Clotiazepam (Clozan) Fact Sheet & Harm Reduction Guide
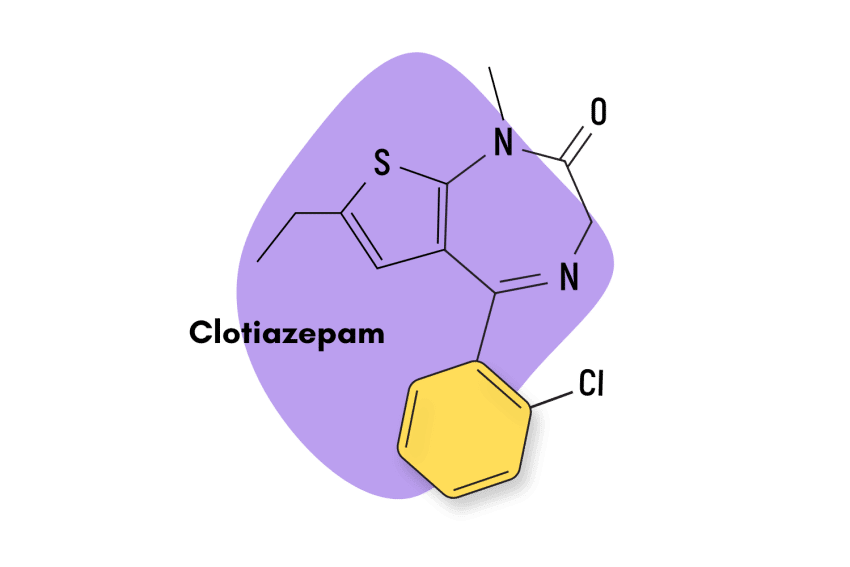
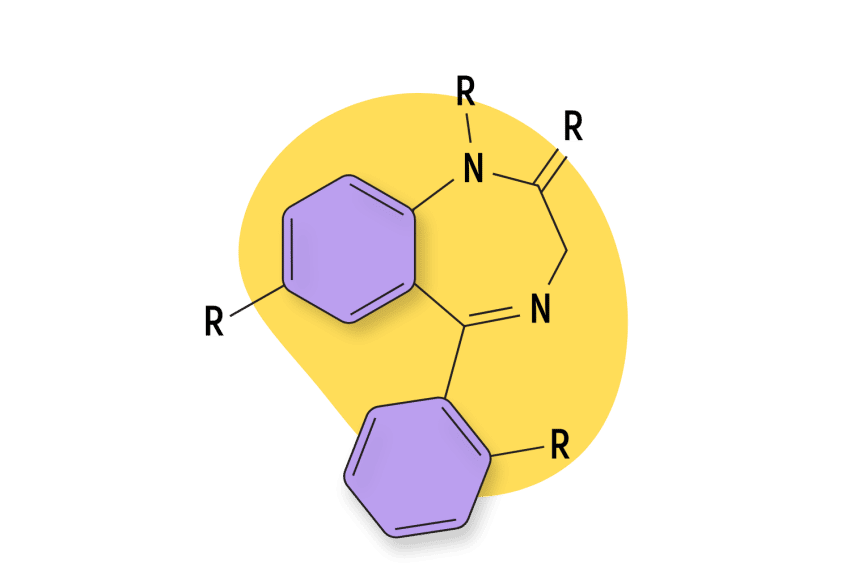
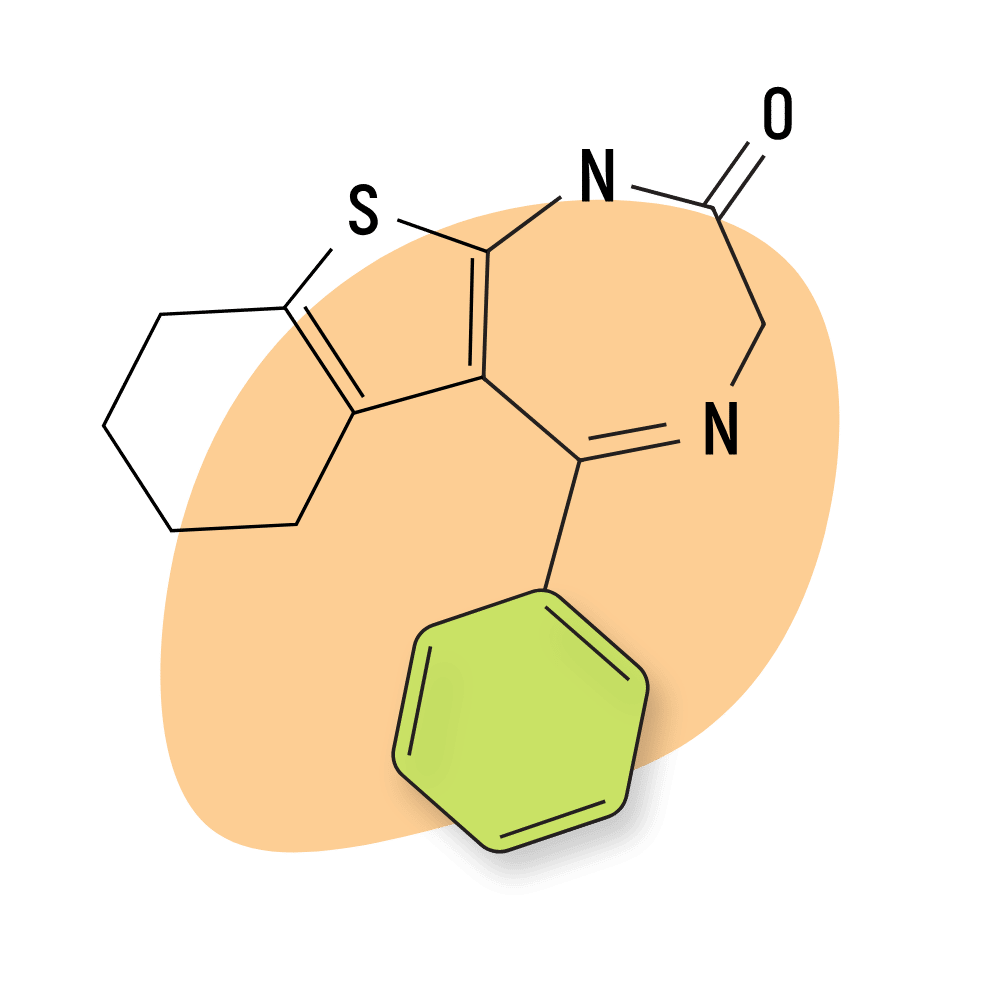
Clotiazepam — sold under the trade names Veratran, Rize, and Clozan — is a benzodiazepine belonging to the thienodiazepine subclass.
Clotiazepam is not approved for sale in the United States or Canada, but it is available in other countries like France and Japan.
Like most benzodiazepines, clotiazepam has recognized anxiolytic, skeletal muscle-relaxant, anticonvulsant, hypnotic, and sedative properties. However, its hypnotic qualities do have an interesting particularity: they increase stage 2 non-REM sleep without affecting the amount of time in REM (rapid-eye-movement eye movement) sleep [1].
As opposed to most benzodiazepines, thienodiazepines like clotiazepam do not interfere with important stages of sleep, like stage 2 non-REM sleep (deep sleep) and REM.
In the countries where it is approved, clotiazepam is used for the short-term management of anxiety and treating sleep-related disorders. To a lesser degree, it’s also used as a premedication in some countries.
