Medazepam (Nobrium) Fact Sheet: Dosage, Safety, & Closest Alternatives
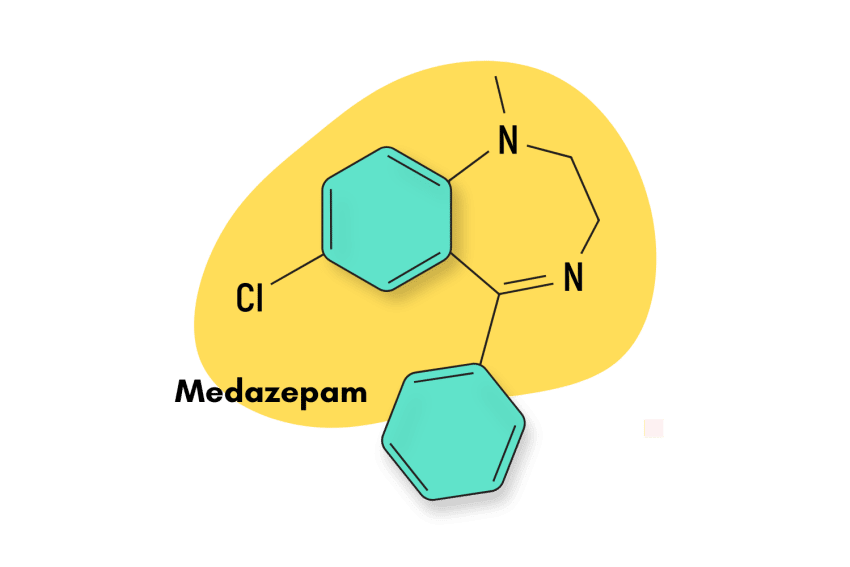
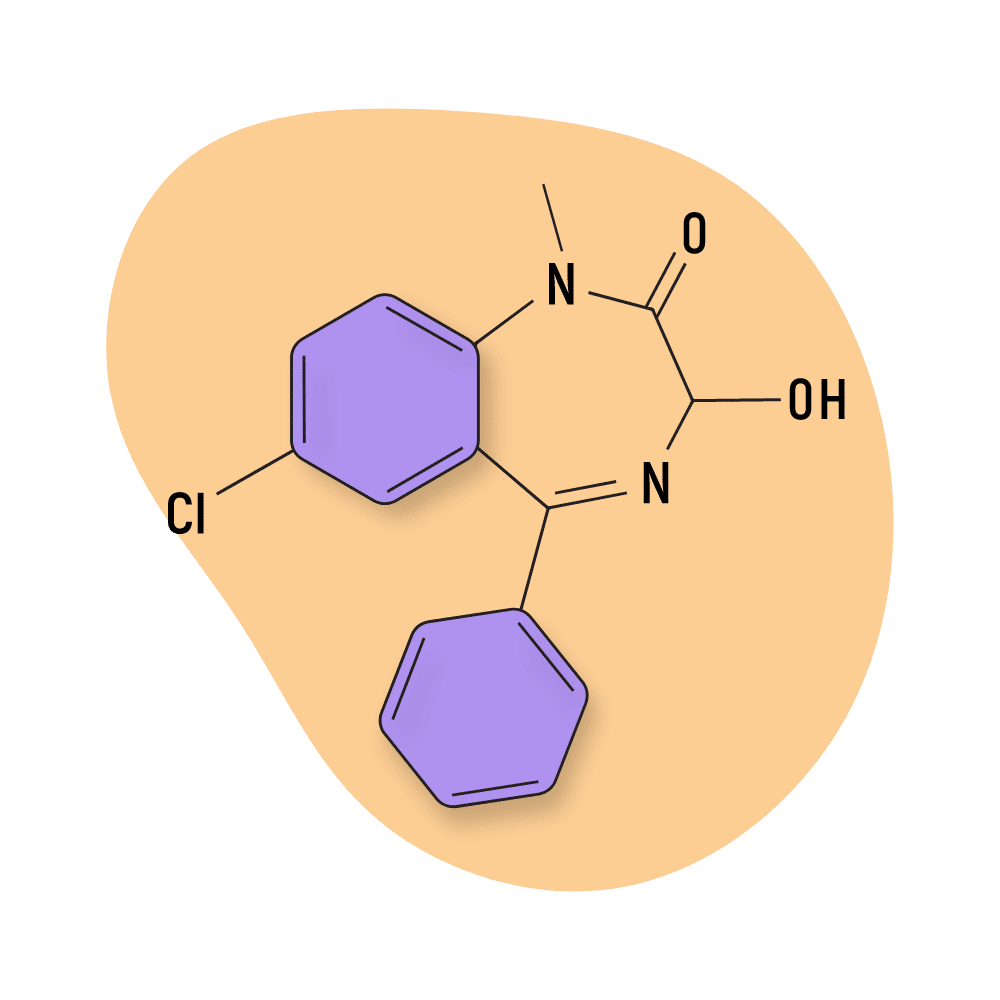
Medazepam, sold under different brand names such as Azepamid, Nobrium, Tranquirax, Rudotel, Raporan, Ansilan, Mezapam, and others, is a benzodiazepine prodrug.
