Do Amanita muscaria Mushrooms Contain Psilocybin?
Amanita muscaria is a psychoactive mushroom species with an iconic appearance. Although this iconic mushroom has psychedelic properties, it doesn’t contain psilocybin.

Amanita muscaria mushrooms have an iconic appearance. Foragers often overlook these red mushrooms with white spots because many believe they’re poisonous. This is true if consumed raw, but with the proper preparation, Amanita muscaria is very safe and can produce a unique dream-like experience.
The bottom line: Fly Agaric (Amanita muscaria) mushrooms don’t contain psilocybin. However, they do contain muscimol — a psychoactive compound that can induce psychedelic effects.
In this article, we’ll be looking at the following:
- What are Amanita muscaria mushrooms?
- What is psilocybin?
- What is the psychoactive compound in Amanita muscaria?
- What are the effects of Amanita muscaria?
What Are Amanita muscaria Mushrooms?
Amanita muscaria is a species of mycorrhizal mushroom that grows in forests and woodlands across the Northern Hemisphere. They are toadstool mushrooms with red caps and white spots. They’ve appeared in the Mario game, Alice and Wonderland, Fantasia, and other popular stories and movies.
Raw Fly Agaric contains toxic compounds such as ibotenic acid and muscarine. These compounds can cause nausea, vomiting, and in some cases, seizures, coma, and death. However, these toxins are easily removed by heating the mushrooms before use.
Heat converts ibotenic acid to muscimol, which is the primary active ingredient in Amanita muscaria.
Amanita muscaria and the compounds contained within the mushrooms are legal in most countries, including the United Kingdom, the United States, and Canada. However, in certain places such as the state of Louisiana and the countries of Australia, Romania, and, surprisingly, the Netherlands, these mushrooms are illegal.

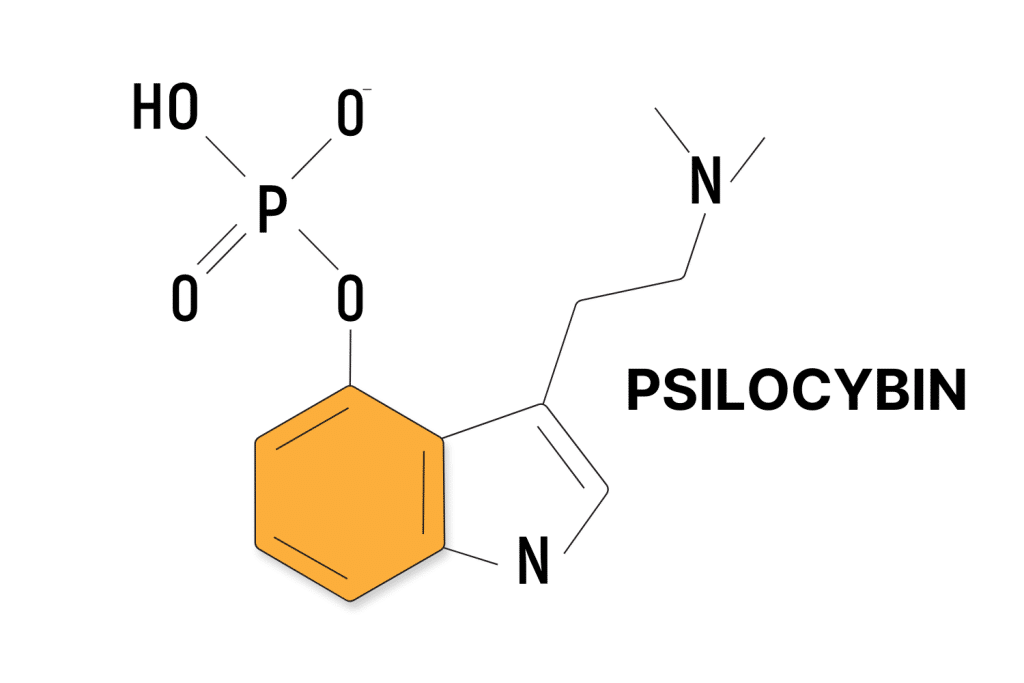
What Is Psilocybin?
Psilocybin is the psychoactive compound found in magic mushrooms. Psilocybin is responsible for producing the psychedelic trip associated with magic mushroom consumption. It’s present in over 200 known species of psychedelic mushrooms, including the popular Psilocybe cubensis.