Clotiazepam Specs
| Status | Approved medication, although not in the United States |
| Common Dosage | 5-10 mg |
| PubChem ID | 2811 |
| CAS# | 33671-46-4 |
IUPAC Name
5-(2-chlorophenyl)-7-ethyl-1-methyl-3H-thieno[2,3-e][1,4]diazepin-2-one
Other Names
Clozan, Distensan, Trecalmo, Rize, Rizen, Veratran
Metabolism
The metabolism of clotiazepam is hepatic and occurs via oxidation [2]. The drug is rapidly absorbed and metabolizes into hydroxy-clotiazepam and desmethyl-clotiazepam. The elimination of clotiazepam and its metabolites ranges from 6.5 to 18 hours [3]. The drug’s half-life is longer in older patients, and the volume of distribution is increased in women.
Liver impairment causes a reduced distribution volume and reduces clearance effectiveness. However, renal impairment does not affect clotiazepam’s kinetics [4].
Duration of Effects
Excluding its metabolites, clotiazepam is a short-acting compound with an estimated duration of effects in the range of four to eight hours.

Benzodiazepine Dosage Equivalency Calculator
**Caution:** Benzodiazepines have a narrow therapeutic window. Dose equivalents may not be accurate in higher doses.
This calculator does not substitute for clinical experience and is meant to serve only as a reference for determining oral benzodiazepine equivalence.
Please consult a medical practitioner before taking benzodiazepines.
How Does Clotiazepam Work?
Clotiazepam shares in the traditional mechanism of action used by most benzodiazepines [5].
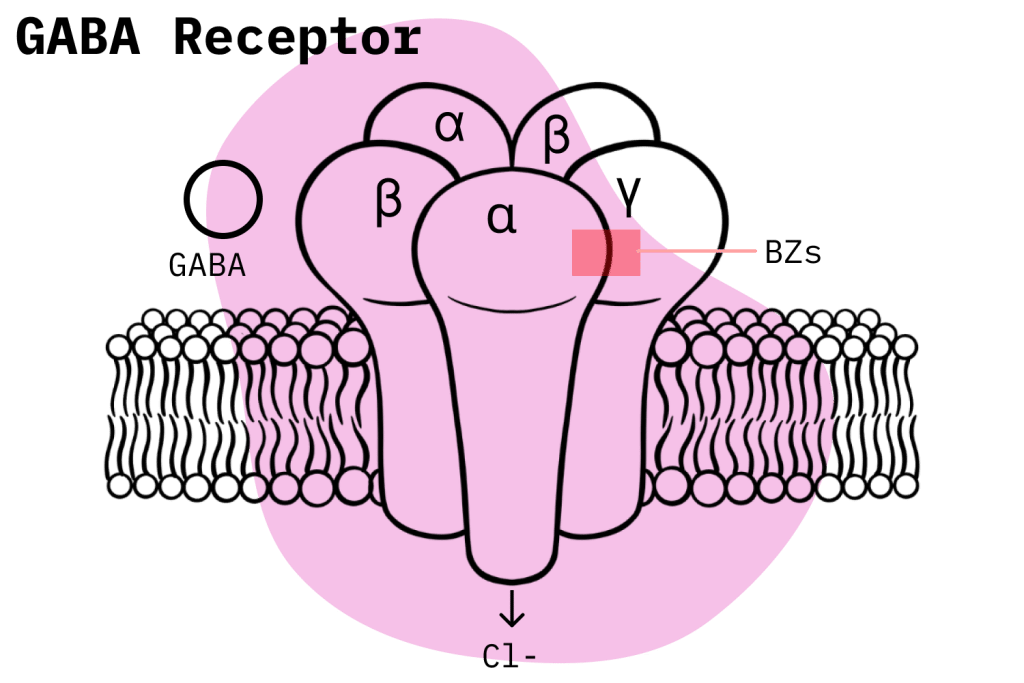
When benzodiazepine molecules enter the body, they bind to GABA receptors sites found along the brain and central nervous system. Once they bind, they agonize the natural inhibitory action of GABA through what is known as an “allosteric effect.”
Specifically, what happens is that the opening frequency of the chloride ion increases, as does the rate of penetration of chloride ions into the inside of the cell membrane. This increases the polarization of the cell, known as hyperpolarization, and thus decreases the probability for the neurons to discharge an action potential, the electrical signals used by the body to communicate.