A prodrug is a biologically inactive compound that, once ingested, is metabolized within the body to produce an active drug.
The liver converts medazepam into the active form, diazepam. Diazepam was one of the first benzodiazepines ever brought to market, where it’s commonly sold under the brand name Valium.
Since diazepam has several pharmacologically active byproducts, including oxazepam, nordiazepam, and temazepam, medazepam could also be considered a prodrug for these compounds.
Medazepam exhibits anxiolytic, myorelaxant, and anticonvulsant action. The drug relieves the feeling of worry, restores emotional calmness, and has a stabilizing effect on the nervous system. It’s used in neurosis, psychopathy accompanied by excitement, stress, elevated irritability, insomnia, and functional neurosis of the cardiovascular system [1].
Some users also take medazepam recreationally or alongside stimulant drugs to combat side effects like agitation, insomnia, or over-excitability.
Medazepam (Nobrium) Specs
IUPAC Name: 7-chloro-1-methyl-5-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodiazepine
Other Names: Azepamid, Nobrium, Tranquirax, Rudotel, Raporan, Ansilan, Mezapam
Metabolism: Medazepam is rapidly metabolized into diazepam and nordiazepam in the liver via biotransformation [2]. These metabolites then follow their standard metabolic pathways.
Duration of Effects: As a prodrug, the duration of the effects of medazepam is minimal. However, the elimination half-life of medazepam’s metabolites and their subsequent byproducts can last anywhere from 36 to 200 hours. Older patients and people with hepatic impairments and slower metabolisms tend to be on the far end of the metabolic spectrum.
Benzodiazepine Dosage Equivalency Calculator
**Caution:** Benzodiazepines have a narrow therapeutic window. Dose equivalents may not be accurate in higher doses.
This calculator does not substitute for clinical experience and is meant to serve only as a reference for determining oral benzodiazepine equivalence.
Please consult a medical practitioner before taking benzodiazepines.
How Does Medazepam (Nobrium) Work?
Once ingested, medazepam is rapidly absorbed and transformed into diazepam and nordiazepam.
Both these compounds are known to exert their effects through their allosteric modulation of GABA-A receptors found in the brain and central nervous system.
When drugs like diazepam and nordiazepam modulate the GABA receptors, it causes our natural GABA to become much stronger. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter, which means it works to inhibit nerve transmission throughout the brain and body. When nerve transmission is inhibited, our thoughts quiet down, we feel calm and relaxed, our muscles become flaccid, and we may even drift off to sleep. This effect explains all the characteristic effects of benzodiazepines.

There’s evidence for the utilization of secondary pathways by diazepam too. For instance, diazepam also binds to a unique benzodiazepine receptor located on the mitochondrial membrane known as the “translocator protein (18 kDa)” [3].
The pharmacological effects of medazepam seem to be heavily influenced by the ratio of its metabolic byproducts, namely diazepam and desmethyldiazepam, although other byproducts, such as oxazepam and temazepam, are also important [4].