When ingested, psilocybin is converted to psilocin which is responsible for the substance’s psychedelic effects. Users can experience altered perceptions of time as well as changes in mood, heightened sensory experiences, and visual hallucinations.
Psilocybin is a controlled substance in many parts of the world. However, there’s a push to legalize it in certain countries as research into its potential benefits gains momentum.
Do Fly Agaric Mushrooms Make You Trip?
Amanita muscaria can produce psychedelic effects, but not in the same sense as psilocybin-containing fungi.
After ingesting Fly Agaric, users won’t experience a psychedelic trip as such. However, their perception may be altered — making everyday objects and their surroundings seem “unusual.”
This substance induces a dream-like state of consciousness while you’re awake. However, the real “trip” begins during sleep, where the active component in the mushroom alters the dream state (more on this later).
Related: What is Lucid Dreaming? How Can I Learn to Lucid Dream?
What’s The Active Ingredients in Amanita muscaria Mushrooms?
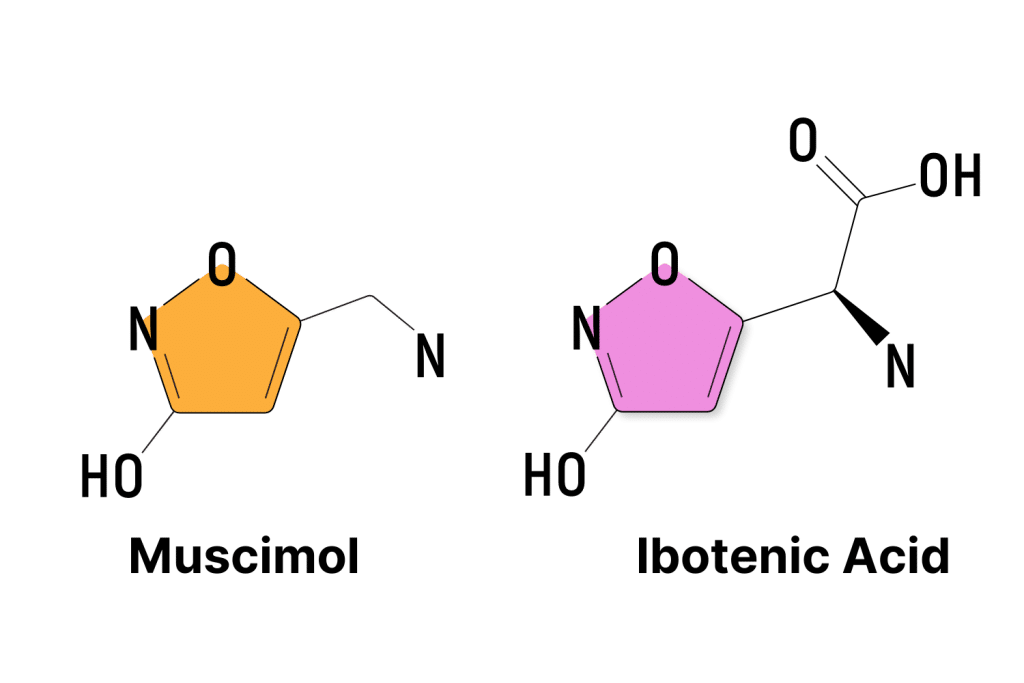
The primary active compounds contained in Amanita muscaria mushrooms are muscimol and ibotenic acid.
Muscimol is a psychoactive compound that induces oneirogenic (dream-like) effects when the mushrooms are consumed. When Amanita muscaria is consumed, muscimol acts on the central nervous system working through the GABAergic, cholinergic, and glutaminergic systems.
Ibotenic acid is converted to muscimol by the liver (while exerting some toxic side effects at the same time). Processing Amanita muscaria mushrooms involves drying and gently heating the mushrooms to convert most of the ibotenic acid into the safer, and psychoactive, muscimol.
Another minor active ingredient is a compound called muscarine, which has both toxic and psychedelic effects.
What Does Amanita muscaria Feel Like?
The effects of Amanita muscaria are different from other psychedelic mushrooms, such as those that contain psilocybin.
Rather than being a tryptamine psychedelic like classic substances such as psilocybin and LSD (lysergic acid diethylamide), the Fly Agaric mushroom is labeled as oneirogen psychedelic with deliriant properties.