This primary mechanism of action is what leads to the generalized depressive effect that benzodiazepines exert on the brain and CNS and gives rise to the spectrum of pharmacological effects they are usually associated with.
Clotiazepam Pharmacokinetics
Even though researchers do understand a lot about how benzodiazepines exert their effects, there is still a lot they don’t know in terms of specifics. Understanding the different qualities of benzodiazepines and how these add up to alter the overall pharmacological profile of a given benzodiazepine is less understood.
However, as time goes on, it is becoming clear that properties like pharmacokinetics and binding affinities to the different GABA-A subunits are quite important in the pharmacology of benzodiazepines and can even determine what clinical situations they are suited for [6].
In this sense, clotiazepam is recognized as a short-acting benzodiazepine (4-8 hours) and has a relatively average potency, with an average dose of around 5 to 10 mg. We also know that clotiazepam is a full receptor agonist rather than a partial agonist. This means that when it binds to a GABA-A receptor site, it elicits the maximum response available at the given receptor.
These qualities have certain consequences when it comes to clotiazepam’s pharmacology. For example, the relatively short elimination half-life means that, when compared to other benzodiazepine hypnotics, clotiazepam is less likely to cause residual “hang-over” effects, a common problem in benzodiazepine-related insomnia treatments.
Is Clotiazepam Safe? Risks & Side Effects
Clotiazepam is listed as a Schedule IV compound under the Controlled Substances Act, meaning that, like most benzodiazepines, it has recognized medical uses but also has the potential for misuse and the development of physical dependence and withdrawal symptoms.
Benzodiazepine treatment should always be approached with extreme care. It’s true that when benzodiazepines are taken strictly with a prescription, they rarely cause severe health events. Still, the truth is that once misuse is factored into the equation, the risk level of benzodiazepines is more significant than what their Schedule IV designation might imply.
If potential benzodiazepine users want to stay safe during treatment, they must assess their ability to avoid misuse. And this doesn’t just mean avoiding recreational use; that would only be the bare minimum. Avoiding misuse implies always taking your benzodiazepines at the right time, in the right formulation, and in the correct dosage, avoiding all possible contraindications, etc.
Furthermore, the dangerous consequences of benzodiazepine misuse are on full display in the United States, where a recent explosion in polydrug abuse has led to benzodiazepines being involved in many drug overdose deaths. For example, in a 2020 study, the CDC found that benzodiazepines were involved in a total of 12.290 deaths in the United States that year.
Side Effects of Clotiazepam
Studies that directly look at the side effects profile of clotiazepam are limited. However, we can still look at what health authorities in countries that have approved clotiazepam have to say.
In Malaysia, health authorities have identified the following side effects with clotiazepam use:
- Amnesia
- Ataxia
- Changes in libido
- Changes in salivation
- Confusion
- Depression
- Drowsiness
- Dysarthria
- Gastrointestinal disturbances
- Headache
- Hepatotoxicity
- Hypotension
- Incontinence
- Lightheadedness
- Muscle weakness
- Sedation
- Slurred speech
- Tremors
- Urinary retention
- Vertigo
- Visual disturbances
These side effects all fall within the standard range of adverse effects associated with benzodiazepines. Most benzodiazepines elicit a common set of side effects because they share the exact broad mechanism of action.
Benzodiazepine Withdrawal & Dependence
Benzodiazepine dependence, and associated withdrawal symptoms, are common factors stemming from benzodiazepine treatment and recreational use.
Benzodiazepine withdrawals are more of a cause for concern than withdrawals caused by other types of drugs. In fact, only withdrawal symptoms stemming from alcohol and benzodiazepines have the chance to turn deadly. Admittedly, this is a rare occurrence and only tends to happen when those who are suffering from benzodiazepine withdrawals do not seek help. But even so, the fact that benzodiazepine withdrawal can be fatal is not trivial.