These byproducts all seem to be quite similar to each other in terms of their effects, but there are significant differences in other regards. For example, desmethyldiazepam is a long-lasting byproduct, and large concentrations of it mean that the total duration of effects for medazepam can be significantly increased.
Studies have concluded that the gamut of medazepam’s byproducts can cause the effects to vary substantially from one patient to another [4].
Is Medazepam (Nobrium) Safe? Risks & Side Effects
Medazepam is classified as a Schedule IV compound in the United States under the Controlled Substances Act. This means it holds largely the same baseline level risk as most other benzodiazepine compounds and that we need to dig a bit deeper to make a more accurate assessment of its risks.
As a prodrug for diazepam and nordiazepam, we can look at the safety profile of these two compounds and draw meaningful conclusions from there.
In the case of diazepam, there is a considerable level of risk. For instance, the clinical literature suggests that the fast onset of the effects of diazepam is a big contributor to its abuse, as well as the fact that it leans heavily towards psychoactive effects, making it popular with recreational users.
Nordiazepam is roughly equal to diazepam in terms of potency and effects. What makes this benzodiazepine dangerous is its long elimination half-life. Whenever a benzodiazepine takes a long to be cleared from the body, there’s a risk of accumulation which can lead to toxicity. This risk is more latent if the compound is used consecutively for an extended period and if the patient happens to be hepatically impaired.
Side Effects of Medazepam
As a prodrug for diazepam and its many byproducts, if we want to understand the side effects of medazepam, we’re better served if we look at diazepam’s adverse effects.
According to the FDA, the following adverse effects have also been identified:
- Antegrade amnesia
- Anxiety
- Blurred vision
- Changes in libido
- Changes in salivation
- Confusion
- Constipation
- Depression
- Diplopia
- Dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Dysarthria
- Elevated transaminases and alkaline phosphatase
- Fatigue
- Gastrointestinal disturbances
- Hallucinations
- Headache
- Hypotension
- Incontinence
- Insomnia
- Irritability
- Muscle weakness
- Nausea
- Skin reactions
- Slurred speech
- Tremors
- Urinary retention
- Vertigo
When we look at governmental reports on medazepam, the conclusions are largely the same. For instance, the Malaysian government reports that, on the whole, medazepam is well tolerated. The only side effect which came up that wasn’t listed under diazepam were rare instances of laryngeal spasm.
Benzodiazepine Withdrawal & Dependence
Virtually all benzodiazepines have the capability of causing symptoms of physical dependence and withdrawal in users. It’s this addictive nature that many doctors are hesitant to prescribe these medications today.
Research suggests four main factors have an outsized role in the formation of benzodiazepine dependence:
- Repeated use — daily benzodiazepine use for a period of more than four months
- High doses — the higher the dose, the higher the dependence liability
- Sudden cessation of benzodiazepine use —withdrawal symptoms quickly lead to emotional instability and compulsivity
- Short-acting benzos — Use of a short-acting benzodiazepine over a longer or intermediate-acting one
Users should also be aware that a physical benzodiazepine dependence has more potential to cause harm when compared to other drugs like antidepressants. They elicit more forceful symptoms and are thus more difficult to deal with.
In rare instances, benzodiazepine withdrawal can even be fatal.
This is because tolerance to benzodiazepines involves reduced GABA receptor activity and increased glutamate activity. When there’s a sudden cessation of benzodiazepine use, the neurological system can fail to regulate hyperactive states. There is also the added risk of excitotoxicity and neuronal damage.
Harm Reduction Tips: Medazepam (Nobrium)
Here are some tips and tricks for staying safe while using benzodiazepine drugs:
- 🥣 Don’t mix — Mixing benzodiazepines with other depressants (alcohol, GHB, phenibut, barbiturates, or opiates) can be fatal.
- ⏳ Take frequent breaks or plan for a short treatment span — Benzodiazepines can form dependence quickly, so it’s important to stop using the drug periodically.
- 🥄 Always stick to the proper dose — The dosage of benzos can vary substantially. Some drugs require 20 or 30 mg; others can be fatal in doses as low as 3 mg.