Onerigen psychedelics induce a dream-like state of consciousness. While awake, Amanita muscaria doesn’t produce strong visual hallucinations as psilocybin-containing species such as psilocybe cubensis do. However, the mushrooms can alter time sense and the perception of objects and the world around you.
Shortly after ingesting the mushrooms, users normally start feeling waves of energy — this is down to the trace amounts of ibotenic acid that are still present in the prepared mushrooms.
As time goes on, the effects begin to become more apparent. The energetic feelings begin to fade away and are replaced with an “indescribable” feeling that can’t be called a “psychedelic trip” but more of an unusual distortion of perception.
Changes in mood, time distortion, and stimulation are replaced with sedative effects at around the 4-hour mark. From here, the experience becomes more dream-like. When the user eventually falls asleep, they’re likely to have bizarre and vivid dreams that are so strange they’re often indescribable.
The experience from this substance is one that’s hard to put into words. You really must try muscimol to understand how the effects truly feel.

Frequently Asked Questions About Amanita muscaria and its Effects
1. Is It Safe to Consume Amanita muscaria for Its Psychedelic Effects?
When properly prepared and taken within the recommended dosage, Amanita muscaria is safe to consume. The raw mushroom or very high doses of extracts can be dangerous, however.
The ibotenic acid and muscarine contained within the mushroom’s flesh is toxic in relatively low doses. If no steps are taken to reduce the levels of these toxins in the mushrooms, severe nausea and vomiting can occur. In more serious cases, these toxins can cause seizures and put people in comas. Death through Amanita muscaria consumption is rare but possible.
2. Are Fly Agaric Mushrooms Legal to Consume, Produce, & Sell?
In most countries, Amanita muscaria is completely legal to harvest, consume, and sell.
In the United Kingdom, Canada, the United States, and most of Europe, you’re free to do what you wish with this mushroom species. However, there are a few places that have criminalized Fly Agarics.
The state of Louisiana has banned Amanita muscaria alongside several other psychoactive plants and fungi under the Louisiana State Act 159.
In Australia, the active compound found in Amanita muscaria mushrooms (muscimol) is listed as a Schedule 9 substance — making it illegal to possess, consume, and sell.
In Europe, the mushroom is widely legal. However, in Romania and the Netherlands, it’s a criminal offense to possess and consume Amanita muscaria.
3. Is It Possible to Have a Bad Trip on Amanita muscaria?
It’s possible to have a bad experience with any psychedelic substance. Although the risks of a frightening hallucinogenic trip are relatively low with Amanita muscaria mushrooms compared to psilocybin mushrooms, you can still have a less-than-pleasant experience.
Amanita muscaria is unpredictable. The effects can vary greatly from person to person, and there are a few side effects to be aware of. This list can also grow dramatically if the mushrooms haven’t undergone the proper preparations necessary to remove as much of the toxic ibotenic acid as possible.
Here are some of the side effects associated with Amanita muscaria consumption:
- Nausea & vomiting
- Sweating
- Salivation
- Low blood pressure
- Lack of muscle coordination (ataxia)
- Mood changes & irritability
- Increased urination
You may experience none, some, or all of these side effects after consuming this psychedelic mushroom. Of course, how many of these side effects (if any) you encounter will alter the quality of your experience.
4. Where Can I Find Amanita muscaria Mushrooms?
Amanita muscaria can be found across the globe in the Northern Hemisphere. It grows across Europe, the United States, Canada, Russia, and parts of Asia.
Its habitat is woodlands of both deciduous and coniferous makeup. This species is definitely more prevalent in older pine forests and pioneering areas of woodland with plenty of birch trees.
This is a mycorrhizal fungi species which means that it develops a symbiotic relationship with certain tree species. The mushrooms provide increased water and nutrient flows to the tree’s root system, and the tree provides carbohydrates from photosynthesis for the mushrooms as a food source.
Amanita muscaria favors birch (Betula), pine (Pinus), and larch (Larix) as its host species. You’re most likely to find these mushrooms growing around the bases of these three trees, but they may develop mycorrhizal relationships with other species as well.
As with most mushrooms, you’ll find Amanita muscaria during the months of autumn. They are usually one of the first mushroom species to pop up in the season and are a sign for foragers across the globe to get out in search of edible mushrooms.