A common misconception among those who use prescription drugs is that physical dependence can only form due to misuse or abnormally long treatment. This is not true in the slightest. There is obviously a lot of difference when it comes to types of drugs, but when it comes to benzodiazepines, the formation of physical dependence can happen in a time span as short as seven to 10 days.
In one study that observed the development of physical dependence in patients who used benzodiazepines for more than four weeks, it was observed that one-third of patients ended up experiencing withdrawal symptoms when they attempted to cease benzodiazepine use [7].
Harm Reduction: Clotiazepam
One of the goals of this article is to equip current or potential prescription drug users with conceptual tools that can help them minimize their risks when using benzodiazepines or any other type of prescription drug.
For prescription users, the number one recommendation will always be the same: try your hardest to avoid any instances of misuse. When prescription drugs are misused, this always raises risk levels. In this sense, Patients should get clear instructions from their prescribing doctor on how to utilize their prescriptions and stick by them religiously.
Before starting their treatment, patients should also talk to their prescribing physicians and should ask them to limit two important factors: dosage and the duration of treatment. The quantity of a drug that is ingested and the amount of time that is taken are the two most important factors that influence the formation of dependence. To hedge against this possibility, patients should speak to their doctors and ask them to limit these factors.
Sometimes doctors cannot limit these factors without affecting the effectiveness of treatment, but patients should still have this conversation.
Regarding recreational users, we do not condone using prescription drugs in this way, but even so, we want people to stay as safe as they can.
Recreational users should try to avoid mixing potent pharmacological compounds, including alcohol. Mixing two drugs will always significantly increase risk levels. Also, letting a friend know if you’re going to use drugs recreationally is always a good idea. Finally, when it comes to benzodiazepines, users should attempt to procure the drug flumazenil and learn how to use it. Flumazenil is a benzodiazepine receptor antagonist and can work to reduce the effects of a benzodiazepine overdose.
Benzodiazepine Harm Reduction Tips:
- 🥣 Don’t mix — Mixing benzodiazepines with other depressants (alcohol, GHB, phenibut, barbiturates, opiates) can be fatal.
- ⏳ Take frequent breaks or plan for a short treatment span — Benzodiazepines can form dependence quickly, so it’s important to stop using the drug periodically.
- 🥄 Always stick to the proper dose — The dosage of benzos can vary substantially. Some drugs require 20 or 30 mg; others can be fatal in doses as low as 3 mg.
- 💊 Be aware of contraindications — Benzodiazepines are significantly more dangerous in older people or those with certain medical conditions.
- 🧪 Test your drugs — If ordering benzos from unregistered vendors (online or street vendors), order a benzo test kit to ensure your pills contain what you think they do.
- 💉 Never snort or inject benzos — Not only does this provide no advantage, but it’s also extremely dangerous. Benzos should be taken orally.
- 🌧 Recognize the signs of addiction — Early warning signs are feeling like you’re not “yourself” without the drug or hiding your habits from loved ones.
- ⚖️ Understand the laws where you live — In most parts of the world, benzodiazepines are only considered legal if given a prescription by a medical doctor.
- 📞 Know where to go if you need help — Help is available for benzodiazepine addiction; you just have to ask for it. Look up “addiction hotline” for more information about where you live. (USA: 1-800-662-4357; Canada: 1-866-585-0445; UK: 0300-999-1212).
Clotiazepam Drug Interactions
Benzodiazepines should never be mixed with other compounds that can depress the CNS, such as opioids, alcohol, barbiturates, and other benzodiazepines. This combination can put the user at extreme risk of respiratory depression: the leading cause of death among drug overdoses.
Clotiazepam Contraindications
Clotiazepam shares the same contraindications as all other benzodiazepines. These include:
- Bronchitis
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Conjunctive use of barbiturates, opiates, or those suffering from alcoholism
- Intellectual disabilities due to frequent paradoxical reactions
- Major depression
- Myasthenia gravis
- Over the age of 65 (high risk)
- Personality disorders
- Sleep apnea
Clotiazepam Dosage
According to health authorities in the Philippines, the proper dosage quantities for clotiazepam can be found below.