- 💊 Be aware of contraindications — Benzodiazepines are significantly more dangerous in older people or those with certain medical conditions.
- 🧪 Test your drugs — If ordering benzos from unregistered vendors (online or street vendors), order a benzo test kit to ensure your pills contain what you think they do.
- 💉 Never snort or inject benzos — Not only does this provide no advantage, but it’s also extremely dangerous. Benzos should be taken orally.
- 🌧 Recognize the signs of addiction — Early warning signs are feeling like you’re not “yourself” without the drug or hiding your habits from loved ones.
- ⚖️ Understand the laws where you live — In most parts of the world, benzodiazepines are only considered legal if given a prescription by a medical doctor.
- 📞 Know where to go if you need help — Help is available for benzodiazepine addiction; you just have to ask for it. Look up “addiction hotline” for more information where you live. (USA: 1-800-662-4357; Canada: 1-866-585-0445; UK: 0300-999-1212).
Medazepam (Nobrium) Drug Interactions
Benzodiazepine users must be aware of the immense dangers of mixing their benzodiazepines with other compounds that can depress the CNS, like alcohol, opioids, barbiturates, other benzodiazepines, and even natural compounds like kava or kratom.
The deadly nature of this combination is due to combining CNS-depressant drugs potentiates their effects and results in the widespread suppression of the neurological system. This can result in respiratory depression (insufficient breathing), coma, and death.
The vast majority of benzo-related fatalities happen because of drug interactions.

Contraindications For Medazepam (Nobrium)
A contraindication is a situation in which a drug should not be used for any reason. In some rare cases, a doctor might still prescribe the medication in spite of a contraindication but under close watch.
Medazepam is contraindicated for the following conditions:
- Bronchitis
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Conjunctive use of barbiturates, opiates, or those suffering from alcoholism
- Driving and the use of heavy machinery
- Intellectual disabilities due to frequent paradoxical reactions
- Lactation
- Major depression
- Myasthenia gravis
- Over the age of 65 (high risk)
- Personality disorders
- Pregnancy
- Sleep apnea
Medazepam (Nobrium) Dosage
The standard treatment dosage for medazepam is 10 mg, taken two to three times daily.
It’s recommended that senior patients start on reduced dosages until their baseline reaction to the drug is understood.
Similar Benzodiazepines
Medazepam isn’t considered a pharmacologically active product by itself. It’s a prodrug that is converted into the active form (diazepam, nordiazepam, and others) only after it’s taken into the body.
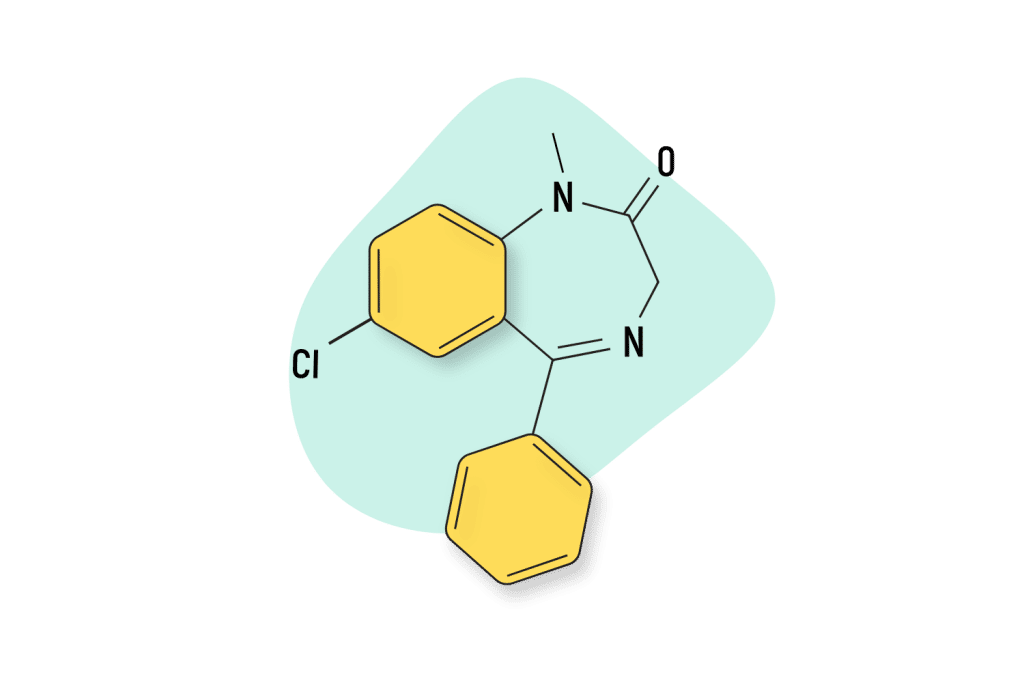
Diazepam (Valium)
Diazepam was the first blockbuster benzodiazepine and is considered to be the reference against which all other benzos are measured. Diazepam has several metabolically active byproducts, such as nordiazepam, temazepam, and oxazepam, increasing its duration of effects considerably. However, these compounds all have roughly the same effects profile as diazepam.
