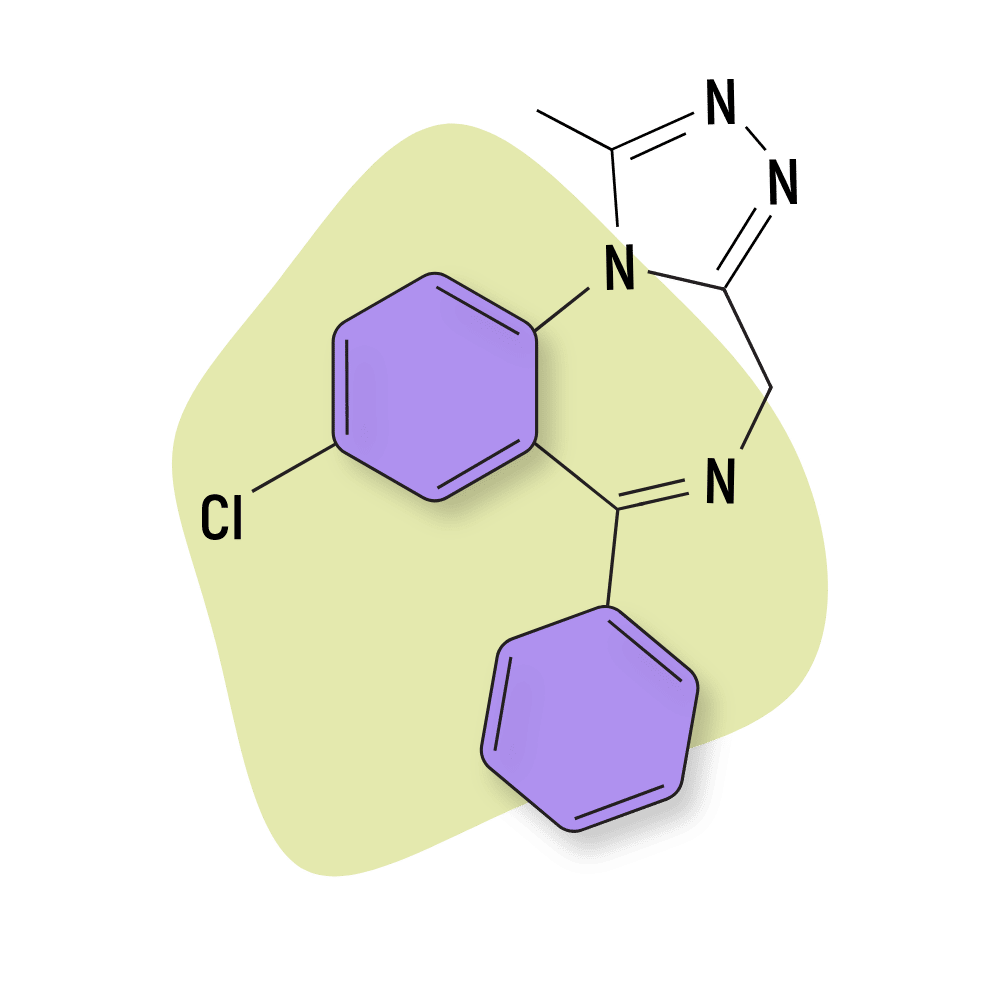
Triazolam (Halcion)
Like other benzodiazepines in its class, triazolam is an extremely potent compound, with a dose of just 0.5 mg being roughly equal to 10 mg of diazepam. However, it does differ significantly from estazolam in its pharmacokinetics. Triazolam is fast-acting, with a half-life of 1.5 to 5 hours and no active metabolites.