For the short-term management of anxiety:
| Age group | Dosage recommendations |
| 🧑🏻 Adults | 5-15 mg in divided doses. Max: 60 mg daily |
| 👨🏽🦳 Older adults | Dose reduction may be necessary |
For sleep disorders:
| Age group | Dosage recommendations |
| 🧑🏻 Adults | 10 mg as a single dose at night. |
| 👨🏽🦳 Older adults | Dose reduction may be necessary. |
Similar Benzodiazepines
Thienodiazepines, the subclass to which clotiazepam belongs, are quite small, with only two other benzodiazepines.
Bentazepam
Bentazepam is a thienodiazepine with comparable pharmacokinetics to clotiazepam as both compounds are short-acting, the elimination half-life of bentazepam being two to four hours. Also, since they belong to the same subclass, it is probably reasonable to assume that they share similar pharmacological profiles.
Alternatives to Benzodiazepines
Here are some excellent natural alternatives to benzodiazepines!
The Kava Plant
Through active ingredients called kavalactones, the kava plant (Piper methysticum) can elicit potent anxiolytic and sedative benefits while offering a more benign side effects profile than pharmacological benzodiazepines [7]. Kava even interacts with GABA-A receptors, just like benzodiazepines, although it does this through a different mechanism of action.
Kratom
The kratom plant (Mitragyna speciosa) is another tropical species with recognized pharmacological effects. However, it can do more than the kava plant! In low doses, kratom acts as a stimulant and a euphoric, while in mid-to-high doses, the kratom plant takes on anxiolytic, analgesic, and even sedative benefits [8]. Kratom has even been effectively used to offer relief for withdrawal symptoms, as sleeping support, and as a weight-loss supplement.

Clotiazepam FAQs
Should clotiazepam be used during pregnancy?
No. Clotiazepam is contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation.
What formulations is clotiazepam available in
Clotiazepam is available in the following formulations: oral, sublingual, and liquid drops. Drops are suggested for a more marked initial effect and the sublingual route for easier administration, especially in the elderly.
References
- Nakazawa, Y., Kotorii, M., Ohshima, M., Horikawa, S., & Tachibana, H. (1975). Effects of thienodiazepine derivatives on human sleep as compared to those of benzodiazepine derivatives. Psychopharmacologia, 44(2), 165-171.
- Greenblatt, D. J., Divoll, M., Abernethy, D. R., Ochs, H. R., & Shader, R. I. (1983). Clinical pharmacokinetics of the newer benzodiazepines. Clinical pharmacokinetics, 8(3), 233-252.
- Arendt, R., Ochs, H. R., & Greenblatt, D. J. (1982). Electron capture GLC analysis of the thienodiazepine clotiazepam. Preliminary pharmacokinetic studies. Arzneimittel-forschung, 32(4), 453-455.
- Ochs, H. R., Greenblatt, D. J., & Knüchel, M. (1986). Effect of cirrhosis and renal failure on the kinetics of clotiazepam. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 30(1), 89-92.
- Yakushiji, T., Fukuda, T., Oyama, Y., & Akaike, N. (1989). Effects of benzodiazepines and non‐benzodiazepine compounds on the GABA‐induced response in frog isolated sensory neurones. British journal of pharmacology, 98(3), 735-740.
- Vgontzas, A. N., Kales, A., & Bixler, E. O. (1995). Benzodiazepine side effects: role of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Pharmacology, 51(4), 205-223.
- Pittler, M. H., & Ernst, E. (2003). Kava extract for treating anxiety. Cochrane Depression, Anxiety and Neurosis Group. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 3.
- Eastlack, S. C., Cornett, E. M., & Kaye, A. D. (2020). Kratom—Pharmacology, clinical implications, and outlook: a comprehensive review. Pain and therapy, 9(1), 55-69.