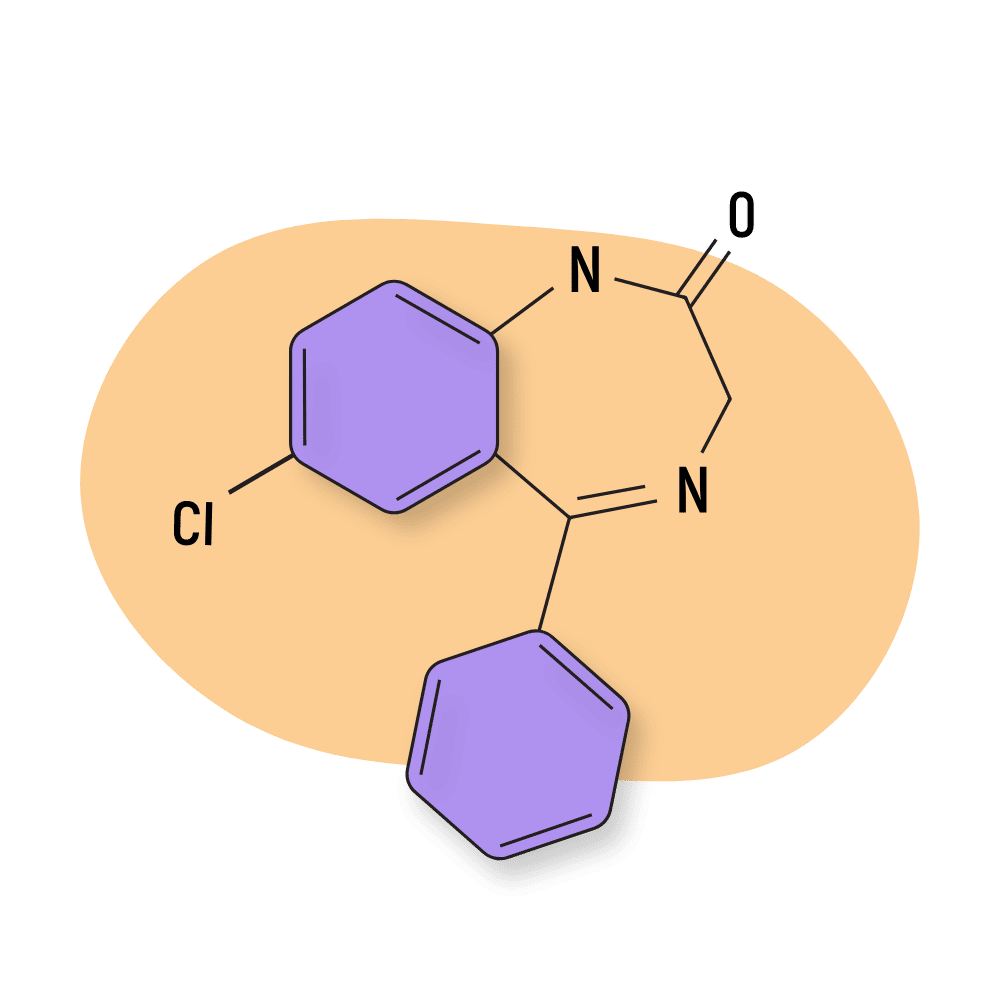
Nordiazepam (Madar)
Nordiazepam is one of the few naturally-occurring benzodiazepines on Earth and is a byproduct of diazepam. It has roughly the same potency and effects as diazepam but is much longer-lasting, with an elimination half-life of up to 200 hours. Pharmacologically, it has a strong emphasis on anxiolytic and muscle-relaxing effects.