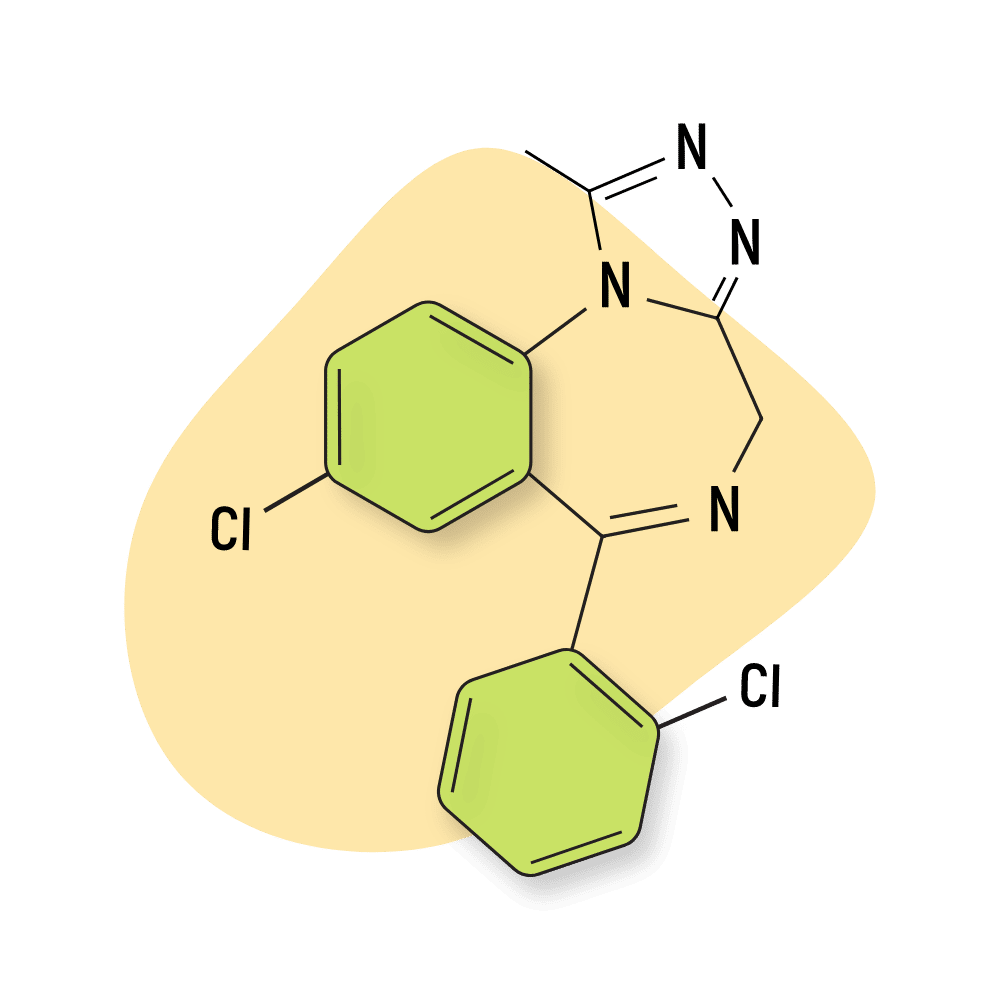
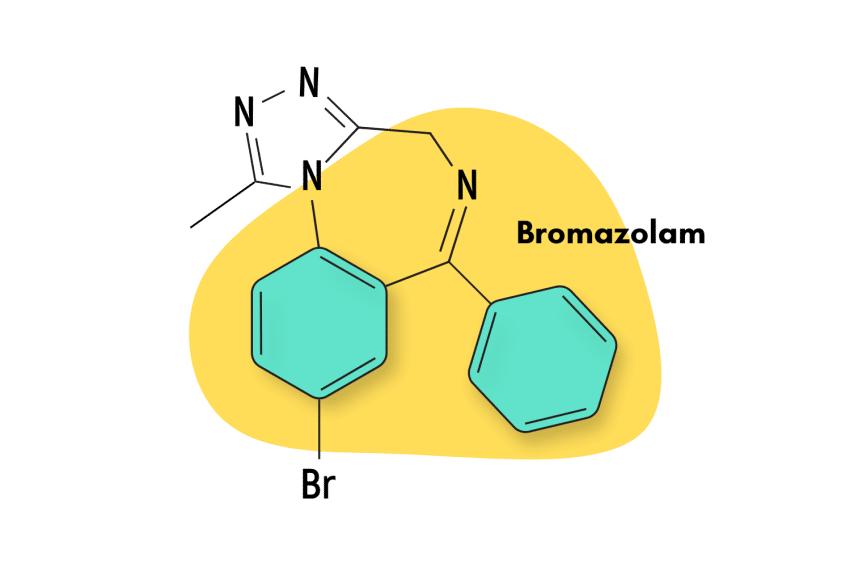
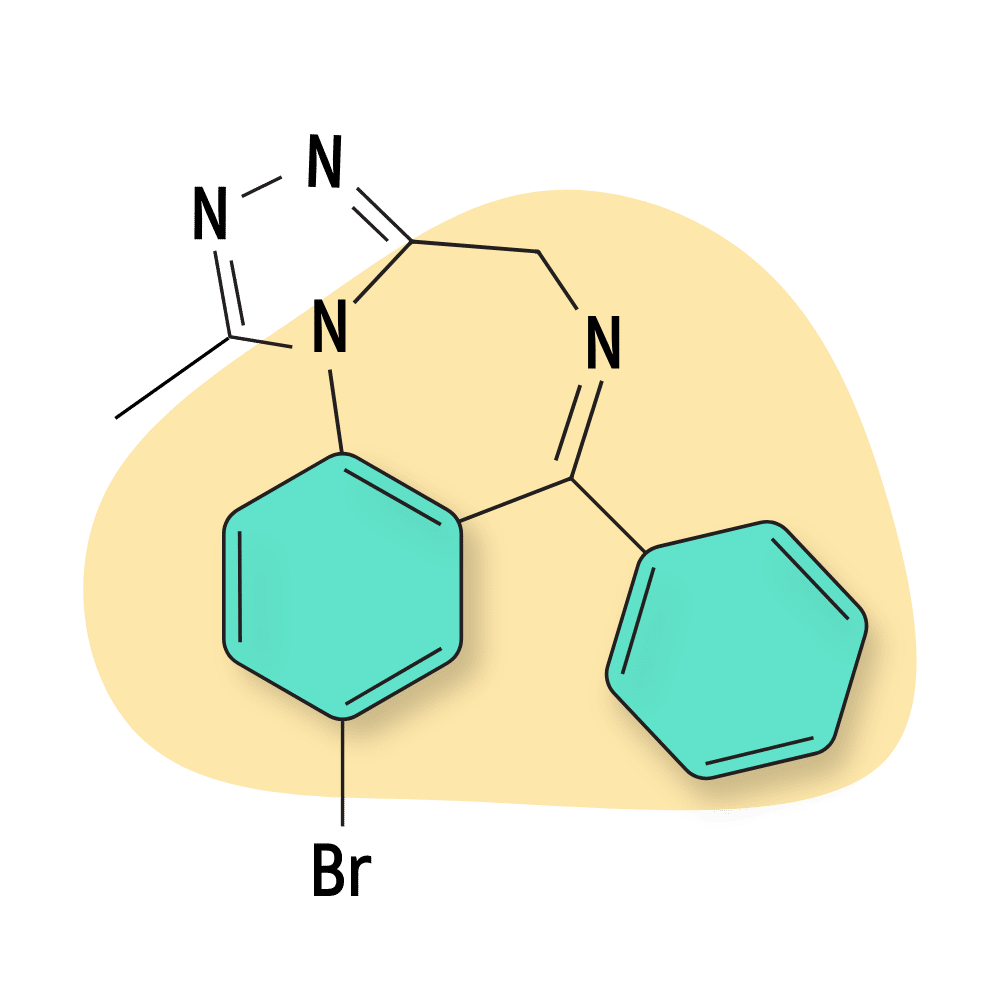
Bromazolam
Bromazolam shares a similar chemical structure to estazolam and has a comparable pharmacological profile. However, being a bromine derivative of alprazolam, it more closely resembles that drug.