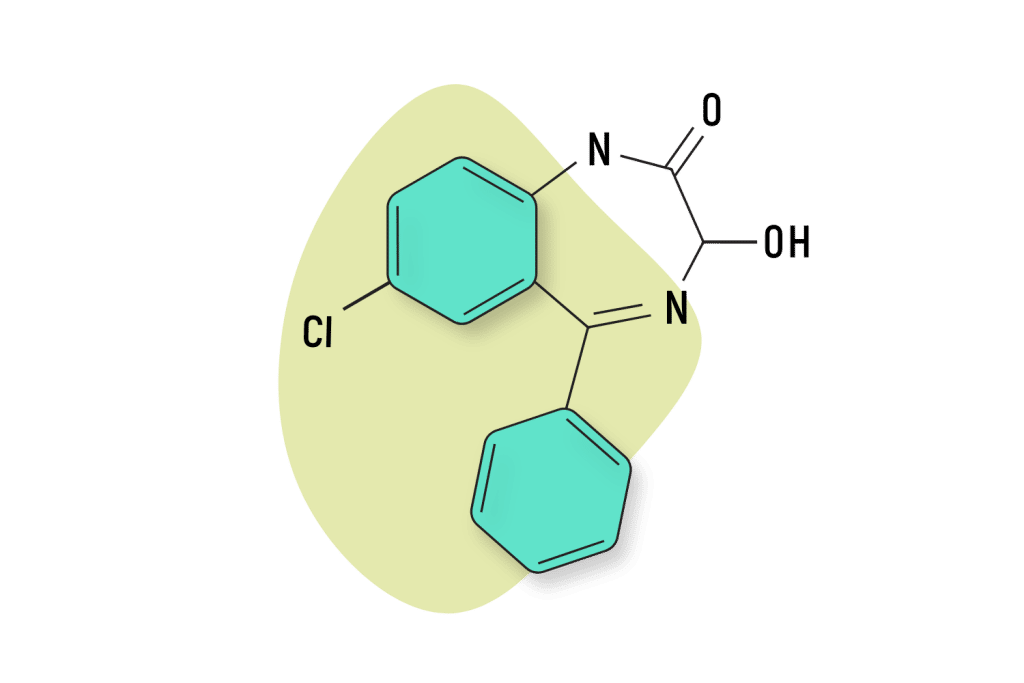
Oxazepam (Serax)
Oxazepam is another byproduct of diazepam. It is roughly half as potent as its parent compound and only has an estimated duration of effects of ten to 20 hours. Oxazepam used to be popular in the treatment of anxiety, insomnia, and alcohol withdrawal but has been largely replaced by more potent drugs.
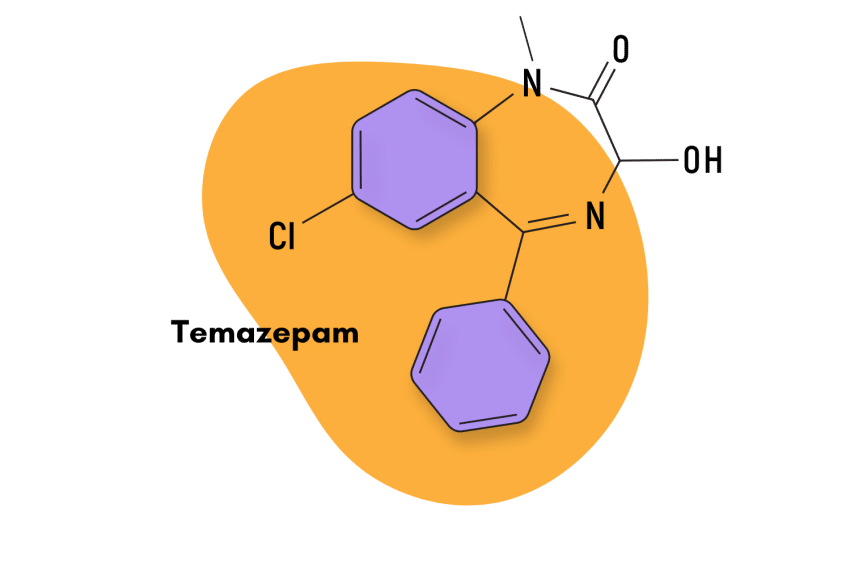
Temazepam (Restoril)
Temazepam is somewhat different when compared to other metabolic byproducts of diazepam. Instead of having a higher affinity for anxiolytic and muscle-relaxing effects, temazepam is more of a hypnotic benzodiazepine. It was a popular treatment for insomnia-related conditions before being replaced by a variety of Z-drugs.
In terms of potency, it’s the weakest diazepam byproduct and has an intermediate-acting half-life of eight to 20 hours, which is excellent for a hypnotic, as its effects can last throughout the night but are not long-acting enough to cause residual drowsiness.
Natural Alternatives to Benzodiazepines
Growing awareness of the inherent risks of benzodiazepine use and many other prescription drugs has seen a marked rise in the popularity of plant-based products that can offer some of the same effects.
Natural alternatives like kratom, kava, valerian, and L-theanine can’t offer the whole range of benzodiazepine-related effects like anticonvulsant action and muscle-relaxing effects and, consequently, may not be an option for everybody.
However, they have been shown to have effective anxiolytic, sedative, hypnotic, and analgesic potential, among other benefits.
Natural alternatives cannot match prescription products in potency. However, they can still provide effective relief in many cases, all while offering fewer side effects and less possibility of physical dependence.
Medazepam (Nobrium) FAQs
Does medazepam impair motor function?
In a study that compared diazepam, medazepam, and lorazepam when it came to their effects on driving performance, the following findings were reached [4]:
- Lorazepam was found to impair all the measured skills significantly more than diazepam and medazepam.
- Medazepam impaired only reactive skills and flicker fusion, the latter remaining impaired for as long as five hours after the administration.
- The magnitude and duration of the effects of diazepam were intermediate between those of lorazepam and medazepam. Diazepam impaired perceptual speed and reactive and co-ordinative skills, as well as flicker fusion discrimination and visual parameters related to driving.
- It was concluded that patients receiving a 2.5 mg dose of lorazepam should not drive or operate machinery for 24 hours after the administration. After diazepam (10 mg) or medazepam (15 mg), patients should refrain from driving or participating in skilled performances for only five to seven hours.
What is medazepam indicated for?
Medazepam is indicated for the short-term treatment of anxiety disorders. Additionally, it is also used in dentistry procedures.
Is medazepam well absorbed?
Yes. Medazepam is absorbed rapidly from the GI tract (oral) and reaches peak plasma concentrations after one to two hours.
References
- R.S. Vardanyan, V.J. Hruby, 5 – Anxiolytics (Tranquilizers), Editor(s): R.S. Vardanyan, V.J. Hruby, Synthesis of Essential Drugs, Elsevier, 2006, Pages 69-82, ISBN 9780444521668.
- Bond, A. J., Hailey, D. M., & Lader, M. H. (1977). Plasma concentrations of benzodiazepines. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 4(1), 51-56.
- Papadopoulos, V., Baraldi, M., Guilarte, T. R., Knudsen, T. B., Lacapère, J. J., Lindemann, P., … & Gavish, M. (2006). Translocator protein (18 kDa): new nomenclature for the peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor based on its structure and molecular function. Trends in pharmacological sciences, 27(8), 402-409.
- Seppala, K., Korttila, K., Hakkinen, S., & Linnoila, M. (1976). Residual effects and skills related to driving after a single oral administration of diazepam, medazepam, or lorazepam. British journal of clinical pharmacology, 3(5), 831-841.