Alternatives to Benzodiazepines
There are many plant-based alternatives for users who wish to minimize their exposure to the adverse effects of prescription benzodiazepines.
Kava
In recent years, the kava plant has become one of the most popular all-natural medications in the United States. Scientific, peer-reviewed studies have confirmed its anxiolytic and sedative properties, and it has far less potential to cause adverse effects compared to pharmacological drugs like benzodiazepines [7].
However, if we’re talking about estazolam, the kava plant is likely a less suitable alternative, as its benefits are most potent for reducing anxiety.
Kratom
The kratom plant (Mitragyna speciosa) is another solid alternative, as it has a stunning variety of pharmacological effects while offering a more benign side effects profile. However, kratom is not free of risk.
It has the potential to cause physical dependence and, as a CNS depressant, if mixed with drugs such as opioids or benzodiazepines, it could lead to respiratory depression and even death. But, if kratom is used responsibly, the risk is quite manageable.
Kratom has stimulant-like and euphoric properties in small doses, and in mid-to-high doses, it switches over to more anxiolytic and sedative benefits [8]. Kratom has also been useful for several other purposes, such as sleeping support, the relief of withdrawal symptoms, weight loss, etc.
L-Theanine
One of the active ingredients in green and black tea, L-theanine, has been used as a natural anxiolytic for a long time. It has been shown to increase the concentrations of GABA, serotonin, and dopamine levels in the brain and reduce the activity of glutamate, an excitatory neurotransmitter [9].
Estazolam FAQs
1. What are estazolam’s trade names?
Estazolam is available under the following brand names:
- Prosom
- Esilgan
- Eurodin
- Nuctalon
2. What are the contraindications associated with estazolam?
- Patients older than 65
- Pregnancy
- History of drug or alcohol abuse
- Hepatic or renal impairment
- Myasthenia gravis
- Sleep apnea
References
- Pierce, M. W., & Shu, V. S. (1990). Efficacy of estazolam:: The United States clinical experience. The American journal of medicine, 88(3), S6-S11.
- Campo, Soria, C., Chang, Y., & Weiss, D. S. (2006). Mechanism of action of benzodiazepines on GABAA receptors. British journal of pharmacology, 148(7), 984-990.
- Calcaterra, N. E., & Barrow, J. C. (2014). Classics in chemical neuroscience: diazepam (Valium). ACS chemical neuroscience, 5(4), 253-260.
- Choi, Y., & Raymer, B. K. (2019). Sleep modulating agents. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 29(16), 2025-2033.
- Riss, J., Cloyd, J., Gates, J., & Collins, S. (2008). Benzodiazepines in epilepsy: pharmacology and pharmacokinetics. Acta neurologica scandinavica, 118(2), 69-86.
- Grad, R. M. (1995). Benzodiazepines for insomnia in community-dwelling elderly: a review of benefit and risk. Journal of Family Practice, 41(5), 473-481.
- Cairney, S., Clough, A. R., Maruff, P., Collie, A., Currie, B. J., & Currie, J. (2003). Saccade and cognitive function in chronic kava users. Neuropsychopharmacology, 28(2), 389-396.
- Swogger, M. T., & Walsh, Z. (2018). Kratom use and mental health: A systematic review. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 183, 134-140.
- Nathan, P. J., Lu, K., Gray, M., & Oliver, C. (2006). The neuropharmacology of L-theanine (N-ethyl-L-glutamine) a possible neuroprotective and cognitive enhancing agent. Journal of Herbal Pharmacotherapy, 6(2), 21-30.